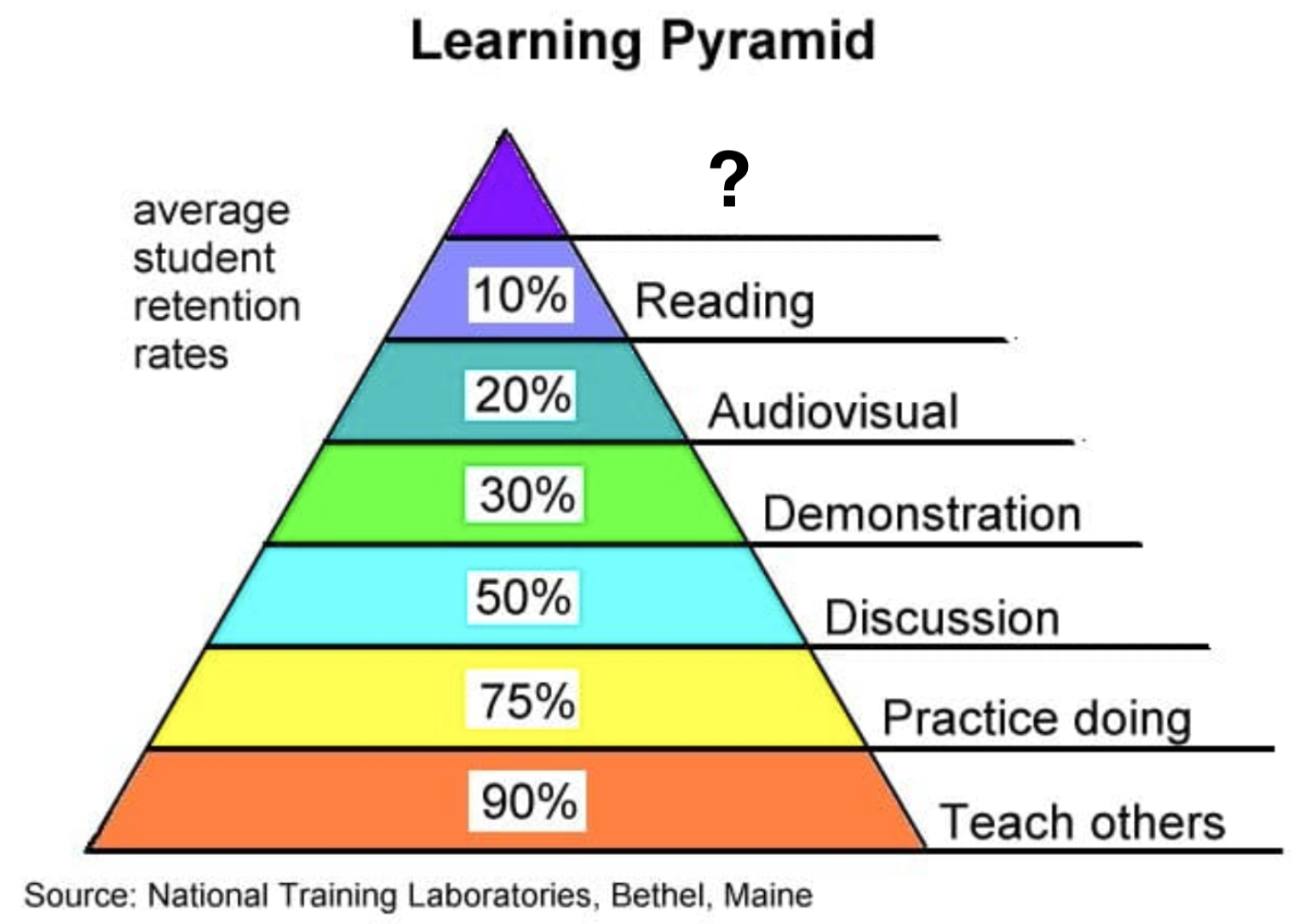
Lecture
