-
What 5 things Makes a tree?
A combination of the following:
- Perennial, Woody plant that is stuck together using lignin
- 15-20 ft tall or larger
- single trunk unbranched for several feet
- mostly defined crown
- Deal with long-term climate
-
What are trees good for?
- Ecosystem Services, Including:
- Carbon sequestering
- Air FIltering
- Provide Wood
- Provide Food
-

What is a Gymnosperm?
"Naked Seed"
Not an enclosed Seed, ovule exposed during pollination
MOSTLY Evergreens and Conifers (not always)
-

What is an Angiosperm?
Flowering Plants
Ovule in ovary at pollination
Ovary--> Fruit
Evergreen or deciduous
-
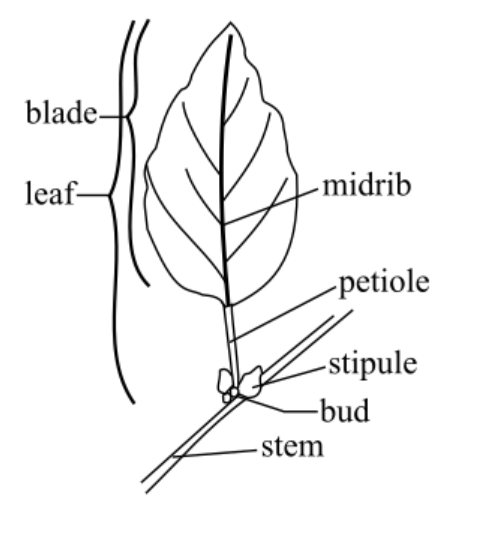
Label the following:
-
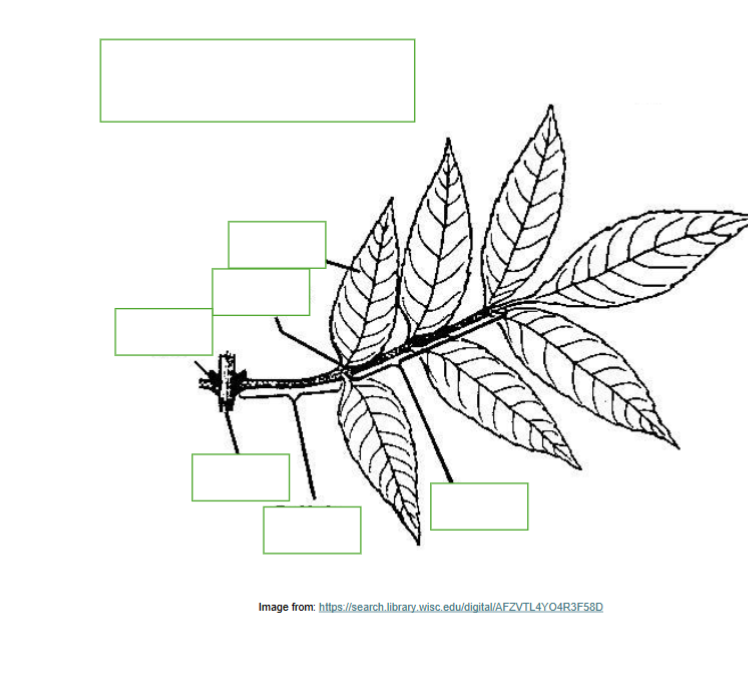
Label the following:
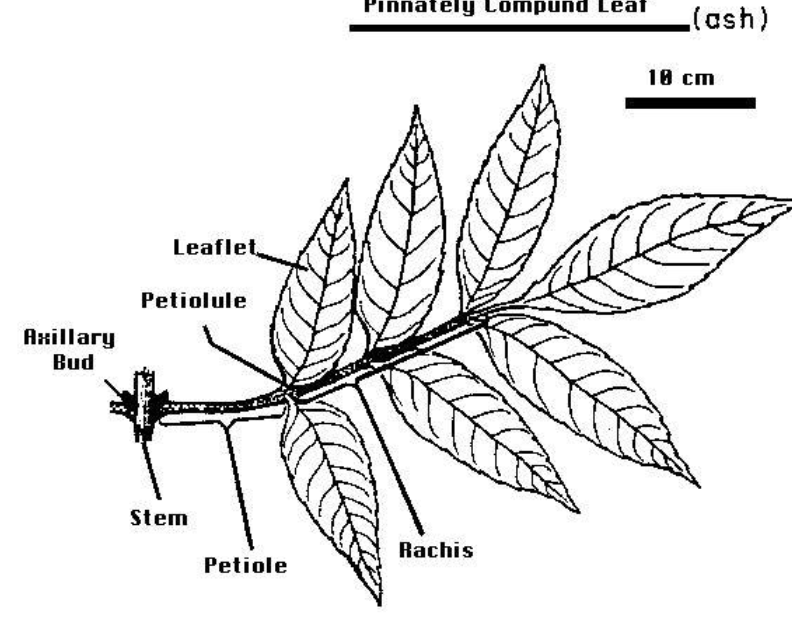
-
Label The following:
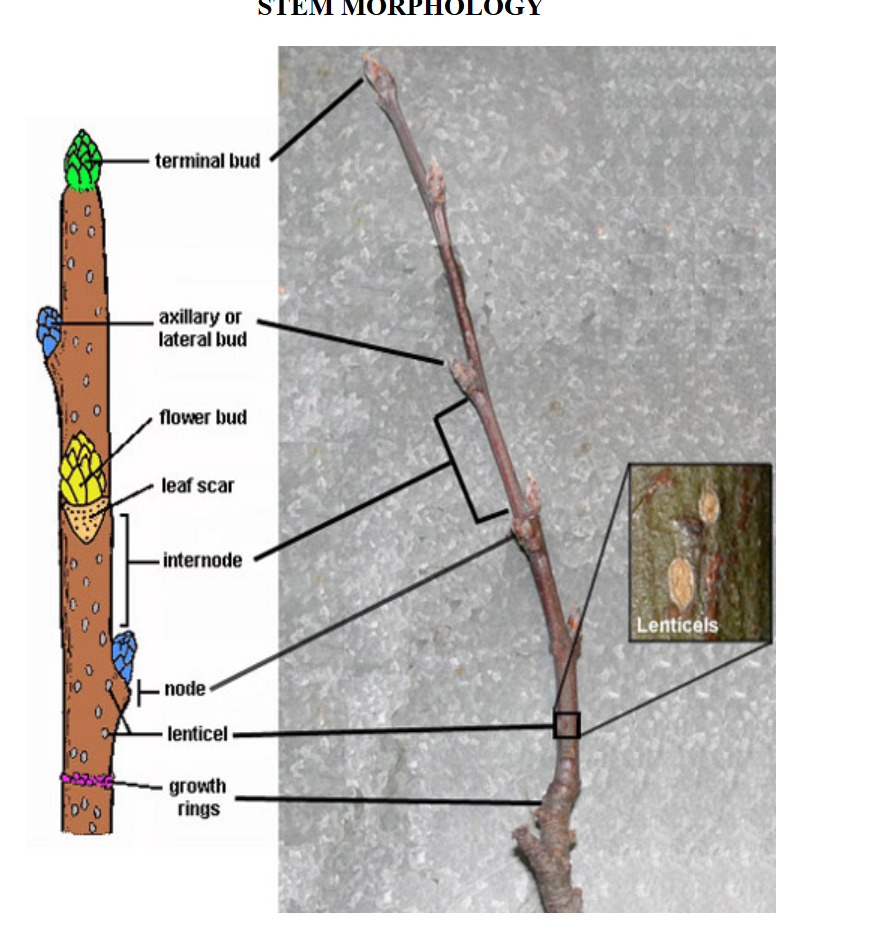
-

Label the Following Leaf Types:
-

Label the Following:
