Supply Chain
A sequence of activities and organizations involved in producing and delivering a good or service
Process
One or more actions that transform inputs into outputs
Cause & Effect Diagram Alternate Names
Ishikawa diagram and Fishbone diagram
Why to use Cause and Effect diagrams
To identify a problem’s potential causes
Order qualifiers
Characteristics that customers perceive as minimum acceptability standards for a product or service to be considered as a potential for purchase
Order winners
An organization’s goods’ or services’ characteristics that cause them to be perceived as better than the competition
Feasible solution space
the set of all feasible decision variable combinations as defined by the constraints
Decision variables
amounts of either inputs or outputs
objective function (definition)
mathematical statement of profit (or cost, etc.) for a given solution
binding constraint definition
a constraint that forms the optimal corner point of the feasible solution space
operations management
the management of systems or processes that create goods and/or provide services
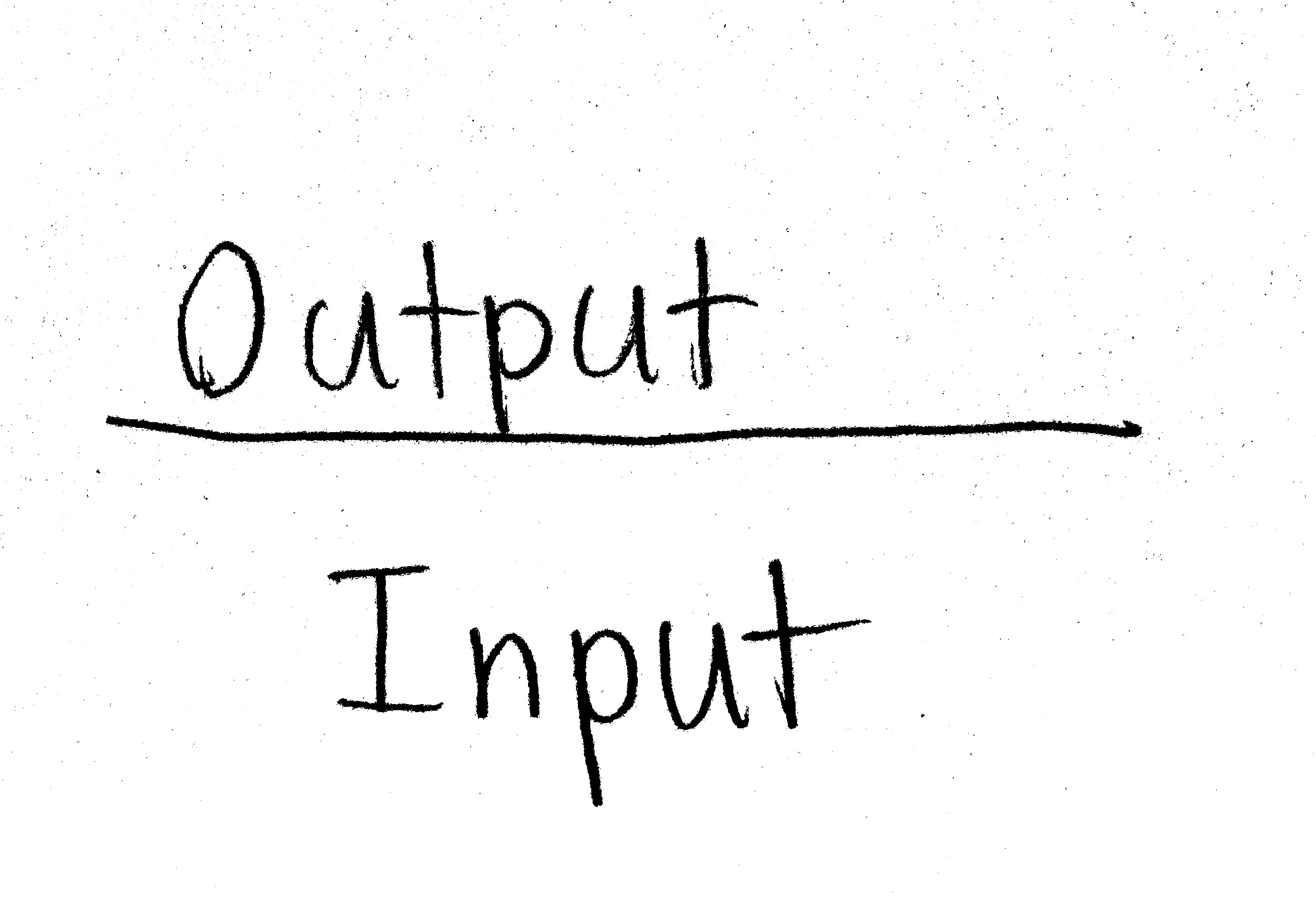
Productivity Formula
bullwhip effect
the amplification of upstream demand variation in the supply chain
Supply chain management’s goal
To match supply to demand as effectively and efficiently as possible
Job shop
small-scale process type used for low volumes of high-variety goods or services
Job shop's processing, flexibility, equipment, and workers
intermittent processing, high flexibility, general-purpose equipment, and skilled workers
Job shop examples
die shop and veterinarian's office
Line balancing's goal
to obtain task groupings that represent approximately equal time requirements
