Membrane Structure and Function I (The Living Cell)
Learning objectives Explain why biological membranes are bilayers Describe the major molecular components of biological membranes and their distribution Describe the role of cholesterol in membrane fluidity Describe the different types of membrane transport
-
Membranes must be...what? (3)
1. Flexible
2. Self-sealing
3. Selectively permeable
-
Why are biological membranes bilayers? (4)

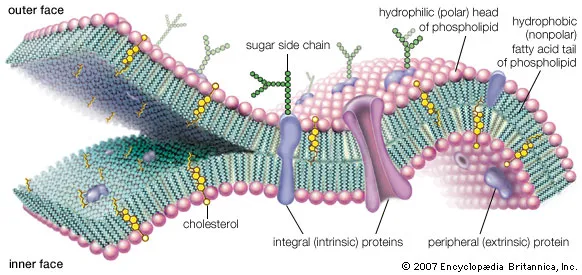
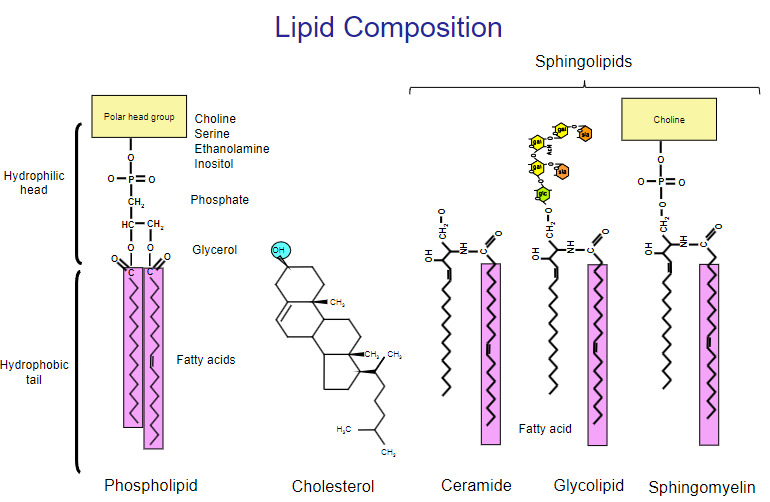
• Biological membranes are composed largely of lipids and proteins
• The lipids are amphipathic, meaning they have a hydrophilic and hydrophobic part
• Assemble spontaneously
• Non-covalent assemblies
-
Picture outlining the various Lipid compositions:
-
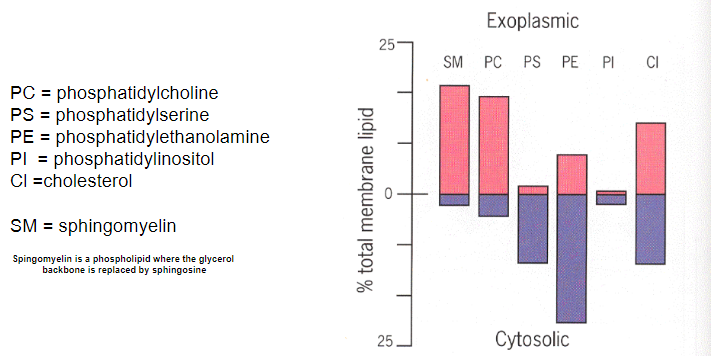
Picture outlining how the contents of the membrane are asymmetrical:
-
Membranes Synthesis Lipids, How? (7)
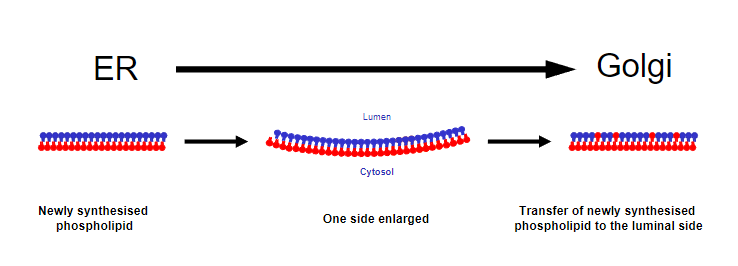
Enzymatic Processes:
Enzymes in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) facilitate lipid synthesis.
Phospholipid Backbone Formation:
Glycerol forms the backbone for phospholipids.
Acyl Chain Addition:
Fatty acid chains are added to form phospholipids.
Sphingolipid Synthesis:
ER and Golgi apparatus synthesize sphingolipids.