Sun Leaves(Right) Vs Shade Leaves (Left)
-
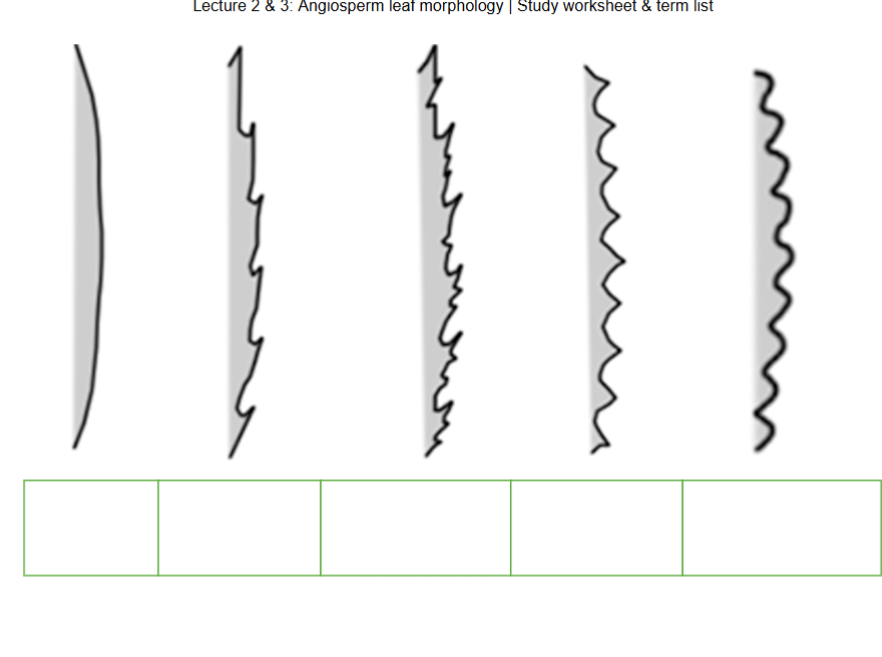
Label the Following:
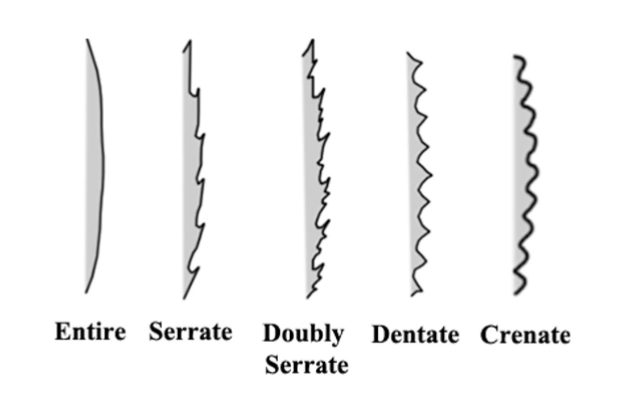
-
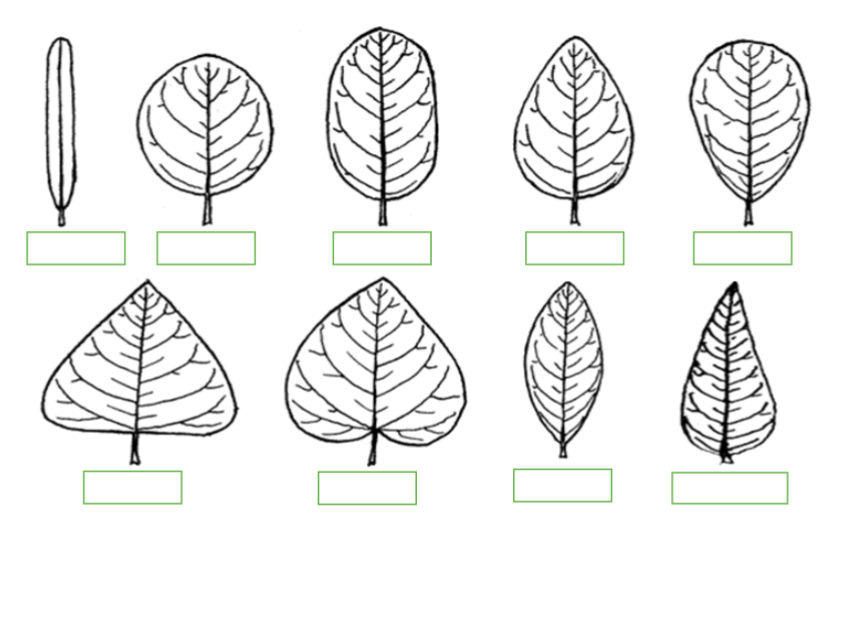
Label the Following:
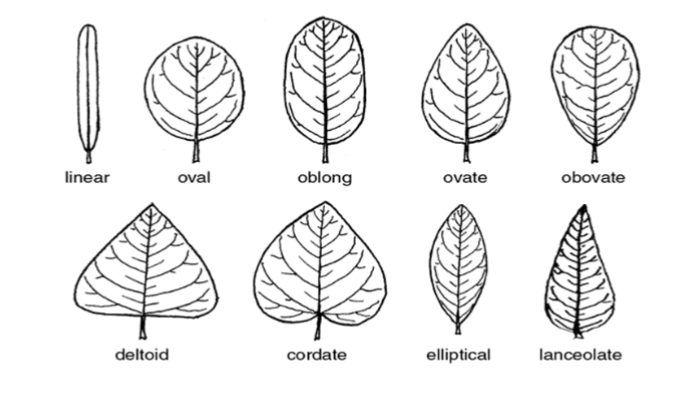
-
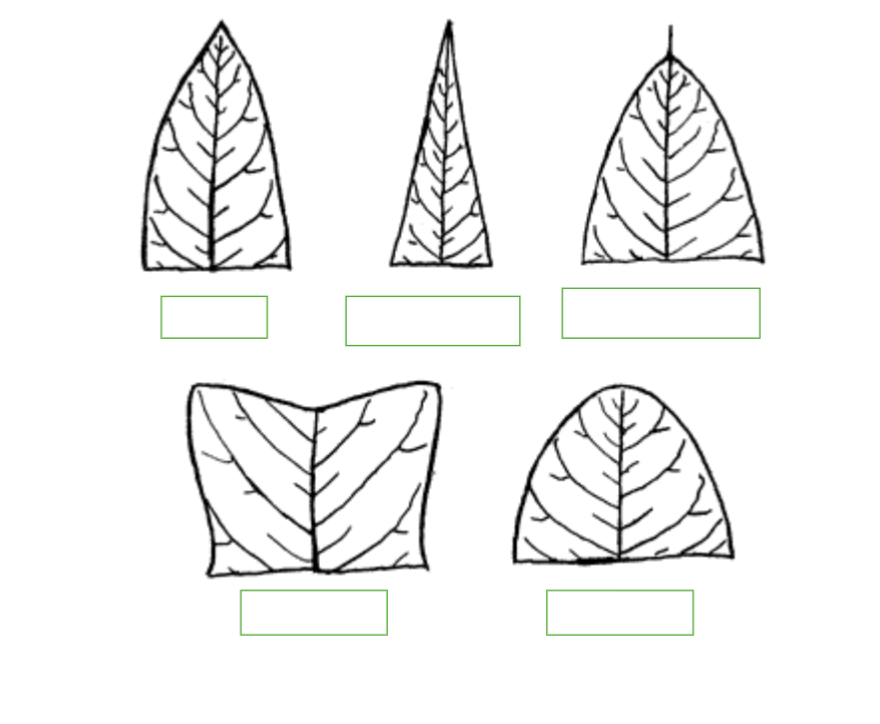
Label the Following:
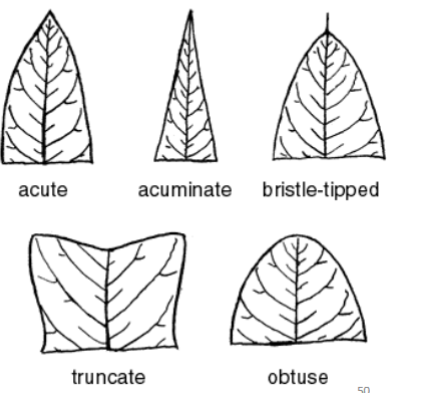
-
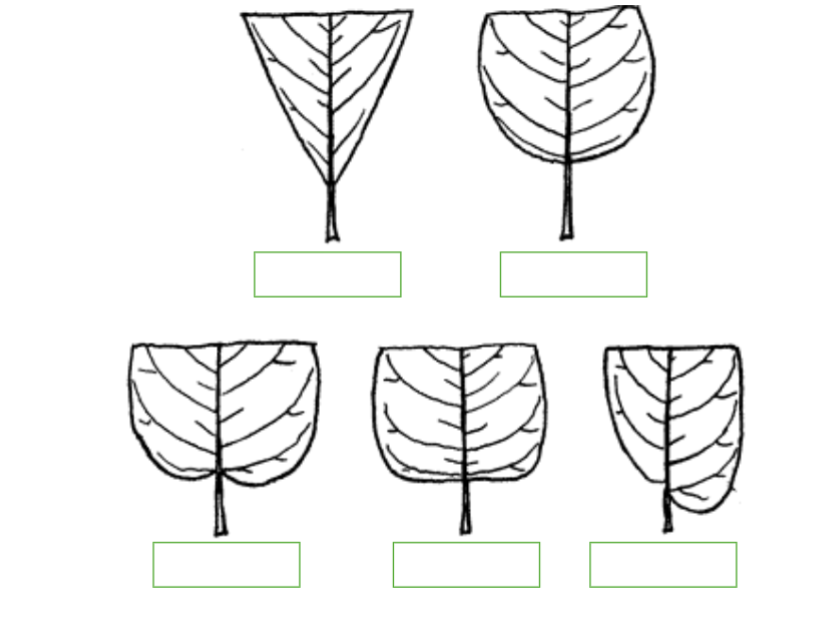
Label the Following:
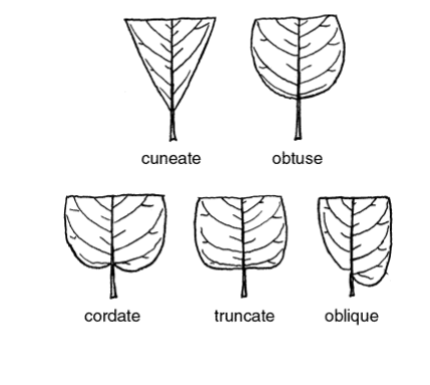
-
