Macroeconomics 142 Test 4 (Currently Incomplete) (from TinyCards)
This deck, custom-made for a class, contains material covered after Test 3. (V.5) (This deck used to be on an amazing spaced-learning service called Tinycards. You can see the original version in all its former glory if you click on it in this archived folder: https://web.archive.org/web/20200829090453mp_/https://tinycards.duolingo.com/collections/2QwH9YRN/macroeconomics-142 ) (I currently have no plans to "complete" this deck and may never be able to do so.)
-
exportsX
-
importsM
-
updated aggregate spending equationC+I+G+X-M C+I+G+NX
-
effect of Europe going into a recession (on the U.S.)Europe imports fewer U.S. goods, which could cause a slowdown in the U.S. economy
-
effect of the U.S. going into a recessionthe entire world goes into a recession
-
effect of imports increasingaggregate spending decreases
-
effect of exports increasingaggregate spending increases
-
reason to tradeVoluntary exchange is mutually beneficial.
-
effect of importsconsumers are better off while producers are worse off
-
effect of exportsproducers are better off while consumers are worse off
-
mpimarginal propensity to import
-
updated spending multiplier equation

-
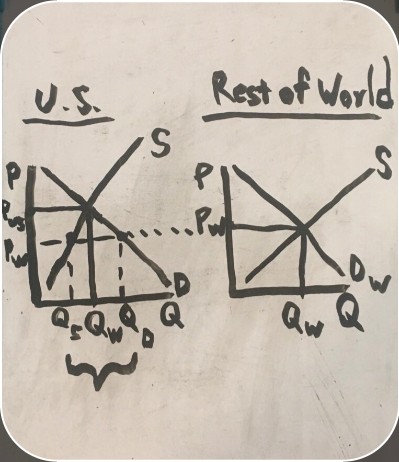
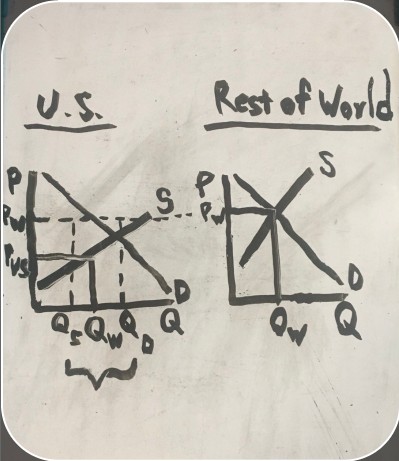
price an item sells for in the U.S.