Sterol Synthesis:
ER synthesizes sterols (steroid-based alcohol) like cholesterol.
Transport to Membranes:
Newly synthesized lipids are transported to membranes.
Membrane Assembly:
Lipids integrate into membranes, forming bilayers.
-
What does Floppase do?
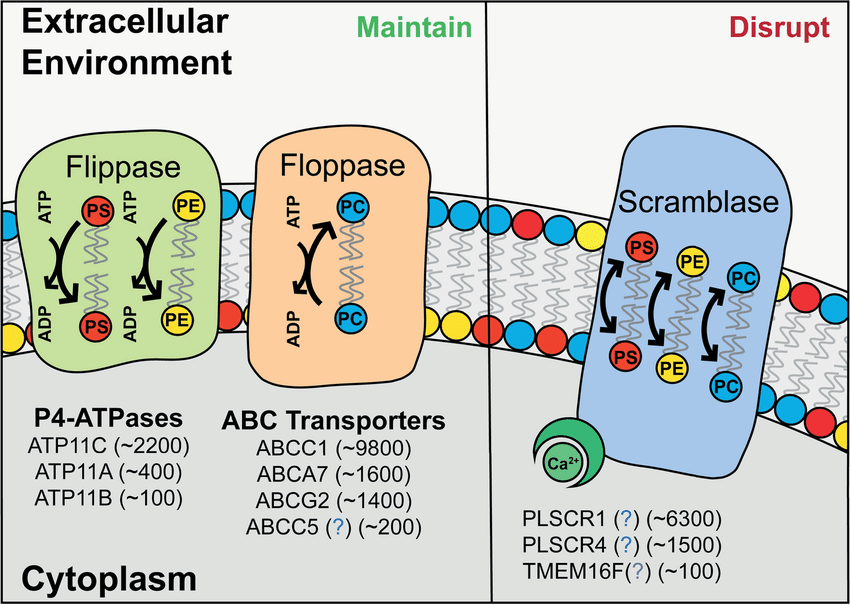
-Moves phospholipids from the inner to the outer leaflet
-Requires ATP
-
What does Flippase (flipase) do?
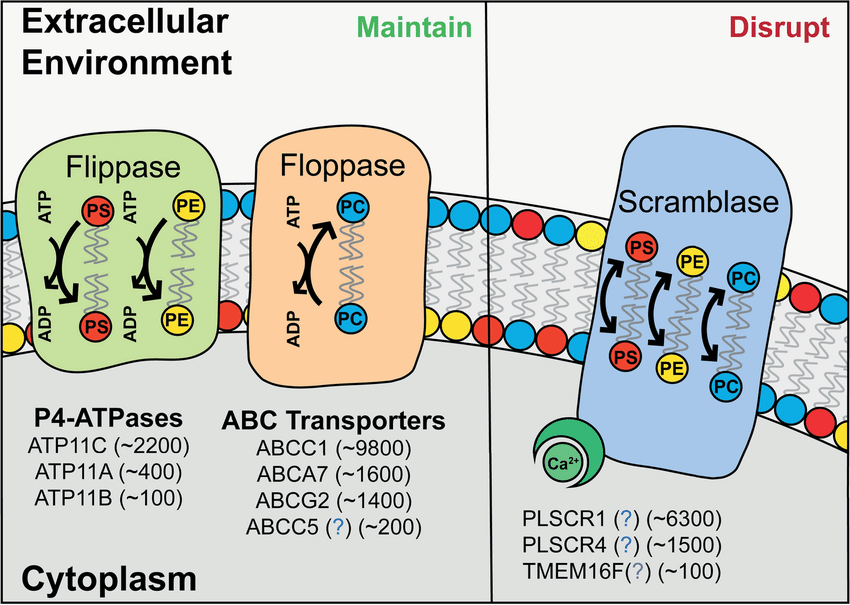
-Moves phospholipids from the outer to the inner leaflet
-Requires ATP
-
What does Scramblase do?
