functions of money
medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account
most important of the functions of money
medium of exchange
characteristics of “good” money
durability, divisibility, portability, and scarcity
the concept that makes money function/what backs up the U.S. dollar
an agreement
M1
official money supply of the U.S.; coins, currency, checking accounts
M2
M1+small time deposits; closely related to M1
M3
M2+large ($200,000) time deposits
type of money that drives policy
M1
monetarily significant event that happened in 1914
The Federal Reserve System (FED) was established.
FED characteristics
any profits go to the treasury and it promotes economic stability
FED functions
controls the U.S. money supply, issues paper money, regulates banks, and is both the government’s bank and the bank’s bank
2019 chair of the FED
Jerome Powell
BoG
Board of Governors
Number of members in the BoG
7
method by which members of the BoG are chosen
they are appointed by the president and approved by Congress
BoG term length and expiry time
14 years; one expires every two years
FOMC
Federal Open Market Committee
number of members in the FOMC
12
official who oversees the FOMC
chairman of the FED
method by which the chairman of the FED is chosen
appointed by the president
term length and appointment time of the chairman of the FED
4 years; one is appointed by the president on even non-presidential election years
FDIC
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
function of the FDIC
insuring the money in banks and federal deposits
RR
Reserve Requirement
Reserve Requirement definition
the percentage of deposited money that the FED requires banks to hold
money multiplier formula
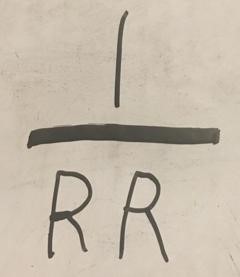
factors that can reduce the size of the money multiplier
people keeping cash on hand or banks holding more money than they are required to hold
U.S. bonds
units of the U.S. debt that are sold when taxes do not raise enough money to fund the U.S. government
interest rate definition
the percentage of money that consumers pay banks when they borrow money from them
discount rate definition
the interest rate that the FED charges banks when banks borrow money from it; has an impact on the interest rate
Open Market Operations definition
the buying and selling of U.S. bonds
Quantitative easing definition
similar to Open Market Operations, except that the government buys securities
Monetary Controls
changing RR, changing the discount rate, Open Market Operations, and Quantitative Easing
effect of the Reserve Requirement changing
if it decreases, M1 increases; if it increases, M1 decreases
effect of the discount rate changing
if it decreases, M1 increases; if it increases, M1 decreases
effect of Open Market Operations
if the FED buys bonds, M1increases; if the FED sells bonds, M1 decreases
Quantity Equation
MV=PY
M (Quantity Equation)
M1
V (Quantity Equation)
velocity of money
P (Quantity Equation)
price level
Y (Quantity Equation)
national output
PY (Quantity Equation)
GDP
the two assumptions about the quantity equation
V is stable and Y is equal to Y*
velocity of money definition
the average number of times that each dollar is used
velocity of money equation
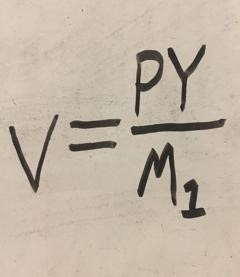
Policy Rule of Neoclassical Marketers
let the money supply grow 4-5% per year
Monetary policies to use to eradicate a recession
reduce the Reserve Requirement, reduce the discount rate, or buy bonds
Monetary policies to use to eradicate inflation
raise the Reserve Requirement, raise the discount rate, or sell bonds
reason why raising the discount rate helps to eradicate inflation
banks will be less likely to borrow money
Monetary policy’s chain of effects in eradicating recessions
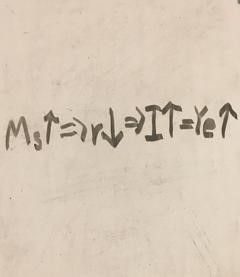
Monetary policy’s chain of effects in eradicating inflation
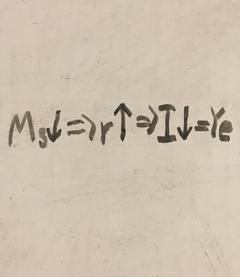
Weaknesses of Monetary Policy
the liquidity trap and the fact that many things affect investment, not just the interest rate
liquidity trap definition
the situation in which interest rates are so low that they do not respond to additional money stimulation
Characteristics of monetary policy
it’s less effective during recessions (the worse the recession, the less effective it is) but works fine for inflation
economic condition in which fiscal policy is less effective
mild recession
Weakness of fiscal policy
crowding out: government borrowing “crowds out" private spending because interest rates are higher
effect of crowding out
the government spends more money, which stimulates the economy, but that also causes higher interest rates, which causes firms to spend less money
best option for eradicating recessions
combining fiscal policy and monetary policy
Timing of policy’s types of lag
recognition lag, action lag, and impact lag
function of the 11 leading indicators
they can be used to predict recessions