Domain II, Comp 4: PPR EC-12
The teacher understands learning processes and factors that impact student learning and demonstrates this knowledge by planning effective, engaging instruction and appropriate assessments.
-
Constructivist Approach:students learn how to learn by giving them the tools and initiative for their own learning experience.
-
Self-directed learning:Students should set their own goals. To become self-directed learners, students must learn to assess the demands of the task, evaluate their own knowledge and skills, plan their approach, monitor their progress, and adjust their strategies as needed
-
Discovery learning:Encourages learners to build on past experiences and knowledge, use their intuition, imagination and creativity, and search for new information to discover facts, correlations and new truths
-
Situated/contextualized learning:Learning takes place in the same context in which it is applied; students are more inclined to learn by actively participating in the learning experience. Knowledge should be presented in authentic context. Requires social interaction and collaboration
-
Graphic organizers:Allow students to display a great deal of information on a single graphic. Diagrams, charts, webs, concepts maps, etc.
-
Learning logs:A personalized learning resource for children. In the learning logs, the children record their responses to learning challenges set by their teachers. Each log is a unique record of the child's thinking and learning. Used to reflect on metacognition
-
Learning/classroom centers:Give the child an opportunity to make decisions and choose the timing of her learning
-
Authentic tasks:An assignment given to students designed to assess their ability to apply standard-driven knowledge and skills to real-world challenges. A task we ask students to perform is considered authentic when students are asked to construct their own responses rather than select from ones presented and the task replicates challenges faced in the real world
-
Interactive read aloud:Read alouds can be used to increase listening and accountable talk skills, promote vocabulary skills and comprehension, and engage students in a way that other materials cannot
-
Sentence stems:This technique gives students the opportunity to respond in the form of a complete sentence to effectively communicate. Sentence stems provide scaffolding to help students get started in speaking or writing without the added pressure of thinking about how to correctly formulate a response.