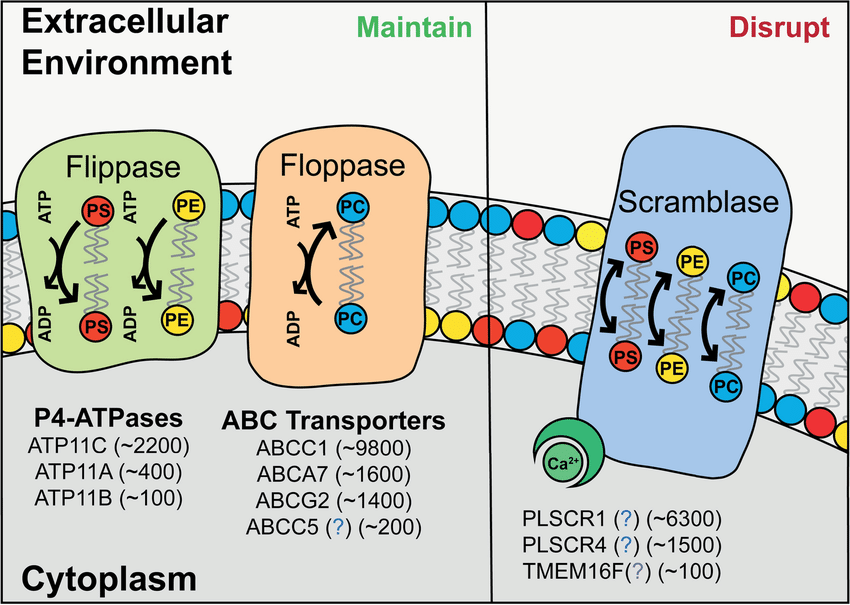
Scramblase – bidirectional movement
-
Phospholipid synthesis takes place where?
On the cytosolic surface of the endoplasmic reticulum
-
Describe the Lateral movement of lipids in the membrane:
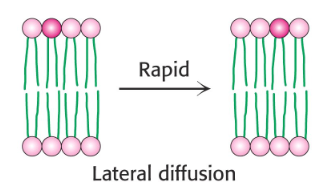
-Rapid
-
Describe the Transverse movement of lipids in the membrane:
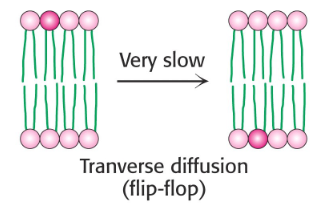
-Slow
-Requires the action of 3 enzymes
-
What 5 factors alter fluidity?
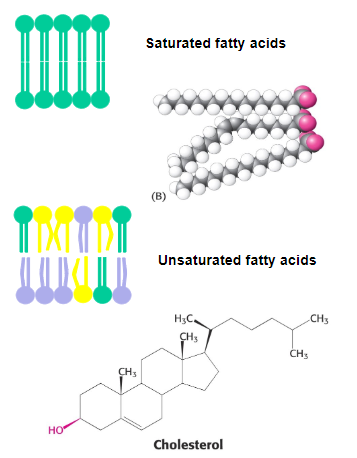
• Temperature
• Fatty acid composition
• Chain length
• Degree and extent of saturation
•Cholesterol content
-
How does cholesterol act in cold temperatures:
-Inserts itself among phospholipids, reducing close packing