Reverse logistics
the process of transporting returned items
Process selection's primary concern
how much variety and volume the process will need to be able to handle
Objective function (example)
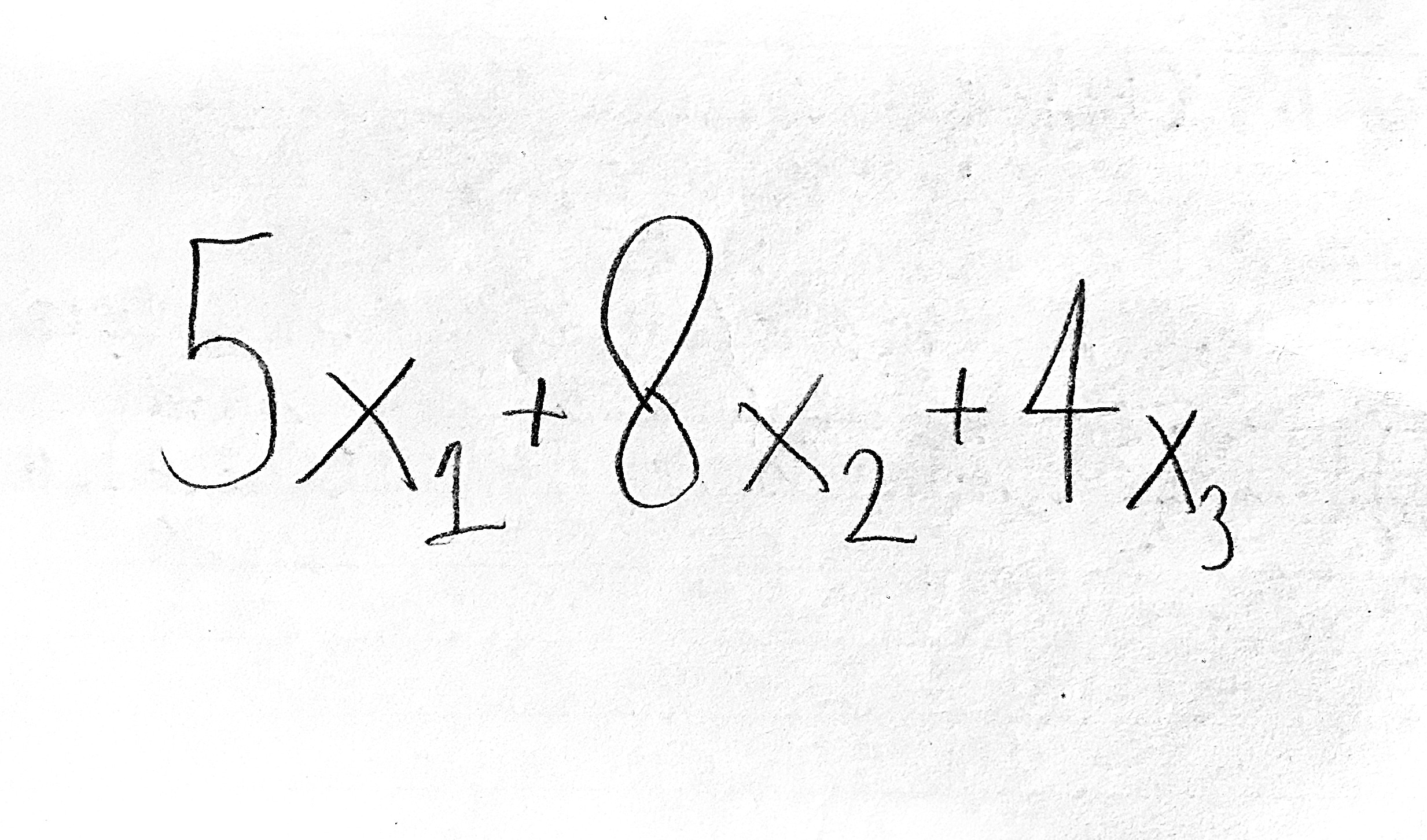
Cause and effect
there is a problem, the effect, and a need to identify the problem's potential causes
Logistics components
movements within a facility, incoming shipments, and outgoing shipments
Supply chain management's goals (key issues)
determining appropriate outsourcing levels, managing procurement, managing suppliers, managing customer relationships, and being able to identify problems quickly and respond to them quickly
Purchasing
has responsibility for procurement of materials, supplies, and equipment and evaluates vendors for quality, reliability, service, price, and ability to adjust to changing demand; also involved in receiving and inspecting the purchased goods
Surplus
the amount by which the result value exceeds the right-hand side value when decision variables' values are substituted into a greater-than-or-equal-to (≥) constraint
Slack
the amount by which the result value is less than the right-hand side value when decision variables' values are substituted into a less-than-or-equal-to (≤) constraint
Binding constraint's purpose
effectively limiting the objective function's value
Non-binding constraint
condition in which there is no value for additional quantities because slack or surplus is present
Variable Cells
Decision variables as mislabeled by Excel
Shadow price
Amount by which the the objective function's value would change with a one-unit change in a constraint's right-hand side value
minimum cycle time
maximum single task time