-
presumptive changes of pregnancy
•Amenorrhea
•Nausea and vomiting
•Fatigue
•Urinary frequency
•Breast changes
•Quickening- “first fetal movement”(could be imaginative or gastric)
-
Quickening
first fetal movement- noticed 16-20 weeks
-
Probable changes of pregnancy
•Goodell’s and Chadwick’s(blueish color of cervix)and Hegar sign
•Enlargement of the abdomen
•Braxton Hicks contractions- practice contractions(16 weeks)
•Uterine soufflé- swish sound during ultrasound- blooding pumping
•Skin pigmentation changes
•Pregnancy tests
-
Nageles Rule for pregnancy dating
Begin with the first day of last missed period, subtract 3 months and add 7 days and add 1 year
-
positive changes of pregnancy
•Fetal heartbeat
•Fetal movement
•Visualization of the fetus
-
Prior to pregnancy
dietary folic acid
-
Weight gain recommendations
◦Underweight: 28 to 40 lb
◦Normal weight: 25 to 35 lb
◦Overweight: 15 to 25 lb
◦Obese: Approximately 11 to 20 lb
◦Twins – 46-62 lb for normal pre-pregnancy weight – adjusted according to BMI
-
Pattern of weight gain
◦First trimester: 2.2 – 4.4 lbs.
◦Second and third trimester: About 1 lb. weekly
◦Twins: Second and third trimesters: 1.5 lbs per week
◦Dieting during pregnancy can result in maternal ketosis
-
Obesity in Pregnancy
Increased risk of:
◦Gestational diabetes
◦Preeclampsia
◦Induction of labor
◦Cesarean birth
◦Anesthesia complications
◦Venous thrombosis
◦Postpartum hemorrhage
◦Endometritis
◦Fetal anomalies
◦Macrosomia
◦Birth injury
◦Stillbirth
-
Pregnancy nutritional concerns
◦Calories in second and third trimester
◦Protein increases 25 g daily ( 46 non pregnant + 25 )
◦Water – 3 L daily
◦Caffeine concerns
◦Mercury in fish
◦Artificial Sweeteners
◦Listeria
-
Vegetarian Diets During Pregnancy
◦There are different types of vegetarian diets
◦Lacto-ovo vegetarians: Dairy and egg products
◦Lacto-vegetarians: Dairy products but no eggs
◦Vegans: No foods from animal sources
◦Most vegans need additional supplementation – vitamins B12, D, and calcium
-
If the placenta attaches over the cervix what is this called ?
placenta previa
-
What is the mother at risk for if the placenta covers the cervix ?
-Hemorrhage -C- Section/ baby will not be able to pass through the cervix
-
Lightening
dropping of baby
-
Common lab tests for 1st prenatal visit
Complete blood count (CBC)
Blood typing
rubella titer
hepatitis B
HIV testing
STI screening
cervical smears
-
1st trimester
1-13 weeks
-
2nd trimester
12-27/28 weeks
-
3rd trimester
28 weeks 38-42
-
What are some risk factors for adverse pregnancy outcomes?
diabetes
folic acid deficiency
hepatitis B
HIV/AIDS
Obesity
STIs
smoking
alcohol
-
What is a non invasive method to monitor the fetus and when can it be done?
Fetal movement counts (kick counts)
from week 28-38
encourage mom to lay on side
encourage mom to eat
-
Ultrasound
images produced by sound waves to check for possible birth defects
-
what does an ultrasound assess?
-to estimate gestational age, fetal weight, and growth
-location of placenta and amniotic fluid volume
-accompanying invasive procedures
-
Doppler blood flow studies
-Intiated at 15 weeks
-measures blood flow changes in maternal and fetal circulation
-assessment of placental function
-if ratio is elevated may indicate baby not growing well
-looks at sys/dias of heart
-
Why is the doppler blood flow study initiated?
If mother has diabetes or baby is not growing well
-
What is aminocentesis?
A procedure to obtain amniotic fluid
Allows testing of amniotic fluid
-
Why is Aminocentesis done?
This test can provide information about genetic disorders and fetal maturity
-
What are some negatives to having Amniocentesis done?
Hemorrhage
Amniotic fluid embolism
Loss of pregnancy
Rh isoimmunization
Can hurt the fetus
Infection
Cause bleeding
Rupture placenta
Cramping
-
What does Amniocentesis procedure look like?
Large needled going into amniotic cavity
-
What is Chorionic villus sampling?
Catheter is used to withdraw a sample of placental tissue to test for chromosomal abnormalities. Test done after 10-13 weeks.
-
What are the complications of Chorionic villus sampling?
