-
Describe the functions of the circulatory system. (6)Transportation Respiratory Nutritive Excretory Regulatory Protection (injury, immunity)
-
What are the two types of basic blood vessels?arteries, veins
-
Arteries transport blood ____ from heart.AWAY
-
Veins transport blood...back to heart
-
Most arteries carry...blood high oxygen
-
What arteries are the only arteries that does not carry blood high in oxygen?pulmonary arteries
-
The heart's anatomy ensures the ________ flow of blood through it.unidirectional
-
Backflow of blood is prevented by ______ within the heart.valves
-
Describe how the heart works like two side-by-side pumpsThe heart acts like two side-by-side pumps that work at the same rate and pump the same volume of blood; one directs blood to the lungs for respiratory gas exchange, whereas the other directs blood to body tissues for nutrient and respiratory gas delivery.
-
The heart develops ____ ______ through alternate cycles of heart wall contraction and relaxation..blood pressure 1 The heart develops blood pressure through alternate cycles of heart wall contraction and relaxation. Blood pressure is the force of the bloodpushing against the inside walls of the vessels. A minimum blood pressure is essential for pushing blood through the blood vessels.
-
What are the two components of the circulatory system?cardiovascular system composed of heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) lymphatic system composed of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes
-
The heart has how many chambers?FOUR: right and left atria (Upper), right and left ventricles (lower)
-
Trace a drop of blood through the heart noting all major valves, vessels, ventricles, atria, etc.Inferior vena cava→superior vena cava→right atrium→tricuspid valve (aka right atrioventricular valve)→right ventricle→pulonary semilunar valve→pulmonary trunk→pulmonary arteries→pulmonary capillaries→pulmonary veins (now oxygenated)→back to heart to dump oxygenated blood into left atrium→passes through mitral (bicuspid valve)→left ventricle→aortic semilunar valve→aorta
-
What structure seperates the atria?interatrial septum
-
What structure separates ventricles?interventricular septum
-
The coronary sulcus is a...surface depression between atria and ventricles
-
Describe the apex of the heart.
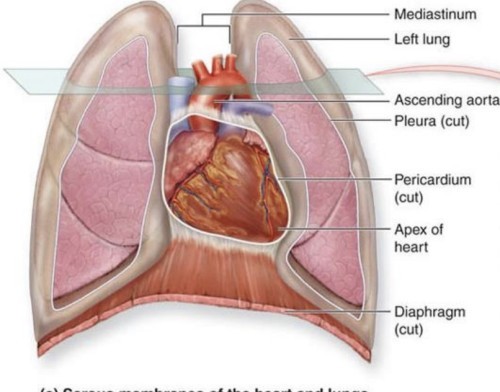 cone shaped end of heart resting on diaphragm
cone shaped end of heart resting on diaphragm -
Describe base of heart
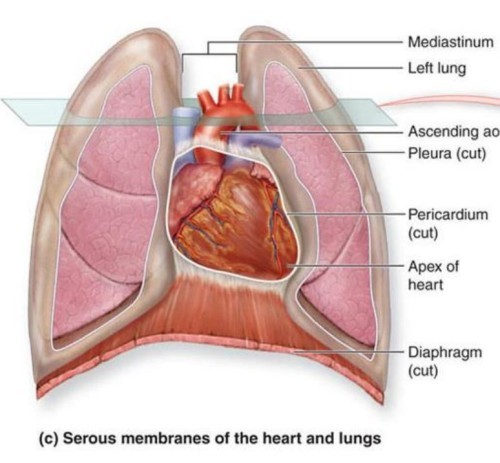 broad superior end where great vessels attach
broad superior end where great vessels attach -
Where is the heart located?