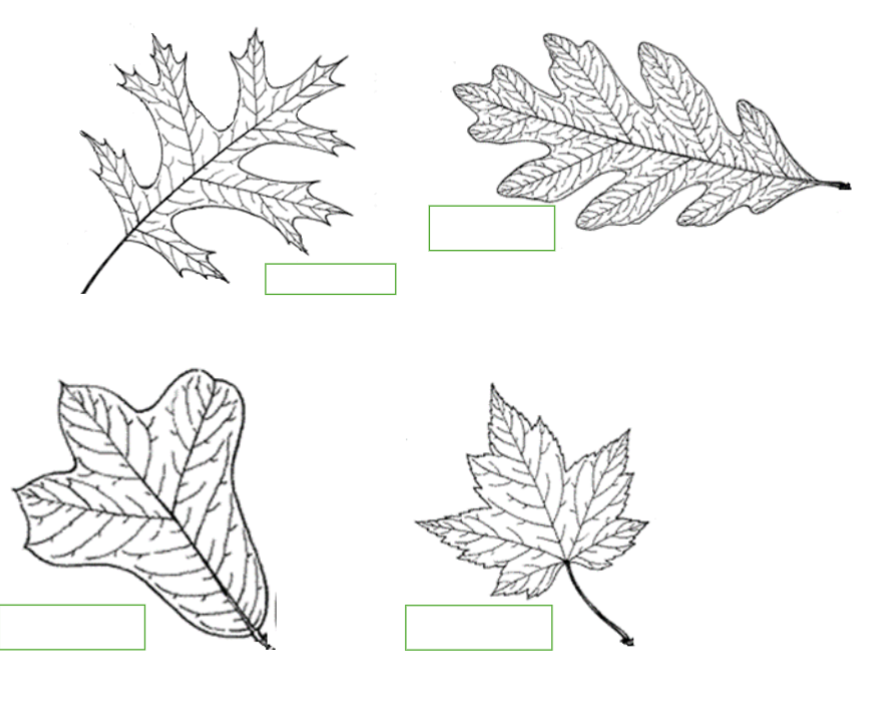
Label the Following:
TL: Incised Lobing
TR: Cleft Lobing
BL: LobedBR: Palmate Lobing
-
Glabrous
Smooth
-
Pubescent
Soft, Fine Hair
-
Tomentose
Matted, Wooly Hair
-
Scabrous
Sandpaper-Like (Rough)
-
Glaucous
White/Waxy (Common Underside)
-
Rugose
Sunken Veins
-
Scaly
Scales Present
-
Coriaceous
Thick and Leathery (Common with Evergreens)
-
Papery
Thin, Membranous
-
Petiole Lengths
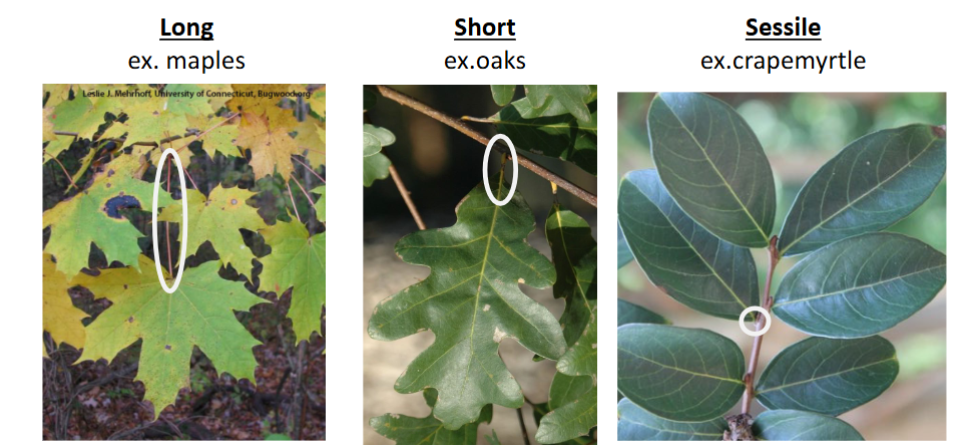
