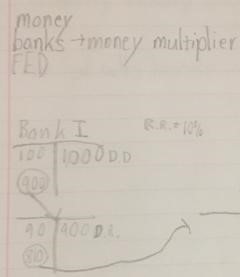
Macroeconomics 142 Test 3 (from TinyCards)
This deck, custom-made for a class, contains material covered after Test 2 through Test 3. (V.6) (This deck used to be on an amazing spaced-learning service called Tinycards. You can see the original version in all its former glory here: https://web.archive.org/web/20200901050747if_/https://tinycards.duolingo.com/decks/PKTgNVsM/macroeconomics-142-test-3 (but you unfortunately can't study it from there).
-
functions of moneymedium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account
-
most important of the functions of moneymedium of exchange
-
characteristics of “good” moneydurability, divisibility, portability, and scarcity
-
the concept that makes money function/what backs up the U.S. dollaran agreement
-
M1official money supply of the U.S.; coins, currency, checking accounts
-
M2M1+small time deposits; closely related to M1
-
M3M2+large ($200,000) time deposits
-
type of money that drives policyM1
-
monetarily significant event that happened in 1914The Federal Reserve System (FED) was established.
-
FED characteristicsany profits go to the treasury and it promotes economic stability
-
FED functionscontrols the U.S. money supply, issues paper money, regulates banks, and is both the government’s bank and the bank’s bank
-
2019 chair of the FEDJerome Powell
-
BoGBoard of Governors
-
Number of members in the BoG7
-
method by which members of the BoG are chosenthey are appointed by the president and approved by Congress
-
BoG term length and expiry time14 years; one expires every two years
-
FOMCFederal Open Market Committee
-
number of members in the FOMC12
-
official who oversees the FOMCchairman of the FED
-
method by which the chairman of the FED is chosenappointed by the president
-
term length and appointment time of the chairman of the FED4 years; one is appointed by the president on even non-presidential election years
-
FDICFederal Deposit Insurance Corporation
-
function of the FDICinsuring the money in banks and federal deposits
-
RRReserve Requirement
-
Reserve Requirement definitionthe percentage of deposited money that the FED requires banks to hold
-
money multiplier formula
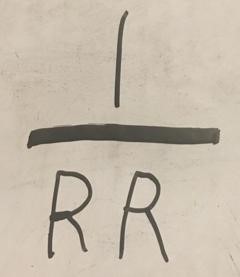
-
factors that can reduce the size of the money multiplierpeople keeping cash on hand or banks holding more money than they are required to hold
-
U.S. bondsunits of the U.S. debt that are sold when taxes do not raise enough money to fund the U.S. government
-
interest rate definitionthe percentage of money that consumers pay banks when they borrow money from them
-
discount rate definitionthe interest rate that the FED charges banks when banks borrow money from it; has an impact on the interest rate
-
Open Market Operations definitionthe buying and selling of U.S. bonds
-
Quantitative easing definitionsimilar to Open Market Operations, except that the government buys securities
-
Monetary Controlschanging RR, changing the discount rate, Open Market Operations, and Quantitative Easing
-
effect of the Reserve Requirement changingif it decreases, M1 increases; if it increases, M1 decreases
-
effect of the discount rate changingif it decreases, M1 increases; if it increases, M1 decreases
-
effect of Open Market Operationsif the FED buys bonds, M1increases; if the FED sells bonds, M1 decreases
-
Quantity EquationMV=PY
-
M (Quantity Equation)M1
-
V (Quantity Equation)velocity of money
-
P (Quantity Equation)price level
-
Y (Quantity Equation)national output
-
PY (Quantity Equation)GDP
-
the two assumptions about the quantity equationV is stable and Y is equal to Y*
-
velocity of money definitionthe average number of times that each dollar is used
-
velocity of money equation
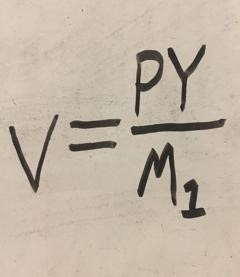
-
Policy Rule of Neoclassical Marketerslet the money supply grow 4-5% per year
-
Monetary policies to use to eradicate a recessionreduce the Reserve Requirement, reduce the discount rate, or buy bonds
-
Monetary policies to use to eradicate inflationraise the Reserve Requirement, raise the discount rate, or sell bonds
-
reason why raising the discount rate helps to eradicate inflationbanks will be less likely to borrow money
-
Monetary policy’s chain of effects in eradicating recessions
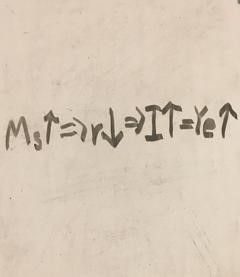
-
Monetary policy’s chain of effects in eradicating inflation
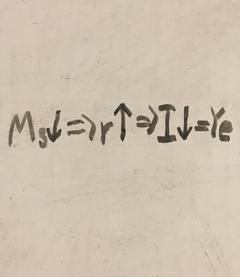
-
Weaknesses of Monetary Policythe liquidity trap and the fact that many things affect investment, not just the interest rate
-
liquidity trap definitionthe situation in which interest rates are so low that they do not respond to additional money stimulation
-
Characteristics of monetary policyit’s less effective during recessions (the worse the recession, the less effective it is) but works fine for inflation
-
economic condition in which fiscal policy is less effectivemild recession
-
Weakness of fiscal policycrowding out: government borrowing “crowds out" private spending because interest rates are higher
-
effect of crowding outthe government spends more money, which stimulates the economy, but that also causes higher interest rates, which causes firms to spend less money
-
best option for eradicating recessionscombining fiscal policy and monetary policy
-
Timing of policy’s types of lagrecognition lag, action lag, and impact lag
-
function of the 11 leading indicatorsthey can be used to predict recessions

