-
Vomiting (emesis) is the ___.
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of chyme from the stomach.
-
What is bulimia?
An eating disorder where the person binges then proceeding to throw everything up (to prevent absorbing calories).
-
Describe the different types of blood in the stool.
Frank blood: fresh, red blood, not digested and usually indicates lesions in the rectum or anal canal.
Occult blood: small, hidden amounts of blood that aren't visible to the eye but only in tests. Small ulcers in the stomach or small intestine.
Melena: dark-colored stool from significant bleeding.
-
What are some causes for dsyphagia?
Fibrosis - scar tissue contracts
Compression - ex. from a tumor
Diverticulum - accumulated food in the pouch obstructs the flow of food down the esophagus
-
What is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)?
A periodic reflux of the contents of the stomach (which contains bile) into the esophagus causing erosion and inflammation.
-
Chronic gastritis is characterized by ___.
the atrophy of stomach mucosa.
-
How do you treat chronic gastritis?
Antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors.
-
What damage to the mucosal barrier do?
It predisposes to development of ulcers.
-
What are some complications of peptic ulcers?
- hemorrhage
- perforation
- obstruction
-
What are some risk factors for gallstones?
- obesity
- hemolytic anemia
- high cholesterol in bile
-
What are the three stages of hepatitis?
1. preicteric
2. icteric
3. posticteric - recovery
-
What is cirrhosis?
A progressive destruction of the liver, when 80-90% of the liver has been destroyed.
-
What is biliary and postnecrotic cirrhosis?
Biliary: associated with immune disorders
Postnecrotic: linked with chronic hepatitis
-
Why is blood supply to the liver interfered with in cirrhosis?
Due to the increasing fibrosis of the tissue (scar tissue doesn't have any capillaries).
-
What happens in third-stage cirrhosis?
Also known as end-stage; where the entire liver tissue has been replaced with fibrotic tissue --> little to no function.
-
Describe the first two stages of cirrhosis.
1. Initial stage: accumulation of fat in liver cells --> fatty liver. Hepatomegaly, can be reversed.
2. Second stage/alcoholic hepatitis: inflammation and cell necrosis occur --> formation of fibrous tissue.
-
Pancreatitis results in the autodigestion of the tissue. Why?
Because the organ lacks a fibrous capsule to protect itself (which would've contained the effects of autodigestion).
-
Celiac disease prevents further digestion of ___ (breakdown product of gluten).
Celiac disease prevents further digestion of gliaden (breakdown product of gluten).
-
What are some chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs)?
- chron's
- ulcerative colitis
-
What region does crohn's and ulcerative colitis typically affect?

-
What is a characteristic of the lesions present in chron's?
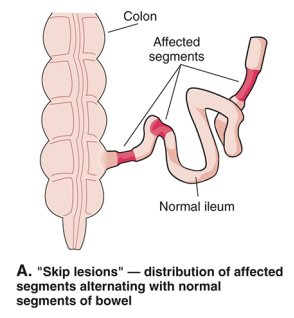
Skip lesions - lesions with normal tissue separating each one.
-
In chron's, inflammation stimulates ___.
intestinal motility.
-
What is diverticular disease?
The development of diverticula (pouches in the intestine).
-
What is an anal fistula?
Wherein a new tract is formed from the anus to another area.

