-
a
Change the slope of phase 0.
a) Na+ channel blocker
b) B-Blocker
c) K+ channel blocker
d) Ca++ channel blocker
-
b
Decrease heart rate and conduction velocity.
a) Na+ channel blocker
b) B-Blocker
c) K+ channel blocker
d) Ca++ channel blocker
-
c
Increase action potential duration & ERP.
a) Na+ channel blocker
b) B-Blocker
c) K+ channel blocker
d) Ca++ channel blocker
-
c
Delay repolarization.
a) Na+ channel blocker
b) B-Blocker
c) K+ channel blocker
d) Ca++ channel blocker
-
d
Slow the rate of rise in phase 4.
a) Na+ channel blocker
b) B-Blocker
c) K+ channel blocker
d) Ca++ channel blocker
-
depolarize; repolarize
Cardiomyocytes ______ quickly but take a long time to ________.
-
ERP; arrhythmia
Without the ____________, contraction of cardiomyocytes occurs
chaotically leading to ________.
-
SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, Bundle branches, Purkinje Fibers
Give the order of electrical current through the heart. (5)
-
right atrium
SA node is found in the _______.
-
purkinje fibers
________ causes ventricles to contract.
-
a
P wave =
a) depolarization of SA node
b) ventricular depolarization
c) ventricular repolarization
d) atrial repolarization
-
b
QRS complex =
a) depolarization of SA node
b) ventricular depolarization
c) ventricular repolarization
d) atrial repolarization
-
c
T wave =
a) depolarization of SA node
b) ventricular depolarization
c) ventricular repolarization
d) atrial repolarization
-
no signal from pacemaker site, development of ectopic pacemaker, development of oscillatory afterdepolarization
What are causes of irregular impulse formation? (3)
-
increased phase 4 slope
How can we tell there is ectopic pacemaker activity?
-
b
What is the cause of Delayed/Late After Depolarization (DAD)?
a) rectifier K+ current repolarization
b) Ca2+ overload
-
a
What is the cause of Early After Depolarization (EAD)?
a) rectifier K+ current repolarization
b) Ca2+ overload
-
a
Phase 3 repolarization is interrupted & membrane potential oscillates.
a) Early-After Depolarization (EAD)
b) Delayed/Late After-Depolarization (DAD)
c) impulse fractionation
d) re-entry
-
b
Cells receive a secondary impulse after RMP is achieved.
a) Early-After Depolarization (EAD)
b) Delayed/Late After-Depolarization (DAD)
c) impulse fractionation
d) re-entry
-
c
Caused by too much vagal tone; atrial stimulation & atrial fibrillation
a) Early-After Depolarization (EAD)
b) Delayed/Late After-Depolarization (DAD)
c) impulse fractionation
d) re-entry
-
d
Abnormal circuit from tissue damage.
a) Early-After Depolarization (EAD)
b) Delayed/Late After-Depolarization (DAD)
c) impulse fractionation
d) re-entry
-
torsades de pointes (TDP)
-polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
-
repolarization of cardiomyocytes during phases 1-3
What is the cause of Torsades De Pointes (TDP)?
-
long QT interval
How does Torsades De Pointes (TDP) look on the ECG?
