exports
X
imports
M
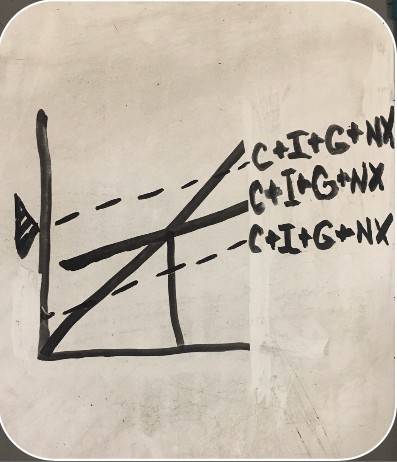
updated aggregate spending equation
C+I+G+X-M
C+I+G+NX
effect of Europe going into a recession (on the U.S.)
Europe imports fewer U.S. goods, which could cause a slowdown in the U.S. economy
effect of the U.S. going into a recession
the entire world goes into a recession
effect of imports increasing
aggregate spending decreases
effect of exports increasing
aggregate spending increases
reason to trade
Voluntary exchange is mutually beneficial.
effect of imports
consumers are better off while producers are worse off
effect of exports
producers are better off while consumers are worse off
mpi
marginal propensity to import
updated spending multiplier equation

price an item sells for in the U.S.

