
MSC 385 Supply Chain Test 1
This may be as many terms as the decks get or I may add how-to cards about the problems (probably only to StudyLib). Kartka.ai link: https://app.kartka.ai/shared/decks/5C7AzqnuWEPX2jzeHisLFdqK
-
Supply ChainA sequence of activities and organizations involved in producing and delivering a good or service
-
ProcessOne or more actions that transform inputs into outputs
-
Cause & Effect Diagram Alternate NamesIshikawa diagram and Fishbone diagram
-
Why to use Cause and Effect diagramsTo identify a problem’s potential causes
-
Order qualifiersCharacteristics that customers perceive as minimum acceptability standards for a product or service to be considered as a potential for purchase
-
Order winnersAn organization’s goods’ or services’ characteristics that cause them to be perceived as better than the competition
-
Feasible solution spacethe set of all feasible decision variable combinations as defined by the constraints
-
Decision variablesamounts of either inputs or outputs
-
objective function (definition)mathematical statement of profit (or cost, etc.) for a given solution
-
binding constraint definitiona constraint that forms the optimal corner point of the feasible solution space
-
operations managementthe management of systems or processes that create goods and/or provide services
-
Productivity Formula
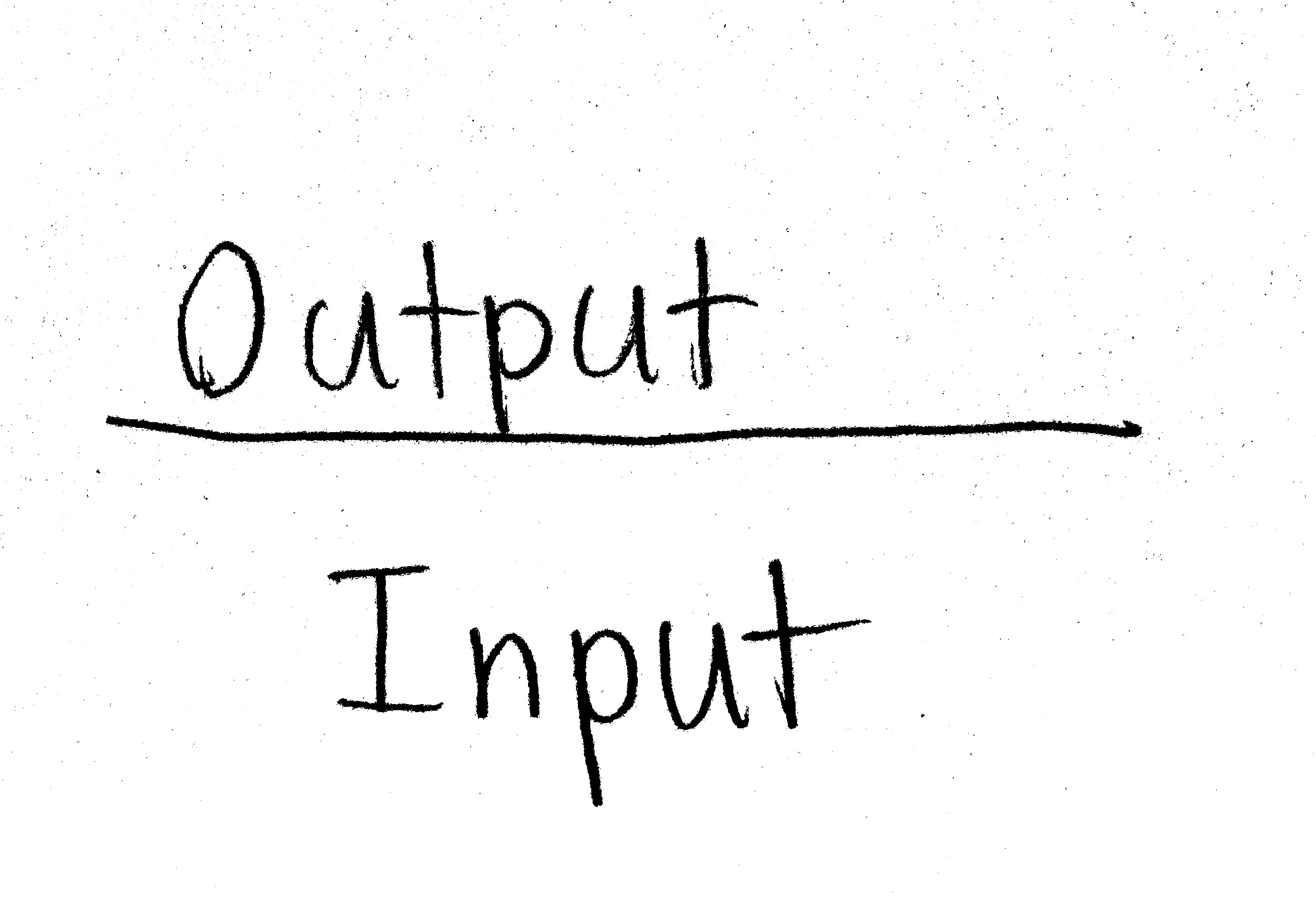
-
bullwhip effectthe amplification of upstream demand variation in the supply chain
-
Supply chain management’s goalTo match supply to demand as effectively and efficiently as possible
-
Job shopsmall-scale process type used for low volumes of high-variety goods or services
-
Job shop's processing, flexibility, equipment, and workersintermittent processing, high flexibility, general-purpose equipment, and skilled workers
-
Job shop examplesdie shop and veterinarian's office