-
Chunking:an approach for making more efficient use of short-term memory by grouping information. Chunking breaks up long strings of information into units or chunks. The resulting chunks are easier to commit to memory than a longer uninterrupted string of information.
-
Think-pair-share:a collaborative learning strategy in which students work together to solve a problem or answer a question about an assigned reading. This technique requires students to (1) think individually about a topic or answer to a question; and (2) share ideas with classmates. Discussing an answer with a partner serves to maximize participation, focus attention and engage students in comprehending the reading material.
-
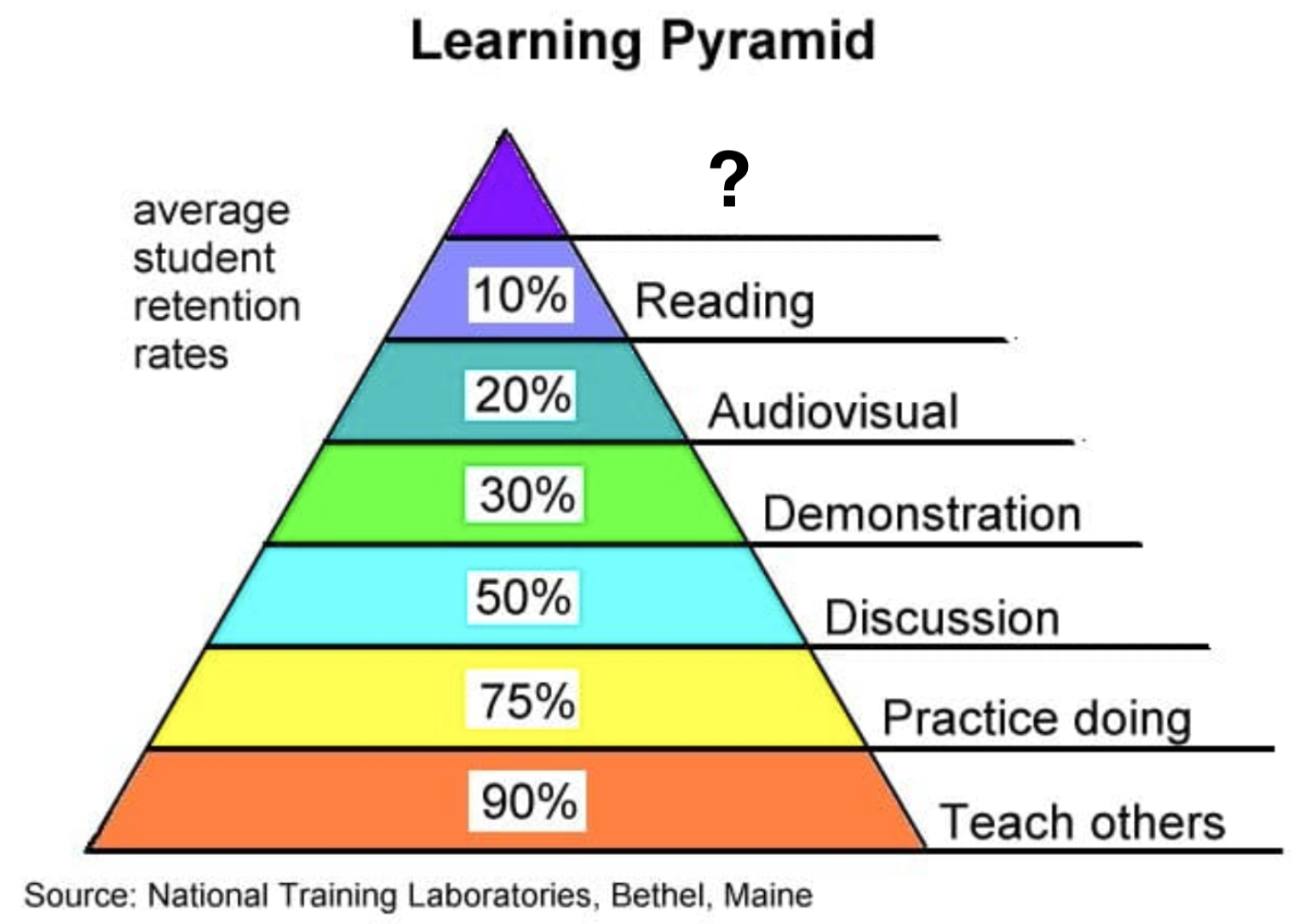
Lecture
-
