Any number to the zeroeth power is equal to _____.
1
X0 = 1
Multiplication of exponents with the same base
XA × XB = X(A + B)
Division of exponents with the same base
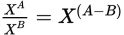
Rule for number that is raised to an exponent and then raised again to another exponent
(XA)B = X(A × B)
Fraction raised to an exponent
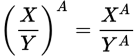
Negative exponent
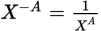
Fractional exponent
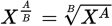
12 = _____.
1
22 = _____.
4
32 = _____.
9
42 = _____.
16
52 = _____.
25
62 = _____.
36
72 = _____.
49
82 = _____.
64
92 = _____.
81
102 = _____.
100
112 = _____.
121
122 = _____.
144
132 = _____.
169
142 = _____.
196
152 = _____.
225
162 = _____.
256
172 = _____.
289
182 = _____.
324
192 = _____.
361
202 = _____.
400
212 = _____.
441
222 = _____.
484
232 = _____.
529
242 = _____.
576
252 = _____.
625
Square root scientific notation shortcut
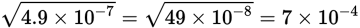
Square roots of 2 and 3

Logarithm rules
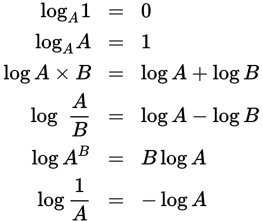
In chemistry, "p" is shorthand for _____
-log(_____)
e.g. pH = -log[H+]
Euler’s number
e = 2.7182818... (use 2.718)
Common logarithms
Base-ten logarithms (log10) are called common logarithms.
Natural logarithms
Logarithms based on Euler’s number (loge or ln) are called natural logarithms.
Conversion from common to natural logarithm equation
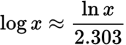
When estimating the logarithm of a number, use _____.
scientific notation
Logarithm of a value in scientific notation
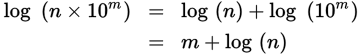
Approximating the logarithm of a value in scientific notation
log (n × 10m) ≈ m + 0.n
where 0.n represents sliding the decimal point of n one position to the left (dividing n by ten)
For example, log (9.2 × 108) ≈ 8 + 0.92 = 8.92 (actual = 8.96).