-
What are the two classification of senses?Somatic and visceral
-
Somatic senses:qreceptors w/in body wall; or musclesqeg: skin, muscles, tendons, jointsqproprioception
-
Visceral senses:qReceptors w/in visceral organs
-
What are the somatic senses? (6)• Touch • Pressure • Heat • Cold • Pain: NOTE-can also be visceral • Proprioception
-
visceral sense-> ______ pain
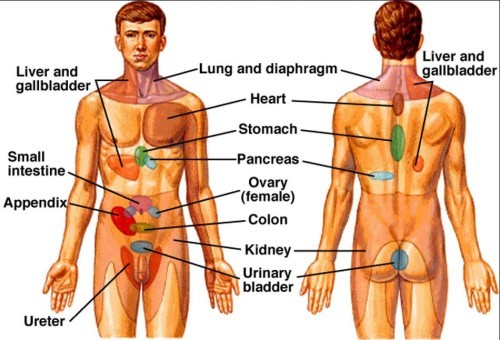 REFERRED
REFERRED -
Where do men most commonly feel pain in a heart attack?left arm pain
-
Where do women most commonly feel pain in a heart attack?jaw
-
Proprioception is also known as the...kinesthetic sense
-
Describe proprioception...conscious awareness of body position and movement • independent of visual input • highly developed in blind people Ascending impulses to cerebellum
-
Where can proprioceptors be found?nProprioceptors: qskeletal muscle (muscle spindle), joint capsules (stretch receptors), tendons qinner ear
-
What are the 5 special senses?Olfaction Taste Vision Hearing Balance
-
Describe olfaction...consists of chemoreception bi-polar neurons perceived in the olfactor cortex Interpretation: temporal, parietal, limbic system
-
Taste is also known as...gustation
-
Describe sensory innervation of gustation.The anterior 2/3rds of the tongue is innervated by cranial neves VII and X (facial and vagus). The posterior third of the tongue is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN IX)
-
What are the receptors involved in gustation?chemoreceptors: a taste buds, gustatory cells
-
Where is gustation or taste perceived?parietal lobe
-
What is the stimulus for the vision sense?photons (light energy)
-
What are the receptors for vision?biopolar neurons in retina rods (black/white); cones (color)
-
Cones detect what?color
-
Rods detect what?black/white
-
Describe the visual sense pathwayOptic nerve -> optic chiasma -> optic tract -> occipital cortex
-
Where is vision interpreted?occipital cortex
-
List the accesory structures for vision. (7)

-
What are the three layers of the eye?fibrous tunic vascular tunic internal tunic (neural)
-
What are the components of the fibrous tunic?sclera-"White of eye" cornea-transparent lens
-
Describe the sclera.aka white of eye dense elastic/collagenous fibers has pain receptors
-
Describe the cornea.has superficial epithelium, avascular,
-
What is the vascular tunic also known as?uvea
-
Describe the components of the vascular tunic. (3)Choroid Ciliary body Iris
-
Describe the choroid.lines the posterior aspect of the bulb vessels visible when retina is examined (retina is transparent)
-
Describe the ciliary body of the eye.contains smooth muscle and suspensory ligaments control shape of lens (accomodation)
-
Describe the iris.continuous with choroid smooth muscles arranged in circular and radial patterns controls pupil size (amount of light entering eye)
-
Describe the components of the internal tunic. (1)also known as the neural tunic -retina
-
Describe the retinapart of neural tunic has an outer pigmented later -inner nervous layer (retina) Photoreceptors (rods, cones)
-
Describe the pathway of retina detecting light, bipolar neurons - ganglia cells - optic nerve
-
How many chambers of the eye are there?anterior and posterior chambers
-
Describe the anterior chamber of the eye.-filled with aqueous humor -supplies nutrients to lens and cornea
-
Describe the subcompartments of the anterior chamber of the eye.anterior segment: b/w cornea and iris posterior segment: b/w iris and lens
-
Where is aqueous humor produced?ciliary body
-
Describe the posterior chamber of the eye.contains vitreous humor (body) the gelatinous consistency contributes the shape of the globe.