Increased risk of injury to fetus
Inability to detect neural tube defects
Risk of failure to obtain placental tissue
risk of contamination of specimen
risk of leakage of amniotic fluid
risk of intrauterine infection
risk of Rh isoimmunization
-
What is Alpha-fetoprotein?
Checks the baby's risk of birth defects and genetic disorders, such as high levels for neural tube defects or low levels for Down syndrome. It is done at 15 to 22 weeks gestation.
-
Nonstress Test
used to assess fetal status using an electronic fetal monitor
If baby moves and heart rate increases-healthy baby
If baby heart rate goes down- unhealthy
-
Fetal kick counts
Provides reassurance of fetal well being(movement 10 x an hour)
-
Reactive non-stress test
FHR acceleration of 15 bpm for 15 seconds in response to fetal movement after 32 weeks
for less than 32 weeks 10 bpm for 10 seconds is acceptable
-
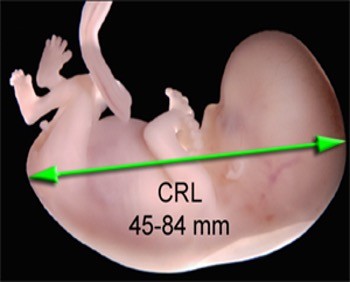
What is crown rump?
Measurement of baby form crown of the head to the buttock shows if the pregnancy is dated correctly
-
Fetal Nuchal Translucency
An intravaginal ultrasound that measures fluid collection in the subcutaneous space between the skin and the cervical spine of the fetus
-
What is fetal nuchal translucency used for ?
-Trisomy 21 -looks to see if there is to much fluid -if there is to much fluid further genetic testing is needed
-
What are the blood test assessments to measure two hormones?
BHCGPAPP-A this is complete the screening for chromosomal abnormalties
-
When is amniocentesis recommended?
Age 35 and older family history of genetic defects blood test or ultra sound hinting at defects
-
When is a Non-stress test (NST) done ?
can be done out patient can be done if the mother is past her due date can be done if there is a medical problem
reactive/nonreactive
-
Nursing interventions if fetus is not moving
lay on left side give sweets wait 30 min give the baby time baby may be sleep they are tiny humans
-
Contraction Stress Test
Given contraction to see how the baby would tolerate labor- would not be done during preterm stage or mother getting a C-section
Enables identification of fetal risk for asphyxia
Fetal monitor is used
Fetal heart rate response to contractions is noted
Healthy fetus usually tolerates contractions
-
Positive Contraction Stress Test
Placenta is not working well because baby is not reacting well to contractions(heart rate decelerates)
-
Biophysical profile ultra sound 5 parameters
- Fetal breathing - Fetal movements body and limbs -Fetal Tone( extension, flextion) - amniotic fluid volume - reactive fetal HR with Reactive NST
-
RH + baby RH - mother
MOM NEEDS ROHGAM
28 weeks pregnant
RH Negative mother after amniocentesis
MUST GET RHOGAM WITHIN 72 HOURS
-
Risk if there is not enough amniotic fluid present during ultrasound ?
Can cause fetal Heart deceleration
-
Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling
Usually for specific circumstances
-to do a blood transfusion
-take blood out
It goes through umbilical cord
-
Routine Assessments
weight and blood pressure (vital signs)
urine testing for protein, glucose, ketones and nitrites
Fundal height measurement to asses fetal growth
Edema
Blood tests
assessment for quickening (fetal movement)
assessment of fetal heart rate- 110-160
-
Danger signs of pregnancy 1st trimester
spotting/ bleeding (miscarriage)
painful urination (infection)
severe vomiting (hyperemesis gravidarum)
fever higher than 100 (infection)
lower abdominal pain with dizziness and shoulder pain (indicative of ruptured or ectopic pregnancy)
-
Danger signs of pregnancy 2nd trimester
regular uterine contractions (preterm labor)
pain in calf, increased foot flexion (DVT)
sudden gush or leakage of fluid from vagina(pre labor rupture of membranes)
absence of fetal movement for more than 12 hours (possible fetal distress or demise)
-
Danger of 3rd trimester
-sudden weight gain; periorbital or facial edema, severe upper abdominal pain; headache with visual changes (indicative of gestational hypertension and/or preeclampsia