Sessile, Short, and Long
-
Primary Growth
Growth from shoots and root tips (Vertical)
-
Secondary Growth
Increases in Diameter (Horizontal)
-
Where Does Growth Occur?
Meristems
-
Primary Growth Meristem? Found in Roots and Shoots
Apical
-
Secondary Growth Meristem? Found in Cambium
Lateral
-
Excurrent Growth
Prolonged along main axis/trunk, Strong Apical Dominance, Upward Growth Prioritized
-
Decurrent Growth
Irregular Growth Pattern, No Defined Main Axis, Weak Apical Dominance
-
Determinate (Fixed) Growth
Stems/leaves formed in bud, overwinter in bud, then expand and elongate the next year, has true terminal bud, straight twigs
-
Indeterminate (Free) Growth
Tissues produced at apical meristems throughout growing season, only stops when conditions are unfavorable, portion of twig beyond last lateral bud dies, pseudo terminal bud exists
-
Bole
Main Stem of a sapling
-
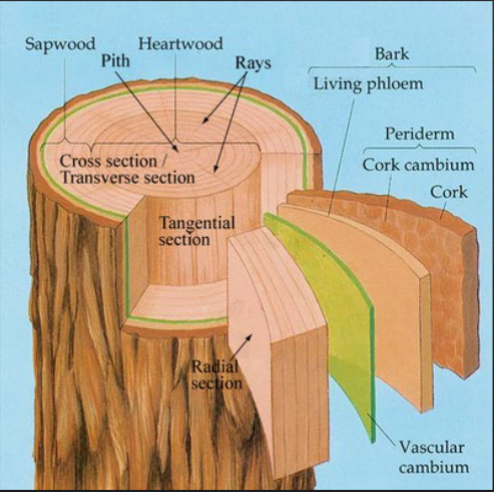
What is Wood?