-
price an item sells for in the rest of the world

-
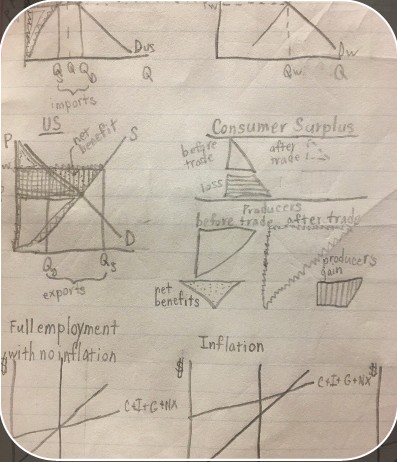
imports on a graph
-
exports on a graph
-
how U.S. exports workleftovers from the U.S. surplus are sold to the world market
-
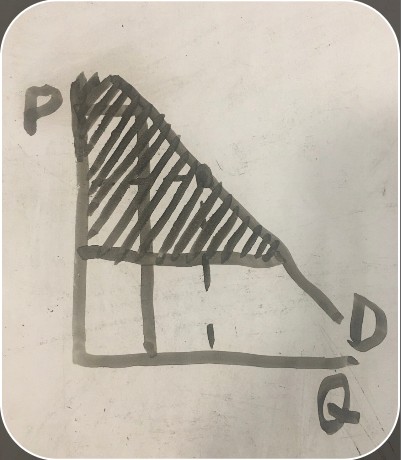
consumer surplus definitionsituation in which the value of something to a consumer is higher than what was paid for it
-
consumer surplus graph
-
price that the consumer is willing to pay for an item (consumer surplus graph)
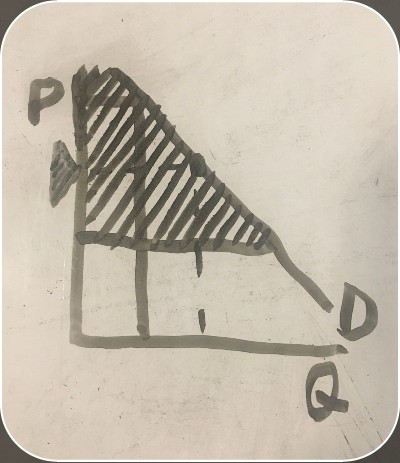
-
the price a consumer paid for an item (consumer surplus graph)
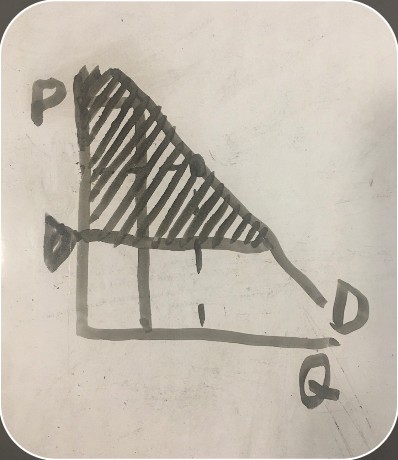
-
producer surplus definitionvalue of the market to producers
-
producer surplus graph
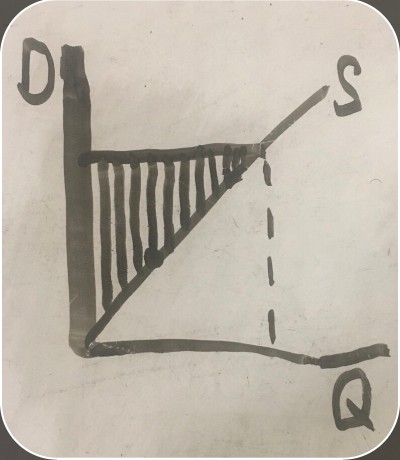
-
market price for an item (price a firm can sell an item for)
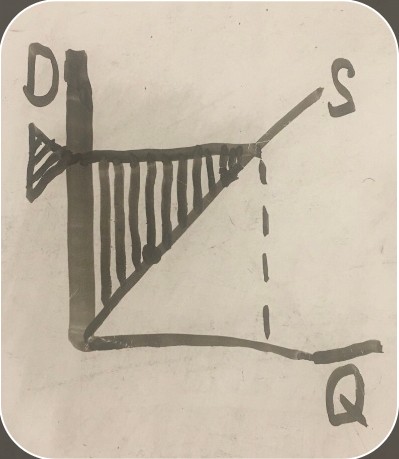
-
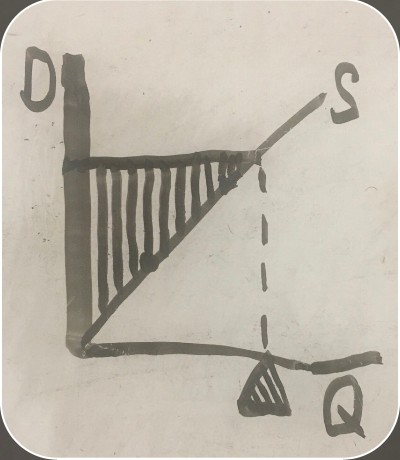
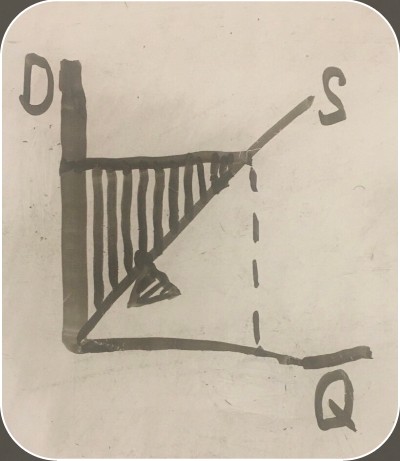
quantity the firm is willing to supply
-
amount of money the firm is willing to produce and sell the item for
-
aggregate demand definitionaggregate spending when prices adjust
-
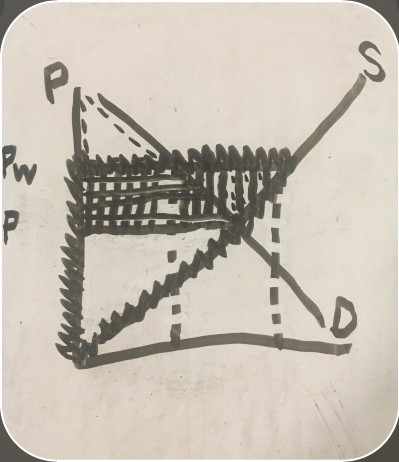
graph showing both consumer and producer surpluses with exports
-
consumer surplus before trade (export consumer and producer surplus graph)