-decrease in fetal daily movement for more than 24 hours (possible demise)
-
Onset of labor
-Uterine stretch -Oxytocin increases -Increased prostaglandins -Progesterone withdrawal
-
Five P's of Labor
Passage way ( birth canal ) Passenger ( Fetus ) , powers (contractions) , position( maternal ) , and psychological response
-
Stage 1 of labor and delivery
Stage 1 is considered true labor and consists of 3 phases Latnet 0-6cmactive 6-8cmTransition phase 8-10cm SHORTEST STAGE MONITOR FETAL HR
-
1s stage of labor -(LATENT PHASE )
0-6 cm moms relaxed contractions every 5-10 min Lonest stage of labor
-
1st stage : Active Phase
6-8 cm dilated contractions every 2-5 min
-
1st stage Transition Phase
8-10 cm mom is ready to push
-
Stage 2 labor
10 cm moms fully effaced Birth of the baby encourage mom to bear down when pushing
-
Stage 3 of labor and delivery
birth of placenta within 30 min Never pull umblicusduring this phase there is an increased risk of infection if placenta isn't fully removed PITOCIN
( Prevents hemmorage )
-
Signs of hemmorrage
Decreased blood pressure Increased Heart Rate
-
stage 4 of labor and delivery
1-4 hours after delivery assess : mom assess : Temerature not over 100.4 assess Hemmorage
-
Placenta Seperation signs
uterus rises upward umblicus lenghtens sudden trickle of blood uterus changes to globular PLACENTA SEPERATION HAPPENS IN THE 3rd stage
-
FUNDUS
Should be firm midlineleveled with umblicus check the fundus and massage it until it is firm if it is soft ( boggy )
assessment
3 x eveyr 5 min
-
Fundus abnormality
displaced above umblicus one sided = bladder distention
-
Methergine medication
medication that treats excessive bleeding after childbirth cannot be given if mom has preeclamisia or HTN
-
Fern test
High estrogens in amniotic fluid cause crystallization of the salts ; crystals appear as a blade of fern
-
what does Tocodynamometer meausure ?
external fetal monitoring records the frequency and duration of the contractions placed on fundus
-
what does transducer meausre ?
Fetal Heart tones bottom
-
Why would IUPC be used ?
cant pick up mothers contractions * obese patients * Oliohydramus * baby Heart rate decreases CERVIX MUST BE OPEN 2 CM water needs to be broken
-
Leopold's Maneuvers determine
Engage fetus in uteri position of baby presentation lie
-
Labor induction medication
cytotec amisaprostale cervidil - thins cervix pitocin oxytocin
-
Abrution placenta
Placenta separates off wall before the baby is born if this happens baby will not receive oxygen or nutrients emergency c section Cause : HTN TRAUMA
-
Bishop score
Pre labor scoring that helps predict success of induction
High bishop score
Favorable for induction 8-9
-
Low bishop score indicates
High risk for c- section cervadil medication cytotec
-
AROM / SROM ( Spontaneous rupture of membranes )
Gush of fluid trickle Pooling in vagina ( SROM) PH greater than 5 ( ninrazine paper) turns blue or green alkaline ph greater than 6.5
-
What three methods do nurses use to assess frequency duration and intensity of contraction?
Palpation External fetal monitoring (tocotransducer)Internal Fetal Monitoring ( IUPC )
-
Systemic analgesia
Morphine
Meperidine
Butorphanol
Nalbuphine (decreases nausea and vomiting)
Fentanyl (hypotension/ respiratory depression)
Hydroxyzine (reduces anxiety)
-
Epidural
regional block
used for labor and cesarean births
patient receive 500 to 1000 ml of normal saline
Oxygen
left lateral position
T8 to T10 of spinal cord
-
Epidural Opioids
Fentanyl
Sudentanil
Ropivacaine
Morphine
-
V C
E H
A O
L P
Variable deceleration- Cord compression
Early decelaration- Head compression
Acceleration- OKAY!
Late deceleration- Placental insufficiency
-
Aminoinfusion
prevents additional cord compression
room temperature saline into uterus with catheter
-
Tocolytics
Medication to relax uterus
Improves blood flow to uterus decreasing/stopping contractions
ex Terbutaline
used for preterm to stop labor
-
L
I
O
N
Left lateral side (turn)
