-
Any number to the zeroeth power is equal to _____.
1
X0 = 1
-
Multiplication of exponents with the same base
XA × XB = X(A + B)
-
Division of exponents with the same base
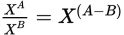
-
Rule for number that is raised to an exponent and then raised again to another exponent
(XA)B = X(A × B)
-
Fraction raised to an exponent
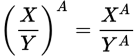
-
Negative exponent
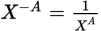
-
Fractional exponent
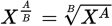
-
12 = _____.
1
-
22 = _____.
4
-
32 = _____.
9
-
42 = _____.
16
-
52 = _____.
25
-
62 = _____.
36
-
72 = _____.
49
-
82 = _____.
64
-
92 = _____.
81
-
102 = _____.
100
-
112 = _____.
121
-
122 = _____.
144
-
132 = _____.
169
-
142 = _____.
196
-
152 = _____.
225
-
162 = _____.
256
-
172 = _____.
289
-
182 = _____.
324
-
192 = _____.
361
-
202 = _____.
400
-
212 = _____.
441
-
222 = _____.
484
-
232 = _____.
529
-
242 = _____.
576
-
252 = _____.
625
-
Square root scientific notation shortcut
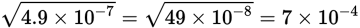
-
Square roots of 2 and 3

-
Logarithm rules
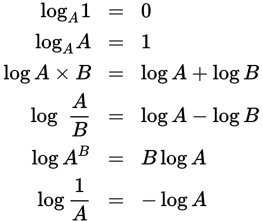
-
In chemistry, "p" is shorthand for _____
-log(_____)
e.g. pH = -log[H+]
-
Euler’s number
e = 2.7182818... (use 2.718)
-
Common logarithms
Base-ten logarithms (log10) are called common logarithms.
-
Natural logarithms
Logarithms based on Euler’s number (loge or ln) are called natural logarithms.
-
Conversion from common to natural logarithm equation
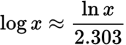
-
When estimating the logarithm of a number, use _____.
scientific notation
-
Logarithm of a value in scientific notation
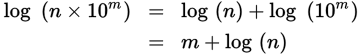
-
Approximating the logarithm of a value in scientific notation
log (n × 10m) ≈ m + 0.n
where 0.n represents sliding the decimal point of n one position to the left (dividing n by ten)
For example, log (9.2 × 108) ≈ 8 + 0.92 = 8.92 (actual = 8.96).