price an item sells for in the rest of the world

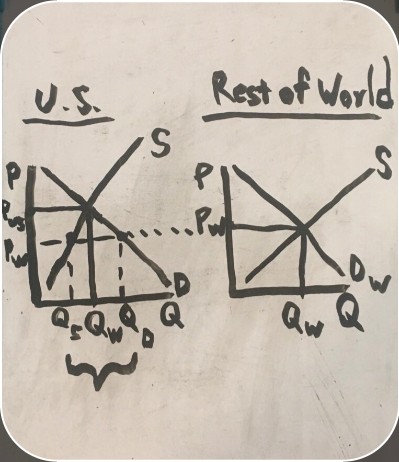
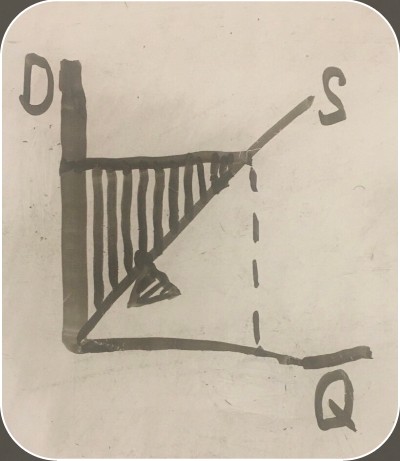
imports on a graph
exports on a graph
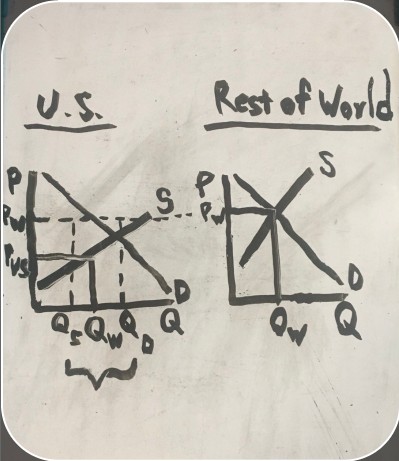
how U.S. exports work
leftovers from the U.S. surplus are sold to the world market
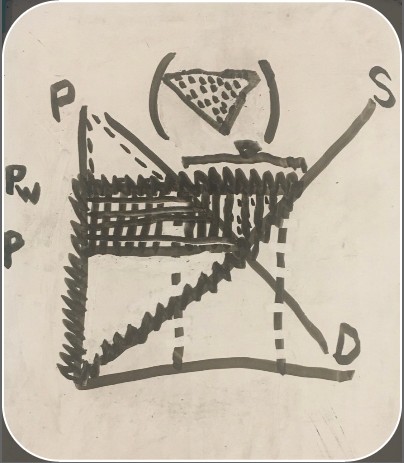
consumer surplus definition
situation in which the value of something to a consumer is higher than what was paid for it
consumer surplus graph
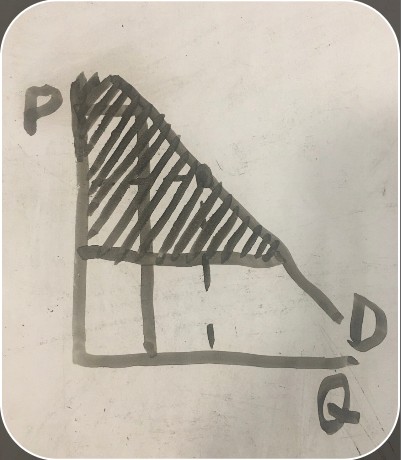
price that the consumer is willing to pay for an item (consumer surplus graph)
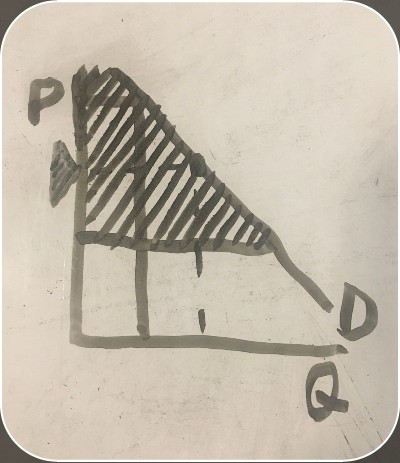
the price a consumer paid for an item (consumer surplus graph)
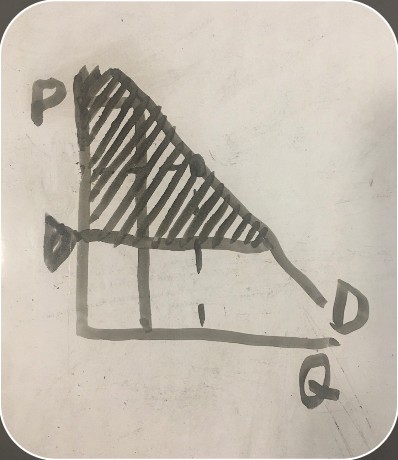
producer surplus definition
value of the market to producers
producer surplus graph
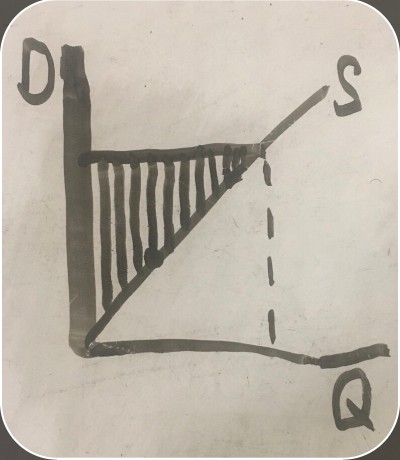
market price for an item (price a firm can sell an item for)
quantity the firm is willing to supply
amount of money the firm is willing to produce and sell the item for
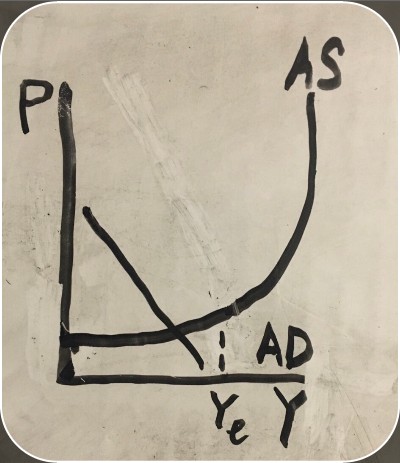
aggregate demand definition
aggregate spending when prices adjust
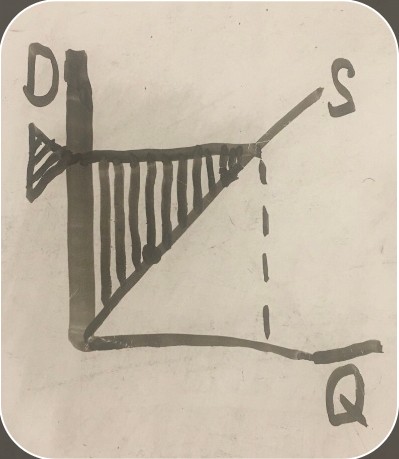
graph showing both consumer and producer surpluses with exports
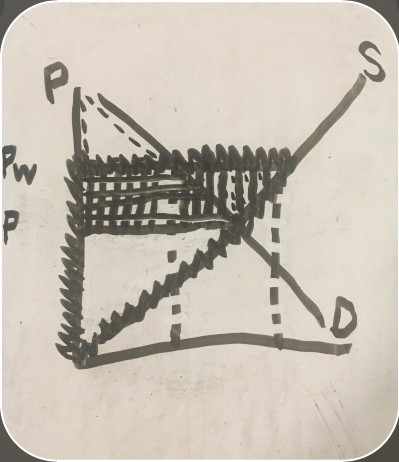
consumer surplus before trade (export consumer and producer surplus graph)