-
Line balancing's goalto obtain task groupings that represent approximately equal time requirements
-
Reverse logisticsthe process of transporting returned items
-
Process selection's primary concernhow much variety and volume the process will need to be able to handle
-
Objective function (example)
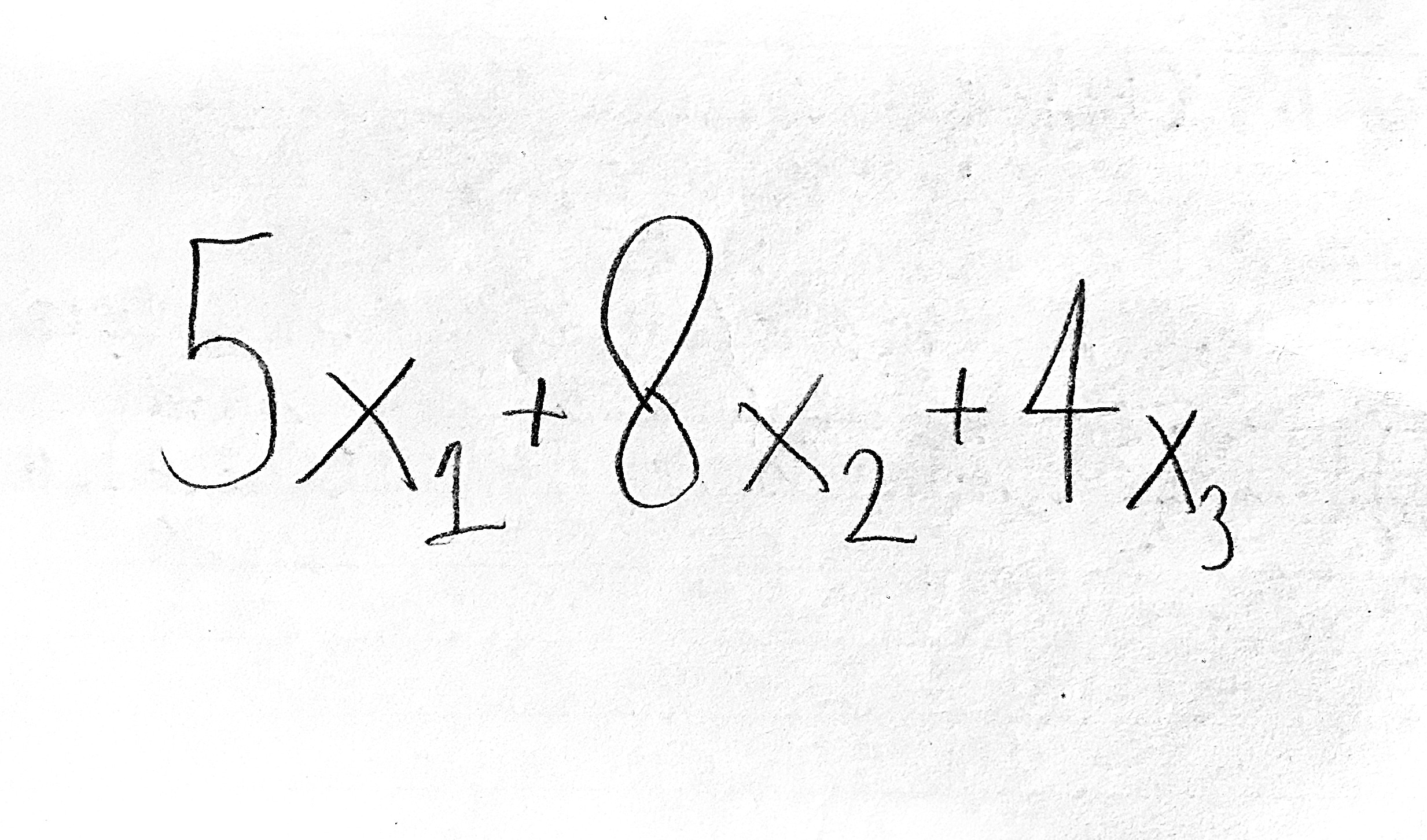
-
Cause and effectthere is a problem, the effect, and a need to identify the problem's potential causes
-
Logistics componentsmovements within a facility, incoming shipments, and outgoing shipments
-
Supply chain management's goals (key issues)determining appropriate outsourcing levels, managing procurement, managing suppliers, managing customer relationships, and being able to identify problems quickly and respond to them quickly
-
Purchasinghas responsibility for procurement of materials, supplies, and equipment and evaluates vendors for quality, reliability, service, price, and ability to adjust to changing demand; also involved in receiving and inspecting the purchased goods
-
Surplusthe amount by which the result value exceeds the right-hand side value when decision variables' values are substituted into a greater-than-or-equal-to (≥) constraint
-
Slackthe amount by which the result value is less than the right-hand side value when decision variables' values are substituted into a less-than-or-equal-to (≤) constraint
-
Binding constraint's purposeeffectively limiting the objective function's value
-
Non-binding constraintcondition in which there is no value for additional quantities because slack or surplus is present
-
Variable CellsDecision variables as mislabeled by Excel
-
Shadow priceAmount by which the the objective function's value would change with a one-unit change in a constraint's right-hand side value
-
minimum cycle timemaximum single task time