Structural Tissue of Woody Plants
-
What is wood composed of?
Cellulose fibers, Lignin, and Xylem
-
Sapwood
Active Xylem Cells
-
Heartwood
Inactive Xylem Cells
-
What are Roots?
Extension of aboveground tissues
-
How much of Plants biomass is below ground?
~ 50%
-
Name the Three Root Types
Tap Root, Fibrous Root, and Adventitious Root
-
Where does a root originate?
Radicle of seed
-
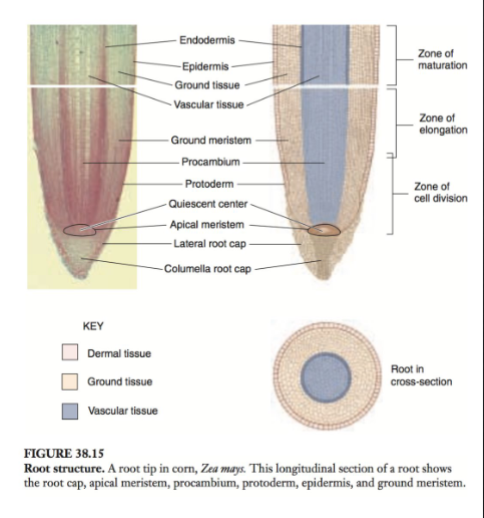
Four zones of a Root?
1. Root Cap
2. Zone of Cell Division
3. Zone of Elongation
4. Zone of Maturation
-
Root Cap
- Unique to Root, no stem equivalent
- Two Cell types, Inner columella and outer lateral root cap cells
- Primary job is to protect the sensitive tissues within
-
Zone of Cell Division
- An apical meristem, focuses on creation/division of new cells
- cells divide every 12-36 hours
- cells are called daughter cells
-
Zone of Elongation
- In this zone the daughter cells rapidly extend to become more longer than horizontal
-
Zone of Maturation
- At this point, the "Daughter" cells mature to become a specified cell type within the root system.
