-
Nageles Rule for pregnancy dating
Begin with the first day of last missed period, subtract 3 months and add 7 days and add 1 year
-
Common lab tests for 1st prenatal visit
Complete blood count (CBC)
Blood typing
rubella titer
hepatitis B
HIV testing
STI screening
cervical smears
-
1st trimester
1-13 weeks
-
2nd trimester
12-27/28 weeks
-
3rd trimester
28 weeks 38-42
-
What is the fundal height at 20 weeks?
by the bellybutton
-
What are some risk factors for adverse pregnancy outcomes?
diabetes
folic acid deficiency
hepatitis B
HIV/AIDS
Obesity
STIs
smoking
alcohol
-
A pregnant patient is complaining about urinary frequency or incontinence. What therapeutic advice can the nurse give?
Try pelvic floor exercises to increase control over leakage
empty bladder when you first feel full sensation
avoid caffeinated drinks
reduce fluid intake after dinner to reduce nighttime urination
-
A pregnant patient is complaining of constant nausea and vomitting. What should the nurse suggest?
avoid an empty stomach at all times
eat dry crackers/toast before arising
avoid brushing teeth right after eating to avoid gag reflex
drink fluids between meals rather than with them
avoid greasy foods
-
What is a non invasive method to monitor the fetus and when can it be done?
Fetal movement counts (kick counts)
from week 28-38
encourage mom to lay on side
encourage mom to eat
-
Ultrasound
images produced by sound waves to check for possible birth defects
-
Quickening
noticed 16-20 weeks
-
what does an ultrasound assess?
to estimate gestational age, fetal weight, and growth
location of placenta and amniotic fluid volume
accompanying invasive procedures
-
Doppler blood flow studies
Intiated at 15 weeks
measures blood flow changes in maternal and fetal circulation
assessment of placental function
if ratio is elevated may indicate baby not growing well
looks at sys/dias of heart
-
Why is the doppler blood flow study initiated?
If mother has diabetes or baby is not growing well
-
What is aminocentesis?
A procedure to obtain amniotic fluid
Allows testing of amniotic fluid
-
Why is Aminocentesis done?
This test can provide information about genetic disorders and fetal maturity
-
What are some negatives to having Amniocentesis done?
Hemorrhage
Amniotic fluid embolism
Loss of pregnancy
Rh isoimmunization
Can hurt the fetus
Infection
Cause bleeding
Rupture placenta
Cramping
-
What does Amniocentesis procedure look like?
Large needled going into amniotic cavity
-
What is Chorionic villus sampling?
Catheter is used to withdraw a sample of placental tissue to test for chromosomal abnormalities. Test done after 10-13 weeks.
-
What are the complications of Chorionic villus sampling?
Increased risk of injury to fetus
Inability to detect neural tube defects
Risk of failure to obtain placental tissue
risk of contamination of specimen
risk of leakage of amniotic fluid
risk of intrauterine infection
risk of Rh isoimmunization
-
What is Alpha-fetoprotein?
Checks the baby's risk of birth defects and genetic disorders, such as high levels for neural tube defects or low levels for Down syndrome. It is done at 15 to 22 weeks gestation.
-
Nonstress Test
used to assess fetal status using an electronic fetal monitor
If baby moves and heart rate increases-healthy baby
If baby heart rate goes down- unhealthy
-
Fetal kick counts
Provides reassurance of fetal well being(movement 10 x an hour)
-
Reactive non-stress test
FHR acceleration of 15 bpm for 15 seconds in response to fetal movement after 32 weeks
for less than 32 weeks 10 bpm for 10 seconds is acceptable
-
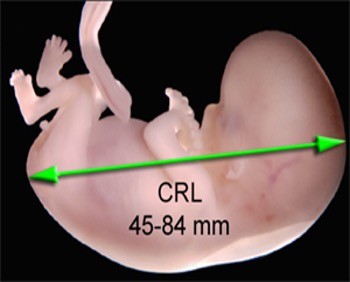
What is crown rump?
Measurement of baby form crown of the head to the buttock shows if the pregnancy is dated correctly
-
Fetal Nuchal Translucency
An intravaginal ultrasound that measures fluid collection in the subcutaneous space between the skin and the cervical spine of the fetus
-
What is fetal nuchal translucency used for ?
-Trisomy 21 -looks to see if there is to much fluid -if there is to much fluid further genetic testing is needed
-
What are the blood test assessments to measure two hormones?
BHCGPAPP-A this is complete the screening for chromosomal abnormalties
-
When is amniocentesis recommended?