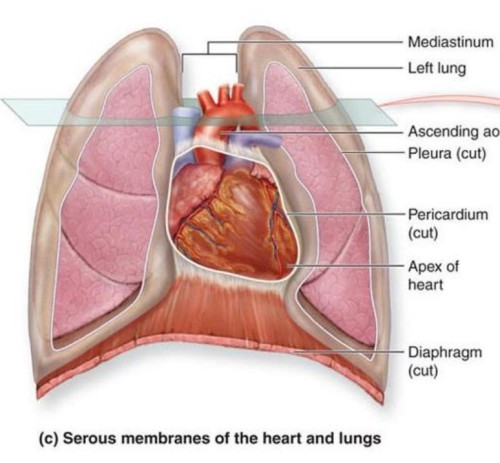 between lungs in the mediatinum
between lungs in the mediatinum -
____ ____ of the heart is left of midlinetwo thirds
-
Describe parietal pericardium-dense fibrous connective tissue -two layers: fibrous pericardium and serous pericardium
-
What layer of parietal pericardium produces pericardial flud?inner serous pericardium
-
Visceral pericardium is also known asepicardium
-
Myocardium is...-cardiac muscle note that thickness varies for each chamber
-
In what chamber of the heart is the myocardium thicker?left ventricle
-
Describe endocardiumit is continuous with endothelium of blood vessels
-
Describe coronary sulcusSurface depression between atria and ventricles
-
Describe Interventricular sulci (anterior & posterior)• Marks division between the ventricles
-
Heart valves ensure what?one-way flow
-
Endocardium is continuous with...endothelium of blood vessels
-
What is the name of the expandable appendage found on the right heart?auricle
-
The right heart receives...systemic venous blood IVC, SVC, coronary sinus
-
The right atrium sends blood through the...right AV valve
-
What type of tissue makes up the endocardium?squamous epithelium
-
What are chordae tendinae?Chordae tendineae are thin, fibrous cords that connect the papillary muscles to the atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral) in the heart
-
What are papillary muscles?Papillary muscles are small, cone-shaped muscles that project from the walls of the ventricles of the heart 1 2. They are attached to the atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and mitral) by thin, fibrous cords called chordae tendineae 1 2. Their function is to contract and maintain tension on the chordae tendineae when the ventricles contract, preventing the valves from being pushed back into the atria and allowing one-way blood flow 1 2 3
-
Right ventricle ejects blood through _____________________to lungspulmonary trunk (and pulmonary arteries)
-
In the left heart, the left atria...(receives...)receives blood from lungs
-
True or False: the left atria has paired right and left pulmonary veins and an auricleTrue
-
The left ventricle has the thickest...myocardium
-
The left ventricle receives blood...receives blood from left atria via left AV valve
-
The left ventricle ejects blood through...ejects blood through aortic semilunar valve note: trabeculae carnae
-
What are trabeculae carnae?The internal wall surface of each ventricle displays characteristic large, smooth, irregular muscular ridges, called the trabeculae carneae
-
What are the three circulatory routes of the heart?pulmonary, systemic, coronary
-
In pulmonary circulation pulmonary arteries carry...deoxygenated blood
-
In pulmonary circulation pulmonary veins carry...oxygenated blood
-
In the systemic circulatory route, what are the components?aorta, vessels of body (not including lungs)
-
Coronary circulation involves what vessels?vessels of the heart
-
From where do the L/R coronary arteries arise from?ascending aorta
-
Coronary arteries travel within...sulci
-
The L/R coronary arteries branch to...supply atrial and ventricular walls
-
What are anastomoses?anastomosis (ã-nas'to-mo'sis; pl., anastomoses, -sez) Union of two structures, such as blood vessels, to supply the same region.
-
L/R coronary arteries branch to form what?anastomoses
-
What are the only branches of the ascending aorta?
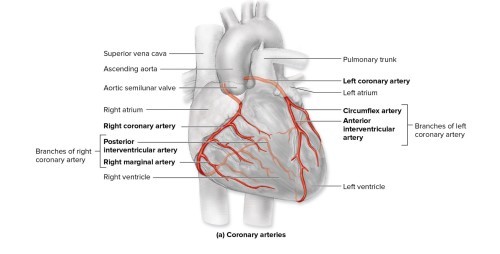 L/R coronary arteries
L/R coronary arteries -
Do the coronary arteries fill with blood when the ventricles contract or when they relax?The coronary arteries fill with blood when the ventricles relax, not when they contract This is because when the ventricles contract, they create high pressure in the aorta, which is where the coronary arteries originate This pressure compresses the openings of the coronary arteries and reduces blood flow to the heart muscle 1 2. When the ventricles relax, the pressure in the aorta drops and the coronary arteries expand, allowing blood to flow into them. The coronary blood flow is also regulated by other factors, such as oxygen demand, metabolic activity, and autonomic nervous system.