-
Root Epidermis
Outer layer of cells in a root
-
Root Hairs
Growth from root epidermis that help in gathering of minerals
-
Cortex
- next layer after epidermis, stores food and water
- inner layer makes up endodermis
-
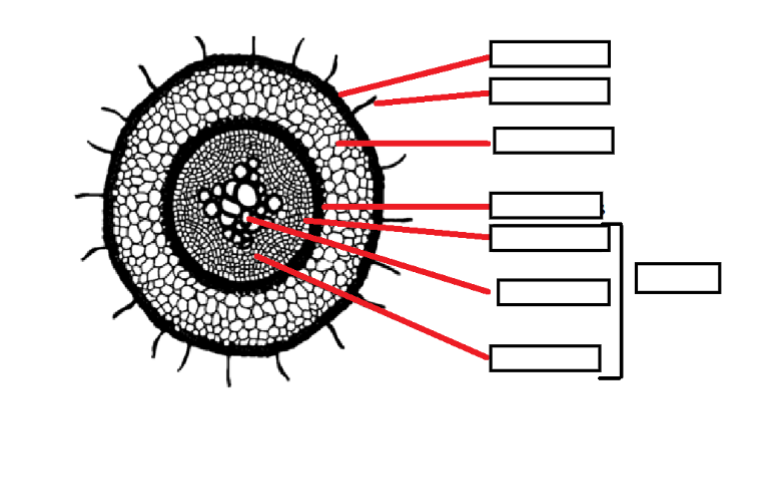
Stele
- Core of root
- Outer layer is the pericycle
- Xylem exists within, transporting water
- Phloem also exists, transporting carbs
-
Modified Roots
Aerial
Adventitious
Buttress
-
Mutualism Symbiosis
- Mycotrophy: Nutrient uptake using mycorrhizae
- Mycorrhizae: symbiotic association of mycorrhizal fungi and tree roots
- Plant provides carbohydrates to fungi
- Fungi enhance the distance that a root system has access to resources within the soil
-
N Fixation
Nitrogen Fixers
-
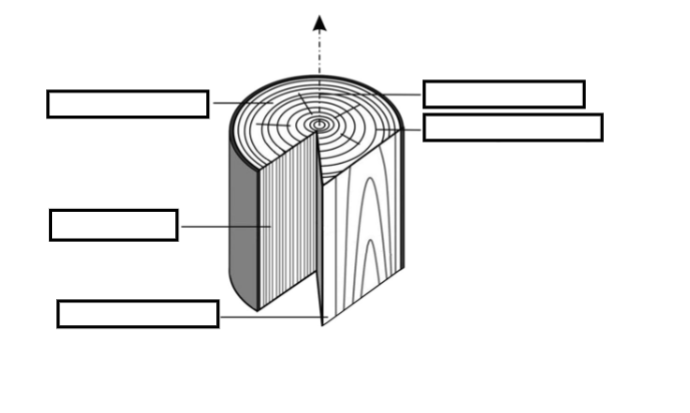
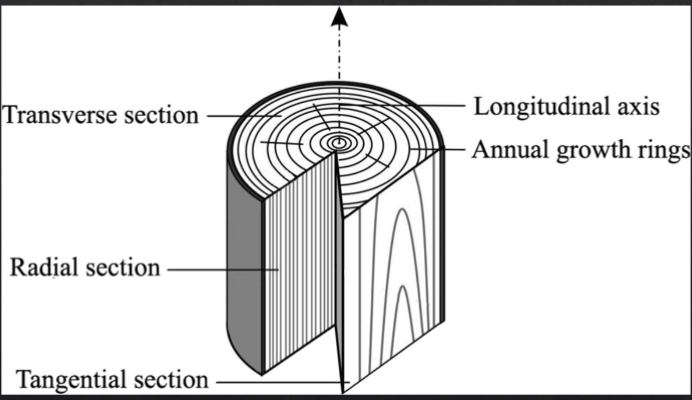
Label The Following
-
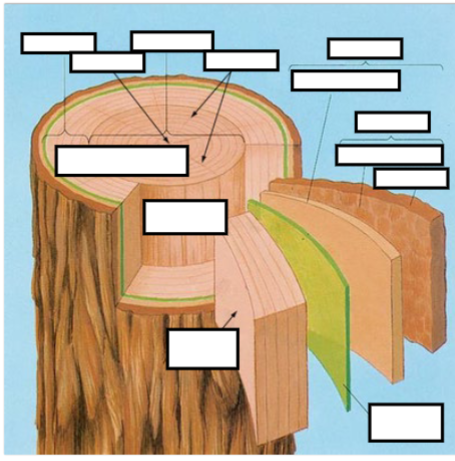
Label The Following
-
Label The Following
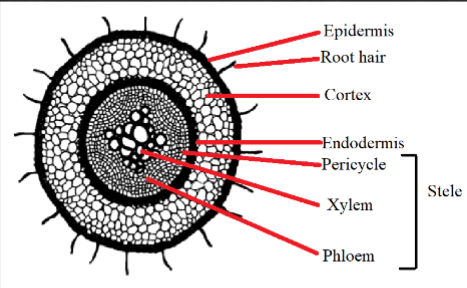
-
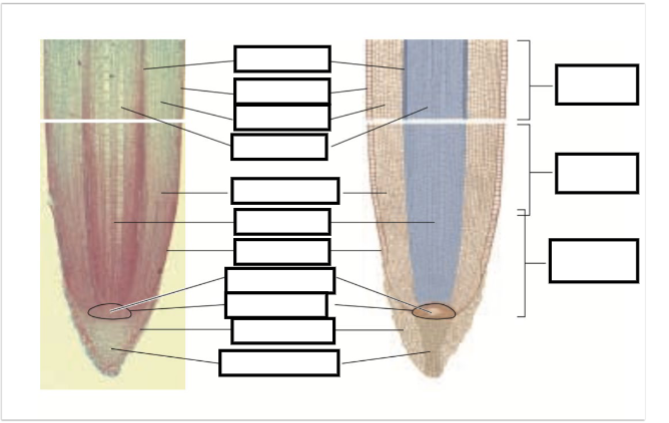
Label The Following