-
What does anatomy mean?
To cut apart; the study of body structures.
-
What does physiology mean?
The study of body functions.
-
Label the level of structural organization from smallest to largest.
1. Chemical
2. Cellular
3. Tisssue
4. Organ
5. System
6. Organism
-
To distinguish between non-living and living organisms, they are the 6 basic processes of life. List and define them.
1. Metabolism: chemical reactions in the body; contains anabolism and catabolism.
2. Responsiveness (irritability): ability to detect and respond to change in the environment.
3. Movement: of the body or just one cell.
4. Growth: of one cell or for wound repair.
5. Differentiation: the function or structure of the cell becomes more specific.
6. Reproduction: Cellular (growth and wound repair) and organismal (perpetuation of the species).
-
What are the pros and cons of differentiation?
Pros: responsible for high level functions in our bodies.
Cons: The less likely to successfully respond to stress, and their ability to regenerate to reduces.
-
What is homeostasis?
Maintenance of an optimal internal environment.
-
- optimal concentration
- optimal temp.
- optimal intra and extra fluid volume
These describe what?
Optimal homeostatic internal environment.
-
What is a negative feedback loop?
Any stressor, is the most common and the response reverses the og. stimulus and returns to the set point.
-
What is a positive feedback loop and give an example.
It enhances the original stimulus, thus moving the body further from the set point.
Ex. blood clotting and labour
-
Describe the anatomical position.
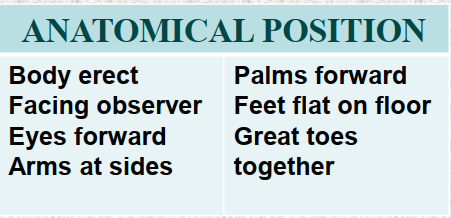
-
What does contralateral mean?
Opposite side of another structure.
-
What does intermediate mean?
Between two structures.
-
What does ipsilateral mean?
Same side as another structure.
-
What is in the thoracic cavity?
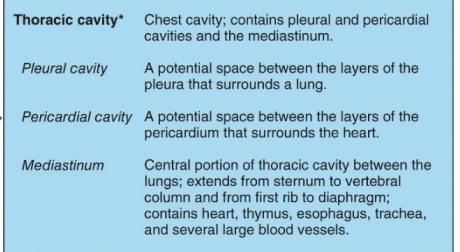
-
What serous membrane covers the lungs?
Parietal and visceral pleura