-
True or False: coronary veins run parallel to the arteries?true
-
The coronary veins converge to form...coronary sinus
-
The coronary veins return blood to...right atrium
-
Flow chart of blood flow through heart including all 3 circulatory routes
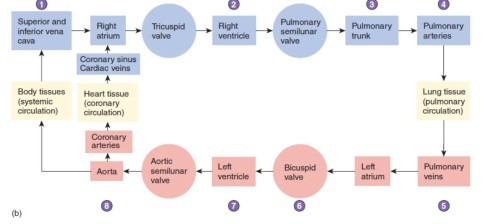
-
What is meant by Intrinsic rhythmicity?Intrinsic rhythmicity is the property of some cells or tissues to generate and maintain their own rhythm of electrical activity without external stimuli 1 2. In the heart, intrinsic rhythmicity is found in the specialized cells of the cardiac conduction system, such as the sinoatrial node (SA node), the atrioventricular node (AV node), the bundle of His, and the Purkinie fibers 2 3
-
The conduction system of the heart has intrinsic ________.rhythmicity
-
How is the intrinisic rhythymicity generated in the heart?conduction myocytes
-
Where does the cardiac cycle initiate?sinoatrial node
-
Systole:contraction of ventricles
-
Diastole:ventricular relaxation
-
Which structures allow muscle impulses to spread rapidly between cardiac muscle cells? a. sarcomeres b. intercalated discs c. chemical neurotransmitters d. AV valvesb. intercalated discs
-
Venous blood from the heart wall enters the right atrium through which vessel? a. superior vena cava b. coronary sinus c. inferior vena cava d. pulmonary veinsb. coronary sinus
-
How is blood prevented from flowing into the right ventricle from the pulmonary trunk? a. closing of the right AV valves b. opening of the pulmonary semilunar valve c. contraction of the right atrium d. closing of the pulmonary semilunar valved. closing of the pulmonary semilunar valve
-
Which of the following is the correct circulatory sequence for blood to pass through part of the heart? a. R. atrium -> right AV valve -> R. ventricle -> pulmonary semilunar valve b. R. atrium -> left AV valve -› R. ventricle -> pulmonary semilunar valve c. L. atrium -> right AV valve -> L. ventricle -> aortic semilunar valve d. L. atrium -> left AV valve -> L. ventricle -> pulmonary semilunar valvea. R. atrium -> right AV valve -> R. ventricle -> pulmonary semilunar valve
-
The pericardial cavity is located between which two structures? a. fibrous pericardium and the parietal layer of the serous pericardium b. parietal and visceral layers of the serous pericardium c. visceral layer of the serous pericardium and the epicardium d. myocardium and the visceral layer of the serous pericardiumb. parietal and visceral layers of the serous pericardium
-
In the developing heart, the atria form from the primitive atrium and which other structure? a. sinus venosus b. bulbus cordis c. primitive ventricle d. conus cordisa. sinus venosus
-
What are the irregular muscular ridges in the ventricular walls called? a. papillary muscles b. trabeculae carneae c. chordae tendineae d. moderator bandsb. trabeculae carneae
-
In what location does the sympathetic innervation of cardiac muscle originate? a. CN X (vagus nerve) b. LI-L2 segments of the spinal cord c. the AV node d. TI-T5 segments of the spinal cordd. TI-T5 segments of the spinal cord
-
.Which of the following does not occur when the ventricles contract? a. closing of the AV valves b. blood ejecting into the pulmonary trunk and aorta c. closing of the semilunar valves d. opening of the semilunar valvesc. closing of the semilunar valves
-
What is the thickest part of the heart wall? a. the pericardium b. the epicardium c. the myocardium d. the endocardiumc. the myocardium