-Inhibits the formation of ice-like crystals in the membrane.
-
How does cholesterol act in Hot temperatures:
-Interferes with phospholipid movement and rotation.
-Provides structural support to the membrane, preventing excessive deformation and permeability
-
What is Spur Cell Anaemia? Why is it associated with lipid metabolism?
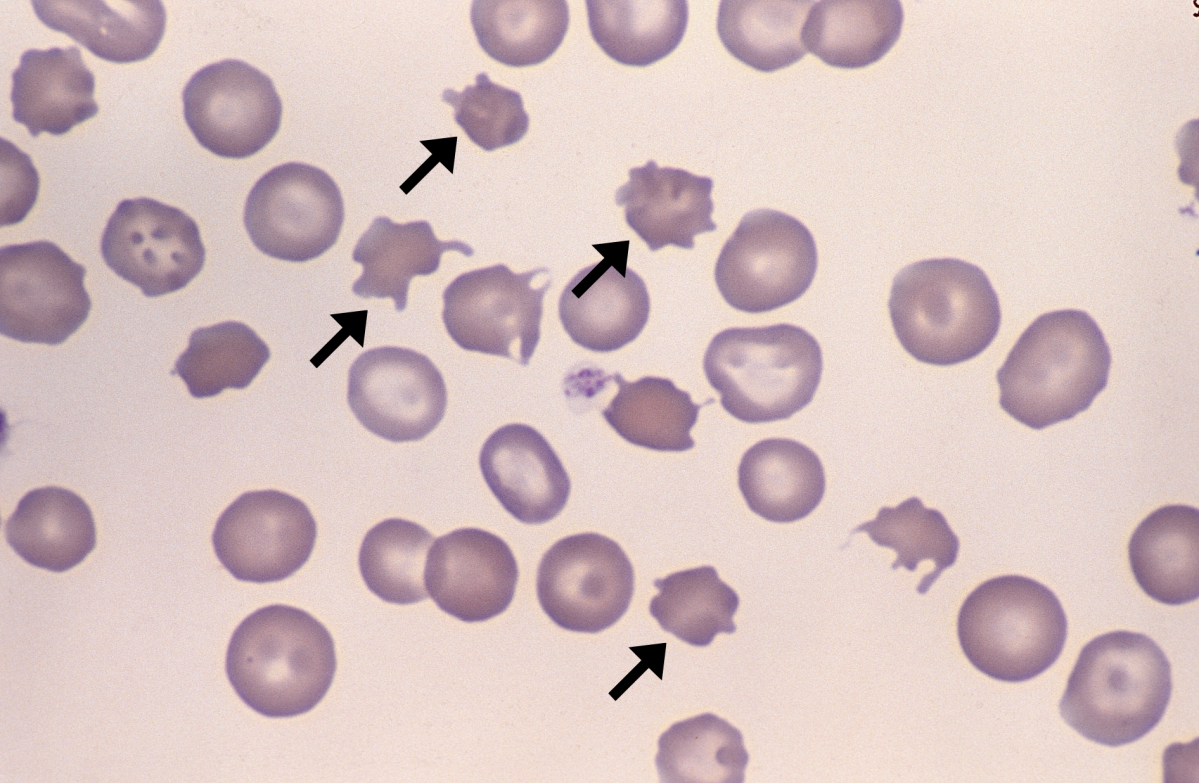
Spur Cell Anaemia:
Characterized by spur cells (acanthocytes) in the blood.
Irregularly shaped cells with spikelike projections.
Association with Lipid Metabolism:
Often linked to disorders affecting lipid metabolism.
Abnormalities in cholesterol and lipoprotein metabolism.
-
In Spur Cell Anaemia, Cholesterol content increased by 25-65%; This leads to what?