Age 35 and older family history of genetic defects blood test or ultra sound hinting at defects
-
Normal baby heart rate
110-160
-
When is a Non-stress test (NST) done ?
can be done out patient can be done if the mother is past her due date can be done if there is a medical problem
reactive/nonreactive
-
Nursing interventions if fetus is not moving
lay on left side give sweets wait 30 min give the baby time baby may be sleep they are tiny humans
-
Contraction Stress Test
Given contraction to see how the baby would tolerate labor- would not be done during preterm stage or mother getting a C-section
Enables identification of fetal risk for asphyxia
Fetal monitor is used
Fetal heart rate response to contractions is noted
Healthy fetus usually tolerates contractions
-
Positive Contraction Stress Test
Placenta is not working well because baby is not reacting well to contractions(heart rate decelerates)
-
Biophysical profile ultra sound 5 parameters
- Fetal breathing - Fetal movements body and limbs -Fetal Tone( extension, flextion) - amniotic fluid volume - reactive fetal HR with Reactive NST
-
RH + baby RH - mother
MOM NEEDS ROHGAM
-
When is Rhogam given to RH - mother
28 wees pregnant
-
RH Negative mother after amniocentesis
MUST GET RHOGAM WITHIN 72 HOURS
-
Nursing education after amniocentesis
its done under ultrasound guidance may expirence cramping pressure after
-
Risk if there is not enough amniotic fluid present during ultrasound ?
Can cause fetal Heart deceleration
-
Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling
Usually for specific circumstances
-to do a blood transfusion
-take blood out
It goes through umbilical cord
-
If the placenta attaches over the cervix what is this called ?
Placenta previa
-
What is the mother at risk for if the placenta covers the cervix ?
-Hemorrhage -C- Section/ baby will not be able to pass through the cervix
-
Prenatal visits
Up to 28 weeks: every 4 weeks
29-36 weeks: every 2 weeks
37 weeks to birth: every weeks
-
Routine Assessments
weight and blood pressure (vital signs)
urine testing for protein, glucose, ketones and nitrites
Fundal height measurement to asses fetal growth
Edema
Blood tests
assessment for quickening (fetal movement)
assessment of fetal heart rate- 110-160
-
Lightening
dropping of baby
-
Fundal height at 16 weeks
below belly button
-
Fundal height at 26 weeks
like 2 cm above the belly button
-
Danger signs of pregnancy 1st trimester
spotting/ bleeding (miscarriage)
painful urination (infection)
severe vomiting (hyperemesis gravidarum)
fever higher than 100 (infection)
lower abdominal pain with dizziness and shoulder pain (indicative of ruptured or ectopic pregnancy)
-
Danger signs of pregnancy 2nd trimester
regular uterine contractions (preterm labor)
pain in calf, increased foot flexion (DVT)
sudden gush or leakage of fluid from vagina(pre labor rupture of membranes)
absence of fetal movement for more than 12 hours (possible fetal distress or demise)
-
Danger of 3rd trimester
-sudden weight gain; periorbital or facial edema, severe upper abdominal pain; headache with visual changes (indicative of gestational hypertension and/or preeclampsia
-decrease in fetal daily movement for more than 24 hours (possible demise)
-
A patient is experiencing extreme fatigue. As the nurse what can you tell her?
Attempt to get a full nights sleep without interruptions
Eat a healthy balanced diet
Schedule a nap in the early afternoon daily
when feeling tired, pause, and rest
-
A patient is experiencing extreme backache. As the nurse what can you tell her?
Avoid standing or sitting in one position for long periods
Apply heating pad (low setting) to the small back
Support lower back with pillows when sitting
Use proper body mechanics for lighting anything
Avoid excessive bending, lifting, walking without rest periods
Wear supportive low heeled shoes: avoid heels
Stand with shoulders back to maintain posture
-
A patient is experiencing extreme leg cramps. As the nurse what can you tell her?
Elevate legs above heart level throughout day
If you catch cramp, straighten both legs and flex feet toward body
Ask health care provider about taking calcium supplements
Stocking to promote better circulation (compression socks)
-
A patient is experiencing hemorrhoids . As the nurse what can you tell her?
Try to establish regular time for bowel movement
Avoid constipation and straining during defecation
Prevent straining by drinking plenty of fluids and eating fiber rich foods and exercise daily
Use warm site baths and cool witch hazel compresses
-
A patient is experiencing constipation. As the nurse what can you tell her?
Increase intake foods high in fiber and drink at least 8 glasses of fluid
Ingest prunes or prune juice (natural laxative )
Consume warm liquids
Exercise each day to promote movement
Reduce amount of cheese consumed
-
A patient is experiencing heartburn/indigestion. As the nurse what can you tell her?
Avoid spicy or greasy foods
Sleep on several pillows so that head is elevated 30 degrees
Avoid laying down 3 hours after meals
take antacids sparingly
-
Onset of labor
-Uterine stretch -Oxytocin increases -Increased prostaglandins -Progesterone withdrawal
-
fetal presentation
occpital bone (O) Chin (M)Buttocks (S)Scapula ( A)
-
Premonitory signs of labor
- Cervical changes- Lightening- Increased energy level ( Nesting )- "Bloody show"- Braxton Hicks contractions- Spontaneous rupture of membranes( water breaks )
-
true labor
Patient will have a cervical change !! Contactions increase in duration , intensity , and frequency Pain that starts in your back-and radiates to belly bloody show spontaneous rupture
-
False Labor
irregular contractions, discomfort is abdominal, contractions decrease with either rest or activity, NO CERVIX CHANGE !