consumer surplus after trade (export consumer and producer surplus graph)
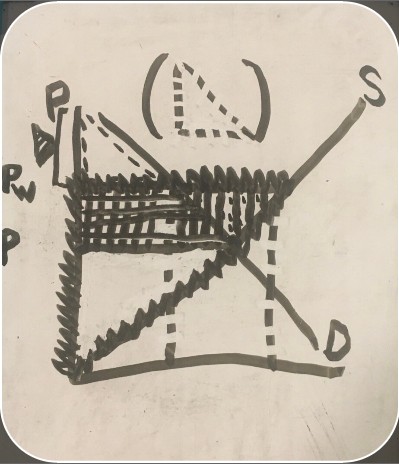
producer surplus before trade (export consumer and producer surplus graph)
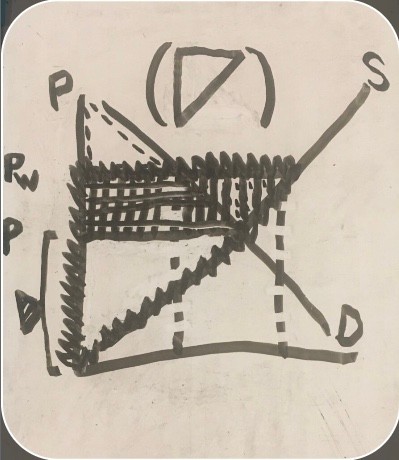
producer surplus after trade (export consumer and producer surplus graph)
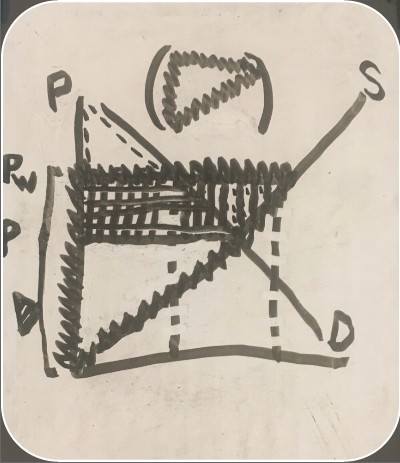
loss (export consumer and producer surplus graph)
gain (export consumer and producer surplus graph)

net benefit (export consumer and producer surplus graph)
U.S. demand (consumer and producer surplus graph)

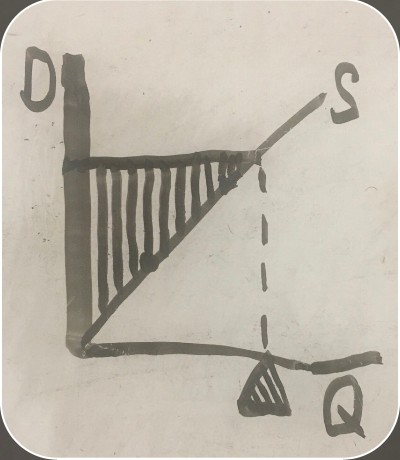
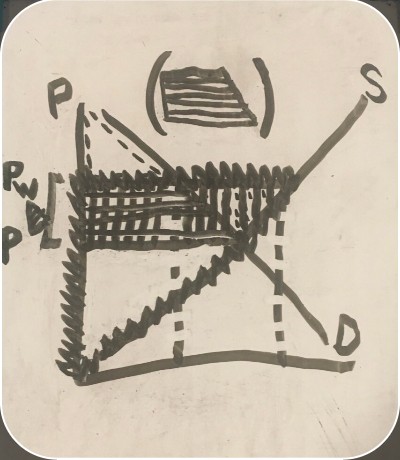
graph showing both consumer and producer surpluses with imports

consumer surplus before trade (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

consumer surplus after trade (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

producer surplus before trade (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

producer surplus after trade (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

loss (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

gain (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

net benefit (import consumer and producer surplus graph)

wealth definition
income that people have earned in the past that they now hold in some kind of asset
reasons why aggregate spending falls as the price index rises
because of the wealth effect, the interest rate effect, and the international trade effect
wealth effect
as prices increase, wealth declines, and therefore spending declines
interest rate effect
as interest rates increase, investment falls
international trade effect
imports increase while exports decrease
wealth effect, interest rate effect, and international trade effect on graph
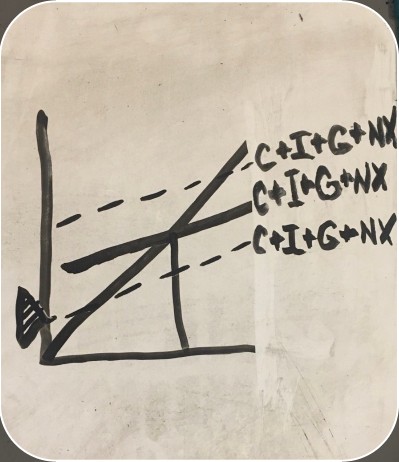
effect of falling prices on graph
aggregate supply graph

recession on an aggregate supply graph
inflation on an aggregate supply graph
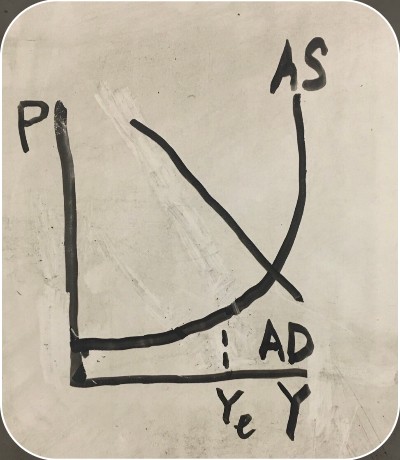
things that affect aggregate supply
energy costs, labor costs, oil, technology, competition, and healthcare