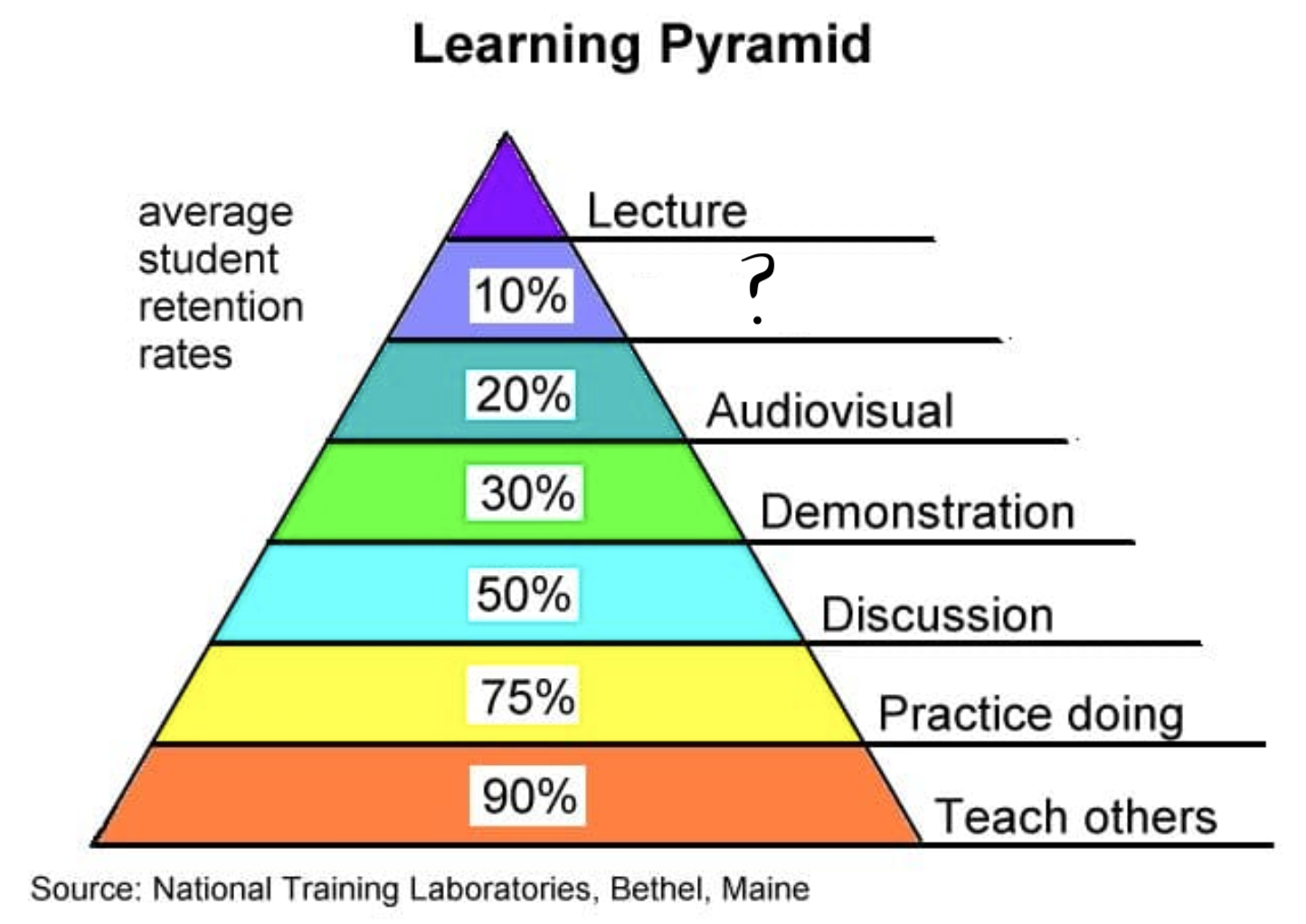
Reading
-
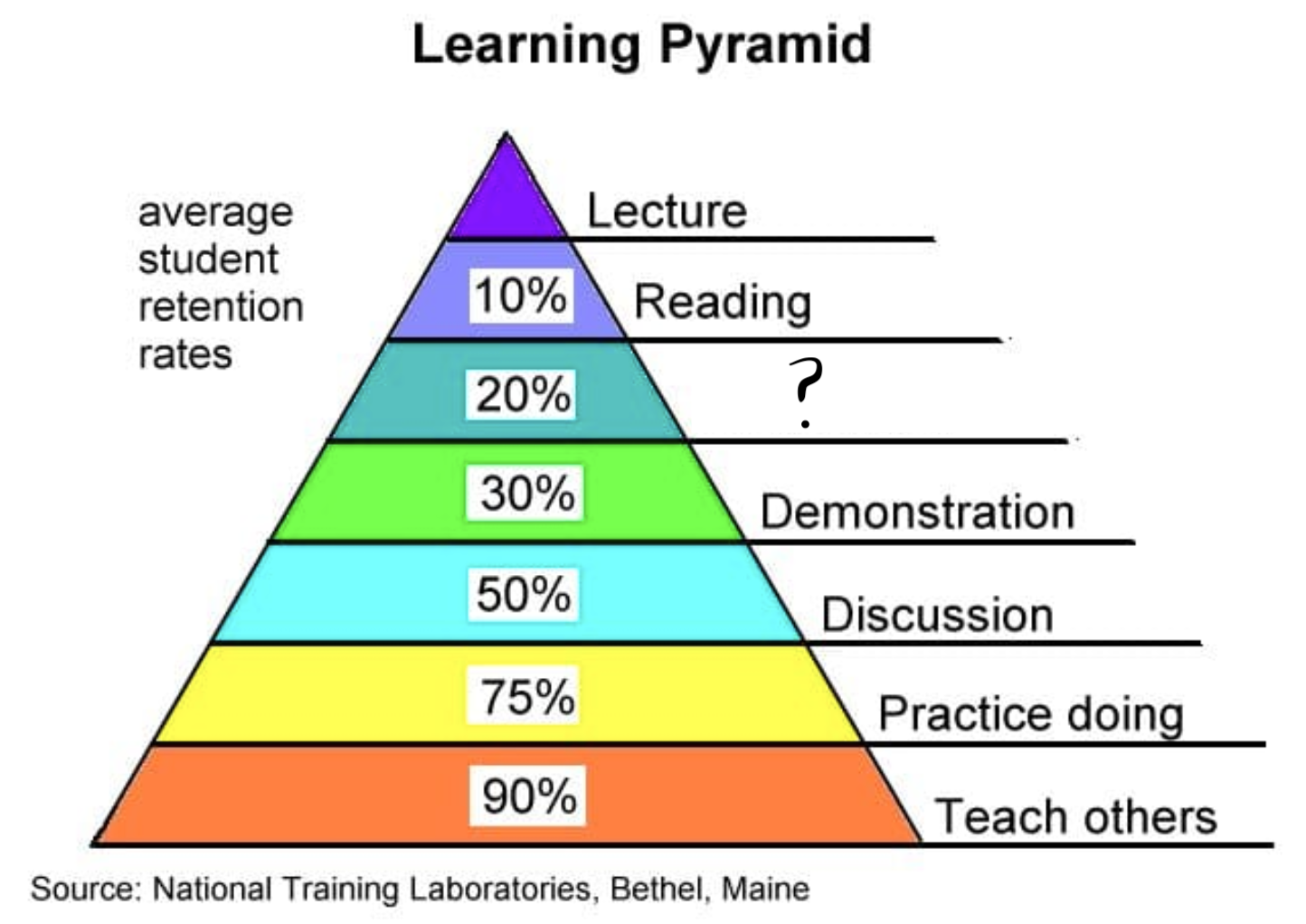
Audiovisual
-
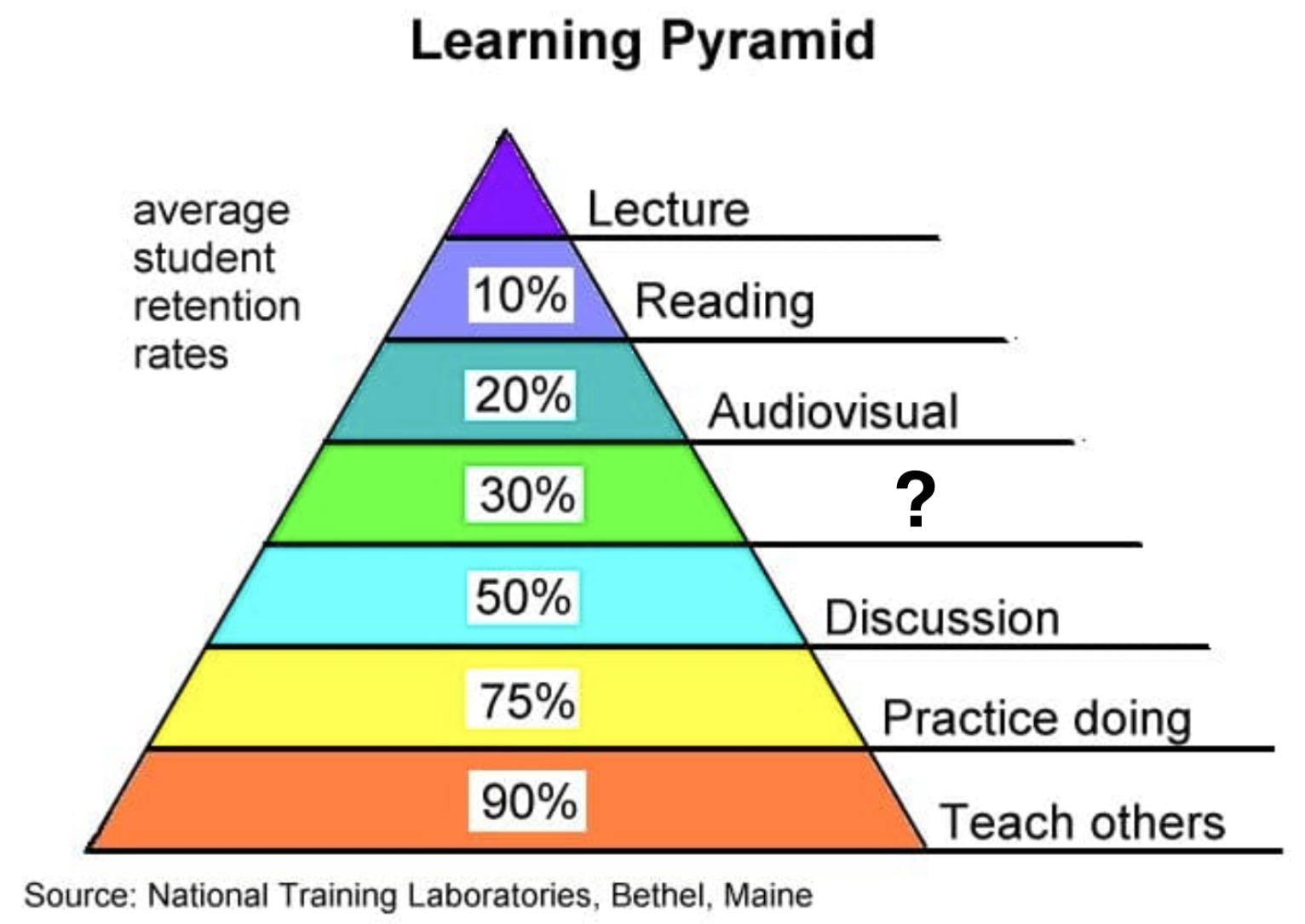
Demonstration
-
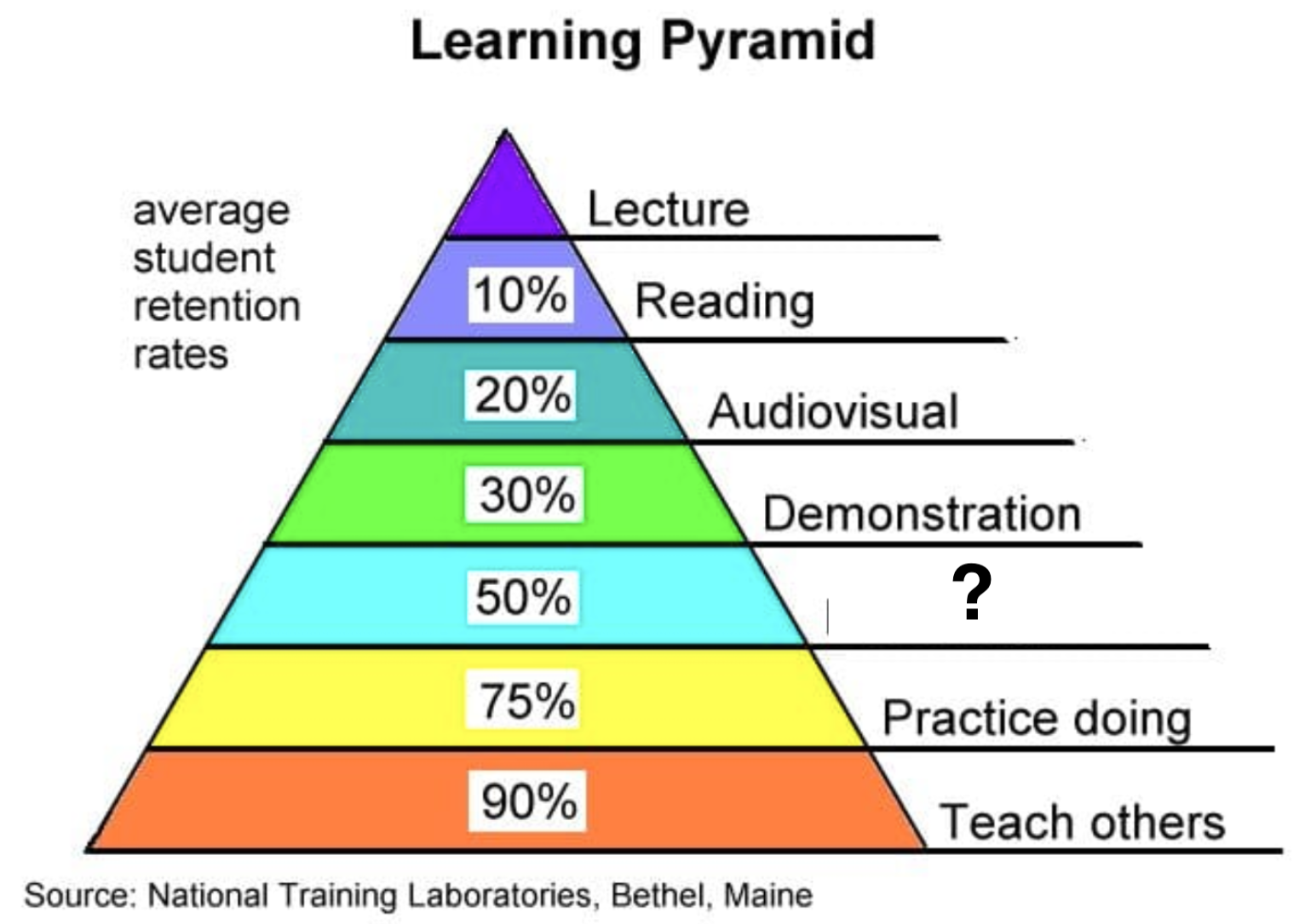
Discussion
-

Practice Doing
-
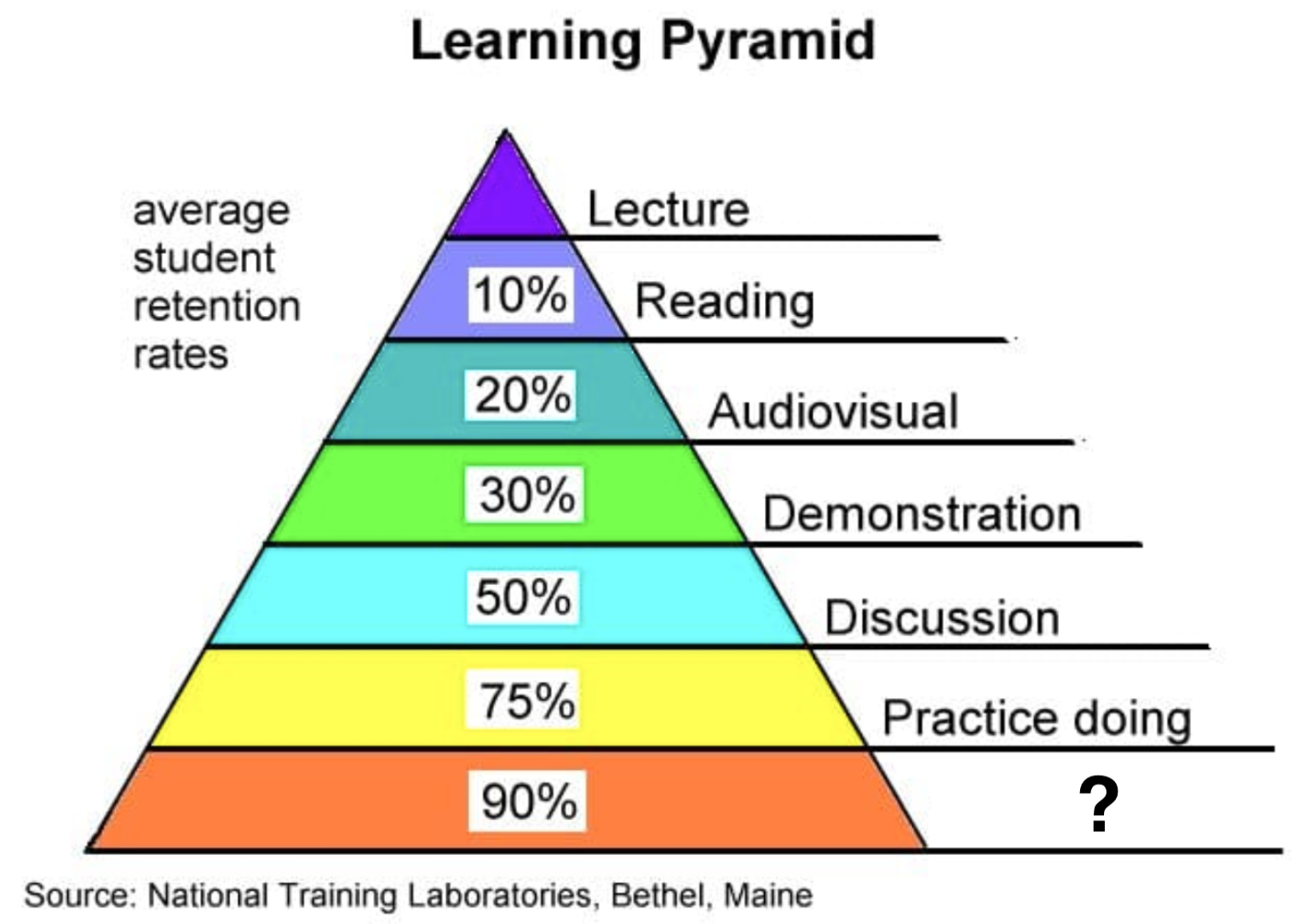
Teach Others
-
Classical Conditioning (Pavlov)
a reflexive or automatic type of learning in which a stimulus acquires the capacity to evoke a response that was originally evoked by another stimulus. (Pavlov's dogs)
-
Operant Conditioning (Skinner)
a method of learning that uses rewards and punishments to modify behavior
-
Social Learning Theory (Bandura)
observation and modeling play a primary role in how and why people learn
-
Attribution Theory (Weiner)
an individual's causal attributions of achievement affect subsequent behaviors and motivation
-
Cognitive Load Theory (Sweller)
explains how people learn and store new information by examining the relationship between working memory and long-term memory. There's only so much info that can be stored in working memory.
-
Cognitive Development Theory (Piaget)
Children move through 4 stages of learning: Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operational, and Formal Operational
-
Discovery Learning (Bruner)
implies that students construct their own knowledge for themselves (also known as a constructivist approach)
-
Social Development Theory (Vgotsky)
learning is a social process that occurs through interactions with others
-
Problem-based learning
a student-centered approach in which students learn about a subject by working in groups to solve an open-ended problem
-
situated learning
students are more inclined to learn by actively participating in the learning experience
-
Inquiry-based learning
encourages students to be active participants in their learning by asking questions, generating data, and applying knowledge
-
Elaboration Theory (Reigeluth)
instruction should be offered to learners in increasing order of difficulty.
-
Experiential learning (Kolb)
the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience in 4 stages: Concrete Experience (CE): feeling
Reflective Observation (RO): watching
Abstract Conceptualization (AC): thinking
Active Experimentation (AE): doing
-
Classical conditioning (Watson):A learning process that occurs when two stimuli are repeatedly paired: a response which is at first elicited by the second stimulus is eventually elicited by the first stimulus alone