-
Five P's of Labor
Passage way ( birth canal ) Passenger ( Fetus ) , powers (contractions) , position( maternal ) , and psychological response
-
Passageway
Make sure the mothers Pelvis can accommodate for the Fetus
-
Passageway: Pelvic Shape
*Gynecoid( preferable )-Android( male shaped not favorable ) *Anthropod (usually adaquate)-Platypelloid ( Not favaroble )
-
passageway soft tissues
Cervix pelvic floor muscles vagina
-
passenger
Fetal skullFetal attitudeFetal lieFetal presentationFetal positionFetal stationFetal engagement
-
fetal presentation
Brow & Face makes birthing process very difficult
-
Effacement
thinning of the cervixcervix pulls back 0/ 50/100
-
Fetal station
Baby location baby presentation in the pelvis
-
Powers
contractions - frequency , duration , intensity
-
Maternal Physiological response to labor
Increased heart rate , Increased cardiac out put , increased blood pressure ( during contractions )Decreased GI NPO Decreased glucose NPO
-
Fetal Physiological response
Decrease in fetal oxygen Fetal heart rate accelerations and decelerations
-
Stages of Labor
Stages 1-4 stage 1 ( contractions get to 10 cm ) stage 2 ( delivery of baby goal push out baby ) stage 3 placenta delivery stage 4 ( postpartum recovery do not make pt bleed )
-
Stage 1 of labor and delivery
Stage 1 is considered true labor and consists of 3 phases Latnet 0-6cmactive 6-8cmTransition phase 8-10cm SHORTEST STAGE MONITOR FETAL HR
-
1s stage of labor -(LATENT PHASE )
0-6 cm moms relaxed contractions every 5-10 min Lonest stage of labor
-
1st stage : Active Phase
6-8 cm dilated contractions every 2-5 min
-
1st stage Transition Phase
8-10 cm mom is ready to push
-
Stage 2 labor
10 cm moms fully effaced Birth of the baby encourage mom to bear down when pushing
-
Stage 3 of labor and delivery
birth of placenta within 30 min Never pull umblicusduring this phase there is an increased risk of infection if placenta isn't fully removed PITOCIN ( Prevents hemmorage )
-
Signs of hemmorrage
Decreased blood pressure Increased Heart Rate
-
stage 4 of labor and delivery
1-4 hours after delivery assess : mom assess : Temerature not over 100.4 assess Hemmorage
-
Placenta Seperation signs
uterus rises upward umblicus lenghtens sudden trickle of blood uterus changes to globular PLACENTA SEPERATION HAPPENS IN THE 3rd TRIMESTER
-
FUNDUS
Should be
firm midlineleveled with umblicus check the fundus and massage it until it is firm if it is soft ( boggy )
-
fundus assessment
3 x eveyr 5 min
-
Fundus abnormality
displaced above umblicus one sided = bladder distention
-
Methergine medication
Methylergonovine is a medication that treats excessive bleeding after childbirth cannot be given if mom has preeclamisia or HTN
-
Cardinal Movements
"Every Day Fine Infants Enter Ready (Eager) and Excited"Engagement, descent, flexion, internal rotation, extension, restitution (external rotation), expulsion
-
Fetal Lie
Vertex- normal
Breech- butt legs up
Shoulder
-
Fetal position
LOP- Left Occiput posterior (back to back)
LOT- Left Occiput transverse
LOA- Left Occiput Anterior (facing front)
ROP- Right Occiput posterior
ROT- Right Occiput transverse
ROA- Right Occiput Anterior
-
Birthing positions
recumbent position
left lateral sims
squatting
semi fowlers
sitting
hand and knees
-
Psychosocial considerations
understanding and preparing for childbirth
support from others
present emotional status
beliefs and values
-
Physiological changes during birth
-increased cardiac output
-increased heart rate
-increased blood pressure during uterine contractions
-increased WBC
-increased respiratory rate
-increase in temperature
-decreased GI motility and absorption
-decreased blood glucose level
-
Fetal side of placenta
Schultze presentation- shiny and smooth
(s for shiny)
-
Maternal side of placenta
Duncan presentation- rough and irregular
(D for dirty)
Can cause excessive bleeding
-
Fern test
High estrogens in amniotic fluid cause crystallization of the salts ; crystals appear as a blade of fern
-
what does Tocodynamometer meausure ?
external fetal monitoring records the frequency and duration of the contractions placed on fundus
-
what does transducer meausre ?
Fetal Heart tones bottom
-
Why would IUPC be used ?
* cant pick up mothers contractions * obese patients * Oliohydramus * baby Heart rate decreases CERVIX MUST BE OPEN 2 CM water needs to be broken