Iv fluids
Oxygen
Notify provider
-
M
I
N
E
Maternal positioning
Identify labor progress
No intervention
Execute intervention
-
Uterine Resuscitation Steps
1. Change maternal position ex: if on her back turn to left side
2. Provide supplemental oxygen if indicated
3. Give IV bolus for late decelerations or Amnioinfusion for variable decelerations
4. Correct maternal blood pressure: did she just get an epidural?
5. Reduce uterine activity
Alter second stage pushing efforts
-
Adverse effects of epidural
•Maternal Hypotension
•Bladder Distention
•Prolonged Second Stage
•Catheter Migration
•Cesarean Birth
•Maternal Fever
•Nausea/Vomiting and Pruritus from Epidural Opioids
•Respiratory Depression up to 24 hours
-
Threatened Abortion
Spotting, cramping, closed cervix, bleeding unto 24-48hrs, may resolve or pregnancy loss
Treatment: Conservative supportive treatment
Possible reduction in activity in conjunction with nutritious diet and adequate hydration
-
Inevitable abortion
Moderate to severe bleeding cramping, abdominal pain(contractions), cervical dilatation, if rupture of membranes may need DC or DE
Treatment: Vacuum curettage if products of conception are not passed to reduce risk of excessive bleeding and infection
Prostaglandin analogs such as misoprostol to empty uterus of retained tissue (only used if fragments are not completely passed)
-
Incomplete abortion (passage of some of the products of conception)
Intense abdominal cramping
Heavy vaginal bleeding
Cervical dilation
Treatment: Client stabilization
Evacuation of uterus via D&C or prostaglandin analog
-
Complete abortion (passage of all products of conception)
History of vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain
Passage of tissue with subsequent decrease in pain and significant decrease in vaginal bleeding
Treatment: No medical or surgical intervention necessary
Follow-up appointment to discuss family planning
-
Missed abortion (nonviable embryo retained in utero for at least 6 weeks)
Absent uterine contractions
Irregular spotting
Possible progression to inevitable abortion
Treatment: Evacuation of uterus (if inevitable abortion does not occur): suction curettage during first trimester, dilation and evacuation during second trimester
Induction of labor with intravaginal PGE2 suppository to empty uterus without surgical intervention
-
Recurrent abortion
History of three or more consecutive spontaneous abortions
Not carrying the pregnancy to viability or term
Treatment:Evacuation of uterus (if inevitable abortion does not occur): suction curettage during first trimester, dilation and evacuation during second trimester
Induction of labor with intravaginal PGE2 suppository to empty uterus without surgical intervention
Identification and treatment of underlying cause (possible causes such as genetic or chromosomal abnormalities, reproductive tract abnormalities, chronic diseases or immunologic problems)
Cervical cerclage in second trimester if incom
-
Management for types of abortion
Ultrasound
•Lab work: pregnancy test, H&H, CBC, T/X
•Bed rest
•Abstinence from sex
•IV / Transfusion
•D & C - Dilation and curettage
•If beyond 12 weeks: induction of labor by oxytocin and Prostaglandins may be used.
•Emotional support and bereavement care
•RhoGAM if Rh negative
-
Ectopic pregnancy signs and symptoms
•Progressive Abdominal pain
•Delayed menses
•Abnormal vaginal bleeding
•If rupture has occurred may experience referred shoulder pain
diagnose: ultrasound, low hcg, progesterone
-
Risk factors for Ectopic pregnancy
Tubal surgery
•Sexually transmitted infections
PID
•Previous ectopic pregnancy
•IUD use
•Progestin-only contraceptive
•Pharmacologic treatment of infertility
•Endometriosis
•Assisted reproductive technologies
-
Ectopic pregnancy treatment
Methotrexate ( folic acid antagonist) Dissolves Pregnancy Given IM
•Must be unruptured, less than 3.5-4cm size or less
•Woman must be in stable condition, no blood , kidney or liver disease
•Surgery-salpingostomy to preserve tube or removal of tube salpingotomy
-
Cervical Insufficiency
-Premature dilatation of the cervix which leads to 2nd trimester loss around 20 weeks
-Painless dilatation
-Can be diagnosed with transvaginal ultrasounds and speculum examinations
-
Incompetent Cervix
•Premature dilatation of the cervix
•Associated with repeated second trimester spontaneous abortions
•Painless, bloodless 2nd trimester abortion
•Minimal uterine contractions until late
•Considered an anomaly (uterine/cervical)
•Intrauterine pressure increases
•Internal cervical os dilates and membranes may protrude and rupture
•Spontaneous effacement and dilatation may occur
-
Placenta Previa
Symptoms
•Painless, quiet onset bright red bleeding
•Bleeding may be intermittent or continuous
•Uterus soft, palpable
•Presenting part is high and deviated to one side
•Associated with preeclampsia
-
Management of Placenta Previa
Expectant Management
-Observation and bed rest/pelvic rest if less than 36 week gestation, normal FHR and mild bleeding that resolves
-No vaginal or rectal exam
-NST/BP once or twice weekly
-Assess bleeding
-Potential emergency
Active Management
-If past 36 weeks gestation – can deliver
-If excessive or continued bleeding can deliver at any gestational age