-
b
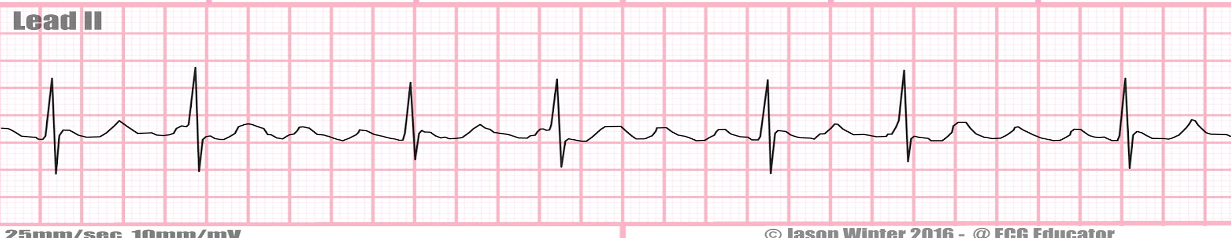
a) premature atrial contraction (PAC)
b) atrial flutter
c) atrial fibrillation
d) torsades de pointes
e) ventricular fibrillation
-
c
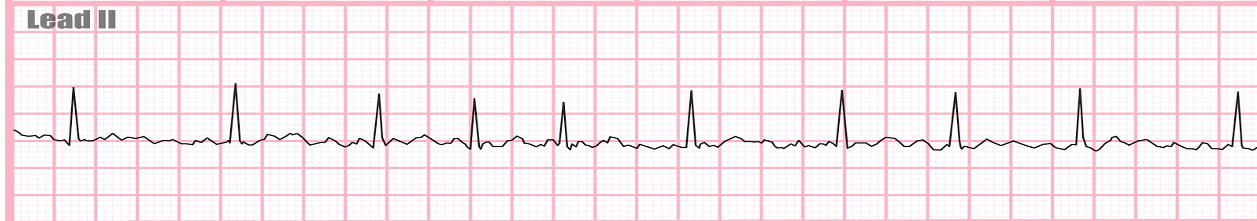
a) premature atrial contraction (PAC)
b) atrial flutter
c) atrial fibrillation
d) torsades de pointes
e) ventricular fibrillation
-
e
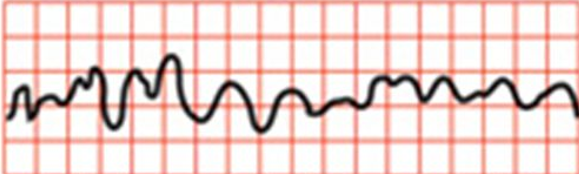
a) premature atrial contraction (PAC)
b) atrial flutter
c) atrial fibrillation
d) torsades de pointes
e) ventricular fibrillation
-
d
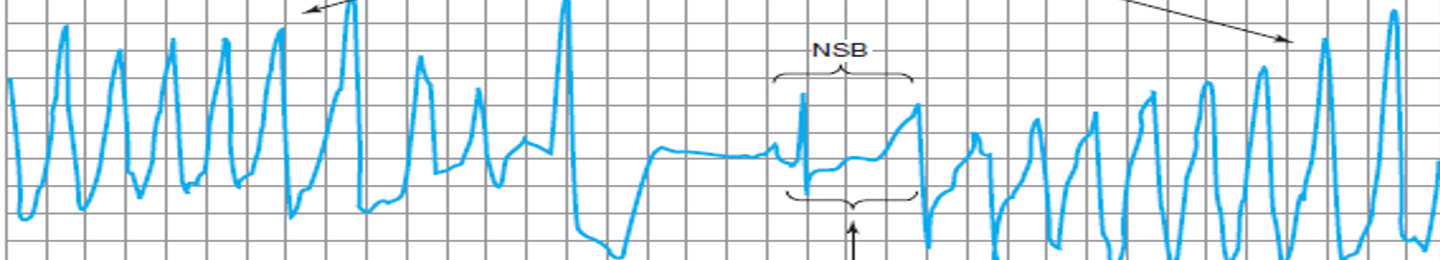
a) premature atrial contraction (PAC)
b) atrial flutter
c) atrial fibrillation
d) torsades de pointes
e) ventricular fibrillation
-
c
Slowed conduction and prolonged P-R interval.
a) 3rd degree AV block
b) 2nd degree AV block
c) 1st degree AV block
-
b
Some supraventricular complexes not conducted; dropped beats.
a) 3rd degree AV block
b) 2nd degree AV block
c) 1st degree AV block
-
a
No supraventricular complexes.
a) 3rd degree AV block
b) 2nd degree AV block
c) 1st degree AV block
-
a
Ventricle generates its own impulse. Complete heart block.
a) 3rd degree AV block
b) 2nd degree AV block
c) 1st degree AV block

