-
recognize substrate; catalyze a reaction with it
What are the two characteristics of enzymes?
-
lower transition state energy; raise ground state energy
How do enzymes work?********
-
initiated; ES complexes
All enzyme-catalyzed reactions are _______ by _________.
-
complementary; transition state; ground state
Enzyme is a flexible template designed to be _____ to structure of substrate at the ________ of reaction, not the _________.
-
specificity; rate acceleration
What are two key factors of enzyme catalysis?
-
cofactor (coenzyme)
- additional molecules that aid enzymes in catalyzing reactions; consists of organic molecules and metal ions
-
amino acid side chains
Active site contains _______ used in catalysis.
-
transition state
Where does maximum binding occur for enzymes?
-
Chiral
What type of catalysts are amino acids?
-
L-amino acids
What is the specific orientation that applies to all amino acids?
-
No; steric hindrance
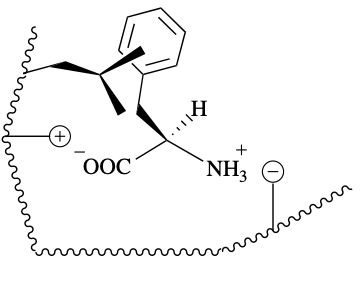
Will this enantiomer form a complex with the substrate? If not why?
-
Yes
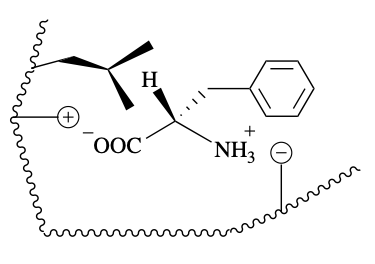
Will this enantiomer form a complex with the substrate? If not why?
-
Turnover number (kcat)
-number of molecules of substrate converted to product per unit time per enzyme active site.
-
slowest step
Rate determining step = ?
-
cystine, serine, histidine, lysine, glutamine, aspartic acid
What are your common site nucleophiles?
-
asp, histidine, serine
What amino acids are a part of the catalytic triad?
-
racemization
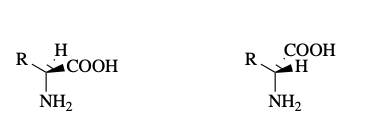
What reaction is this?
-
decarboxylation
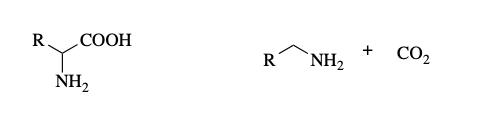
What reaction is this?
-
transamination
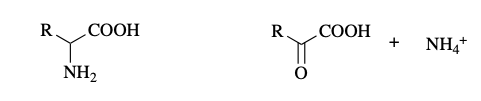
what reaction is this?
-
a-cleavage
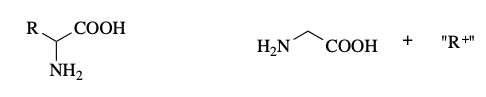
what reaction is this?
-
b-elimination
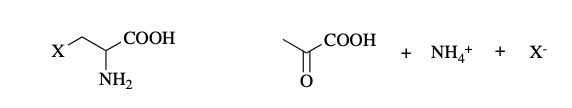
what reaction is this?
-
b-replacement
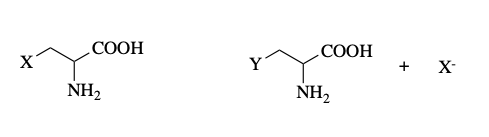
what reaction is this?
-
like a hydride; reduces imide bonds
How does NAD(P)H react?
-
oxidation and oxygenation
Flavin coenzyme catalyzes what type of reactions?
-
oxidation; unsaturated

what kind of reaction is this? And is it saturated or unsaturated?
-
oxygenation

what kind of reaction is this?
-
hydroxylation & epoxidation
What kind of reactions is Heme involved with?
-
c
Which cofactor forms a radical?
a. flavin
b. NADH
c. Heme
d. PLP
-
thiolester
Coenzyme A forms _____
-
true
Thioesters are much more reactive toward acylation of nucleophilic substrates than carboxylic acids and oxygen esters. T/F?
-
protease degradation, poor bioavailability, and allergic responses
What are some drawbacks associated with enzyme therapy?