-
What are the receptors involved in hearing?organ of corti
-
What is the receptor involved with the sense of balance?semicircular canals (aka vestibular apparatus)
-
Where is hearing and balance interpreted in the brain?temporal lobe
-
The outer ear is known as the...pinnae or auricle
-
The middle ear is also known as the...tympanic cavity
-
the middle ear is lined with...mucous membranes
-
What are the auditory ossicles?malleus, incus, stapes
-
How do the auditory ossicles transmit vibrations?tympanic membrane to oval window
-
What window separates the middle from inner ear?vestibular (oval) window, cochlear window
-
The auditory tube is also known as the...eustachian tube
-
The eustachian tube ________ middle ear to nasopharynx.connects
-
The inner ear is also known as the...labyrinth
-
Describe the components of the inner earvestibule semiciruclar canals cochlea
-
describe the vestibulecomposed of utricle and saccule structures that are involved in equilibrium and gravity (linear motion).
-
Describe the semicircular canals.have semicircular ducts involved in equilibrium (rotational motion)
-
Describe the cochlea.has cochlear duct, organ of Corti involved in hearing
-
The labyrinth is ____ filledfluid
-
The fluid in the labyrinth is transmits...vibrations
-
Endolymph:fluid within membranous labyrinth
-
The _____ is part of the labyrinth.cochlea
-
The spiral "tube" has three chambers:scala vestibull, scala tympani, cochlear duct
-
The spiral organ is also known as the...and is the...organ.organ of Corti, hearing organ
-
The organ of Corti is what type of receptor?mechanoreceptor (responds to mechanical vibrations in fluid). the fluid is endolymph
-
True or False: only input from one ear is required for "sense of balance".FALSE: input from BOTH ears is required.
-
What are the other sources of equilibrium sensory input?• visual (photoreceptors), • tactile receptors (touch), • proprioceptors (tendons, muscle, joint capsule)
-
Normal vision is known as...emmetropia
-
nearsightedness is known as...myopia
-
In myopia, rays focus __ ____ of retina.in front
-
farsightedness is known as...hyperopia
-
In _______, rays focus behind the retinahyperopia
-
What type of lens corrects myopia?concave
-
What type of lens corrects hyperopia?convex
-
_______ is when rays do not focus.Astigmatism
-
What type of lens corrects for astigmatism?uneven
-
Which of the following structures contain exteroceptors? • Skin • Skeletal muscles • Walls of visceraCorrect Answer Skin
-
What type of papillae is largest and least numerous? • Vallate • Foliate • Filiform • Fungiform• Vallate
-
Olfactory receptor cells are neurons. • unipolar • multipolar • bipolarCorrect Answer bipolar
-
What type of receptor is found in the mucous membranes? • Interceptors • Exteroceptors • Proprioceptors• Interceptors
-
The limbus is the junction between the sclera and • retina • cornea • choroid O irisCorrect Answer cornea
-
What is the largest structure of the vascular tunic? • Choroid O Ciliary body • IrisCorrect Answer Choroid
-
What structure is filled with pigment from melanocytes? • Cornea O Pupil • Choroid • Ciliary bodyCorrect Answer Choroid
-
The limbus is the junction between the sclera and • choroid • cornea O iris O retinaCorrect Answer cornea
-
Which of the following are true of rods? • They provide crisp, focused vision. • They are concentrated at the visual axis of the eye, near the center of the retina. • They function well in dim light. • They discriminate between colors.Correct Answer They function well in dim light.
-
What structure creates the "blind spot"? • Fovea centralis • Optic disc • Macula luteaCorrect Answer Optic disc
-
Which are activated by high-intensity light? • Cones • RodsCorrect Answer Cones
-
What is the largest structure of the vascular tunic? • Choroid • Iris • Ciliary bodyCorrect Answer Choroid
-
Which fibers cross at the optic chiasm? • All optic nerve axons of the retina • Optic nerve axons from the medial region of the retina • Optic nerve axons from the lateral region of the retinaCorrect Answer Optic nerve axons from the medial region of the retina
-
Perilymph is similar to and endolymph is similar to O intracellular fluid, cerebrospinal fluid • cerebrospinal fluid, intracellular fluidCorrect Answer cerebrospinal fluid, intracellular fluid
-
Endolymph has a sodium and potassium concentration. O high, high O low, low • low, high • high, lowCorrect Answer low, high