-
consumer surplus after trade (export consumer and producer surplus graph)
-
producer surplus before trade (export consumer and producer surplus graph)
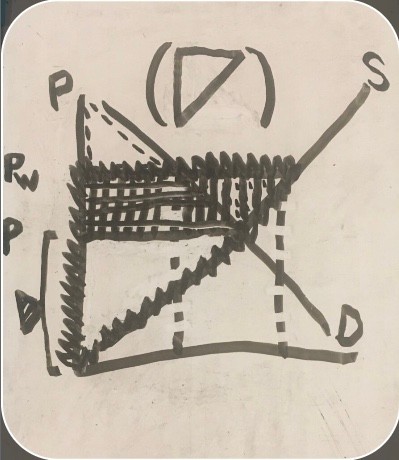
-
producer surplus after trade (export consumer and producer surplus graph)
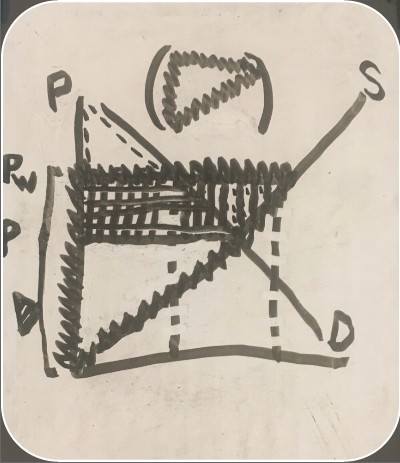
-
loss (export consumer and producer surplus graph)
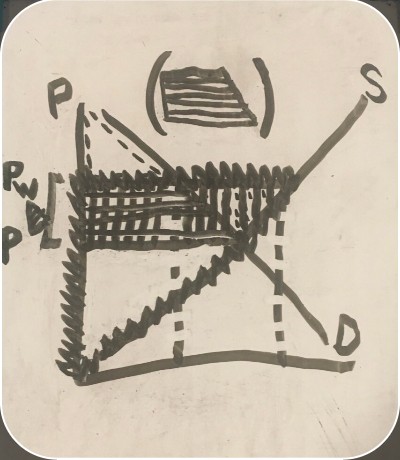
-
gain (export consumer and producer surplus graph)

-
net benefit (export consumer and producer surplus graph)
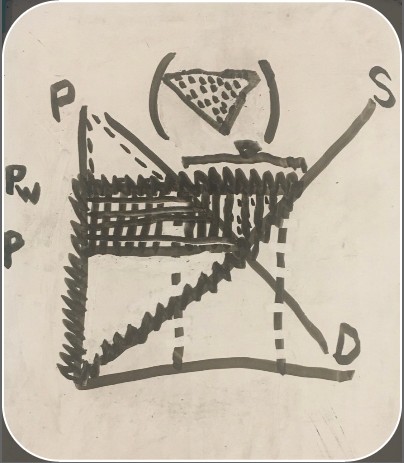
-
U.S. demand (consumer and producer surplus graph)