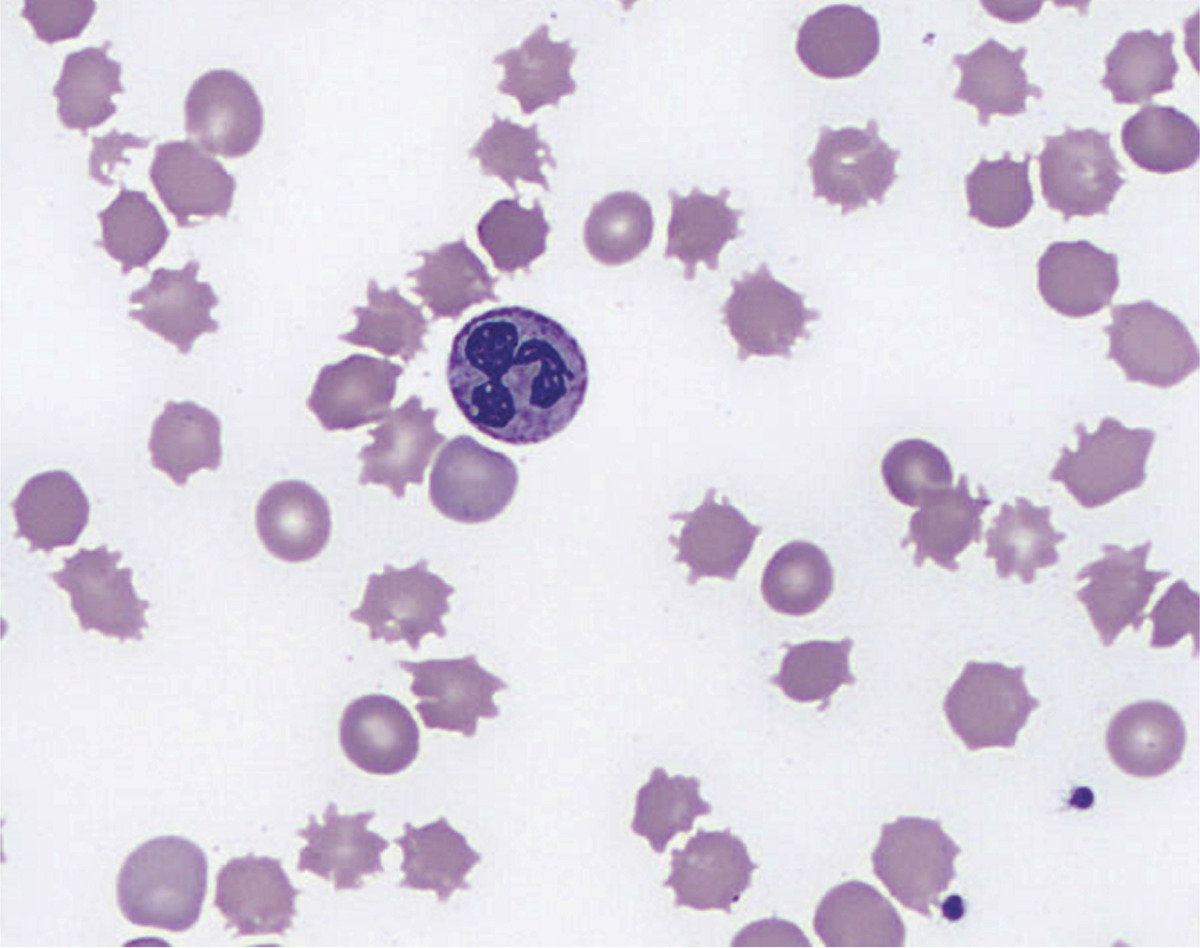
Leading to decreased membrane fluidity
-
Integral membrane proteins can....?(3)
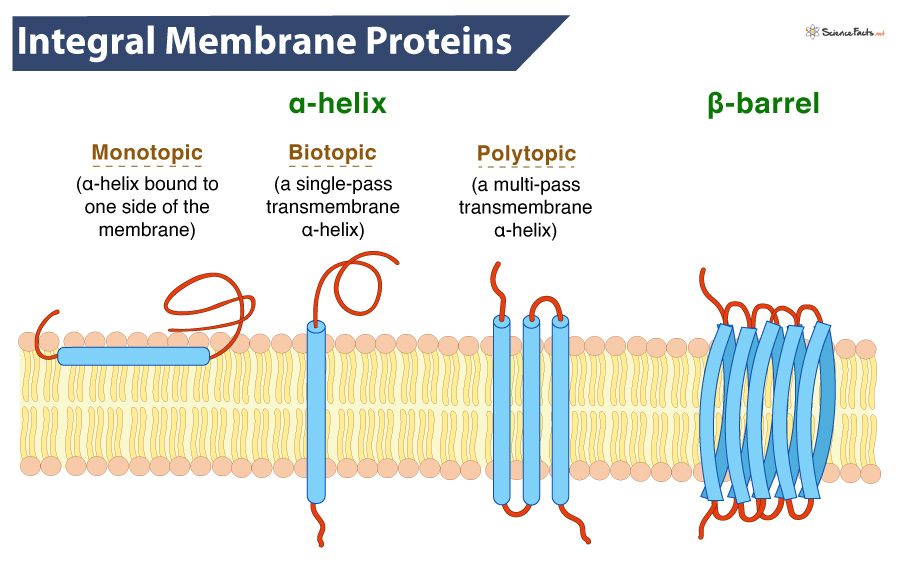
• Be Single or multi pass
• Have Strong non-covalent bonds
• Have Trans-membrane domains, often an a-helix
-
Where are peripheral membrane proteins located? What bonds do they associate with?
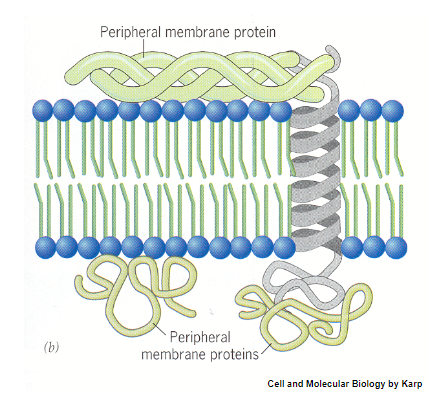
• Located on both the extracellular and cytosolic regions of the membrane
• Associated by non-covalent bonds
-
What are Lipid anchored membrane proteins linked to?
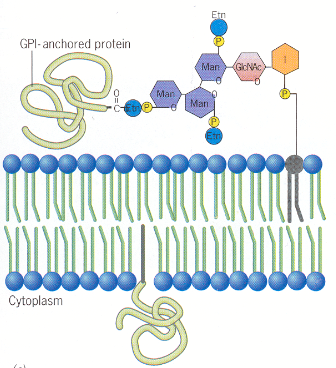
•Covalently linked to a lipid molecule such as glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI)