-
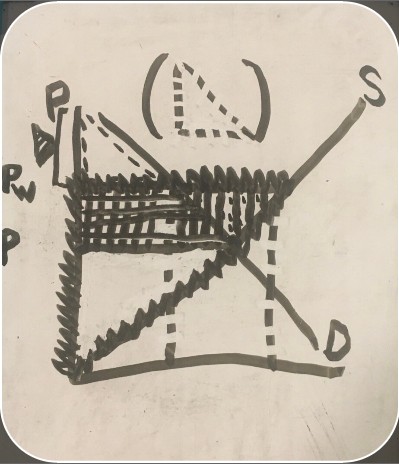
graph showing both consumer and producer surpluses with imports

-
consumer surplus before trade (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

-
consumer surplus after trade (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

-
producer surplus before trade (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

-
producer surplus after trade (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

-
loss (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

-
gain (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

-
net benefit (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

-
wealth definitionincome that people have earned in the past that they now hold in some kind of asset
-
reasons why aggregate spending falls as the price index risesbecause of the wealth effect, the interest rate effect, and the international trade effect
-
wealth effectas prices increase, wealth declines, and therefore spending declines
-
interest rate effectas interest rates increase, investment falls
-
international trade effectimports increase while exports decrease
-
wealth effect, interest rate effect, and international trade effect on graph
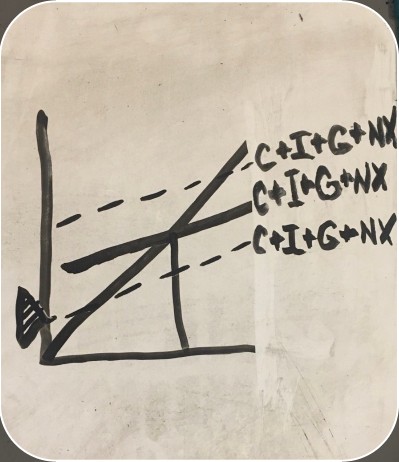
-
effect of falling prices on graph
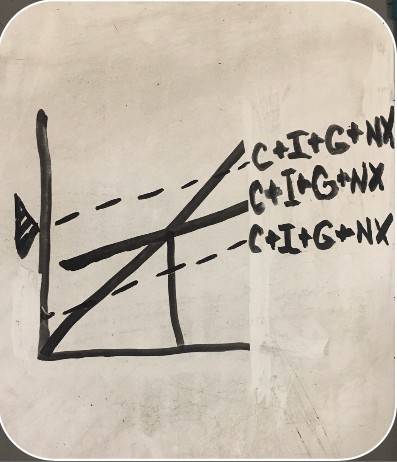
-
aggregate supply graph

-
recession on an aggregate supply graph
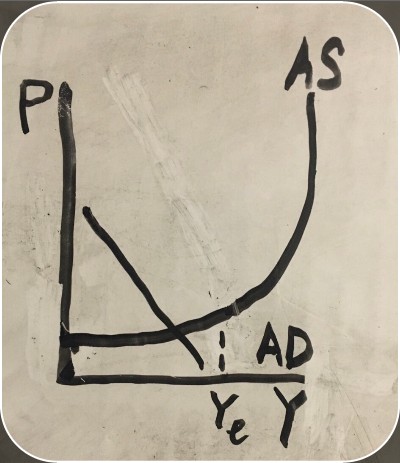
-
inflation on an aggregate supply graph
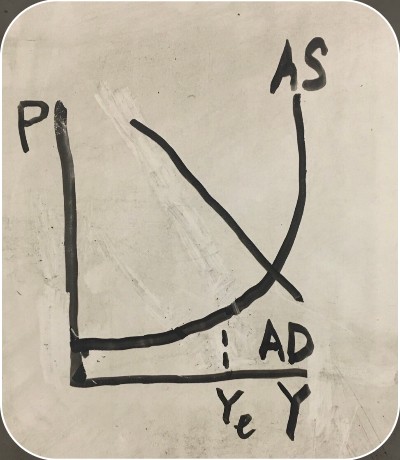
-
things that affect aggregate supplyenergy costs, labor costs, oil, technology, competition, and healthcare