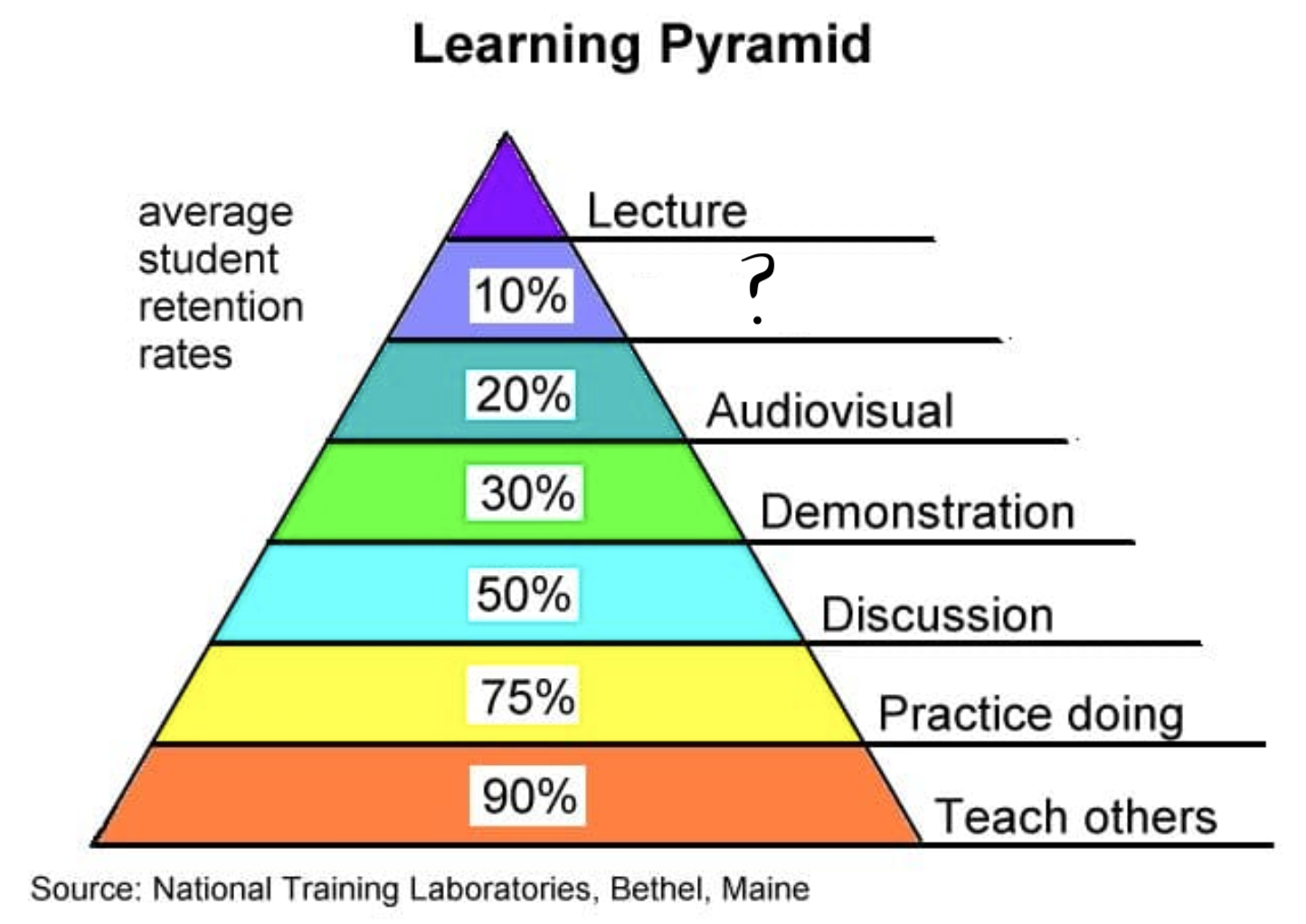
Reading
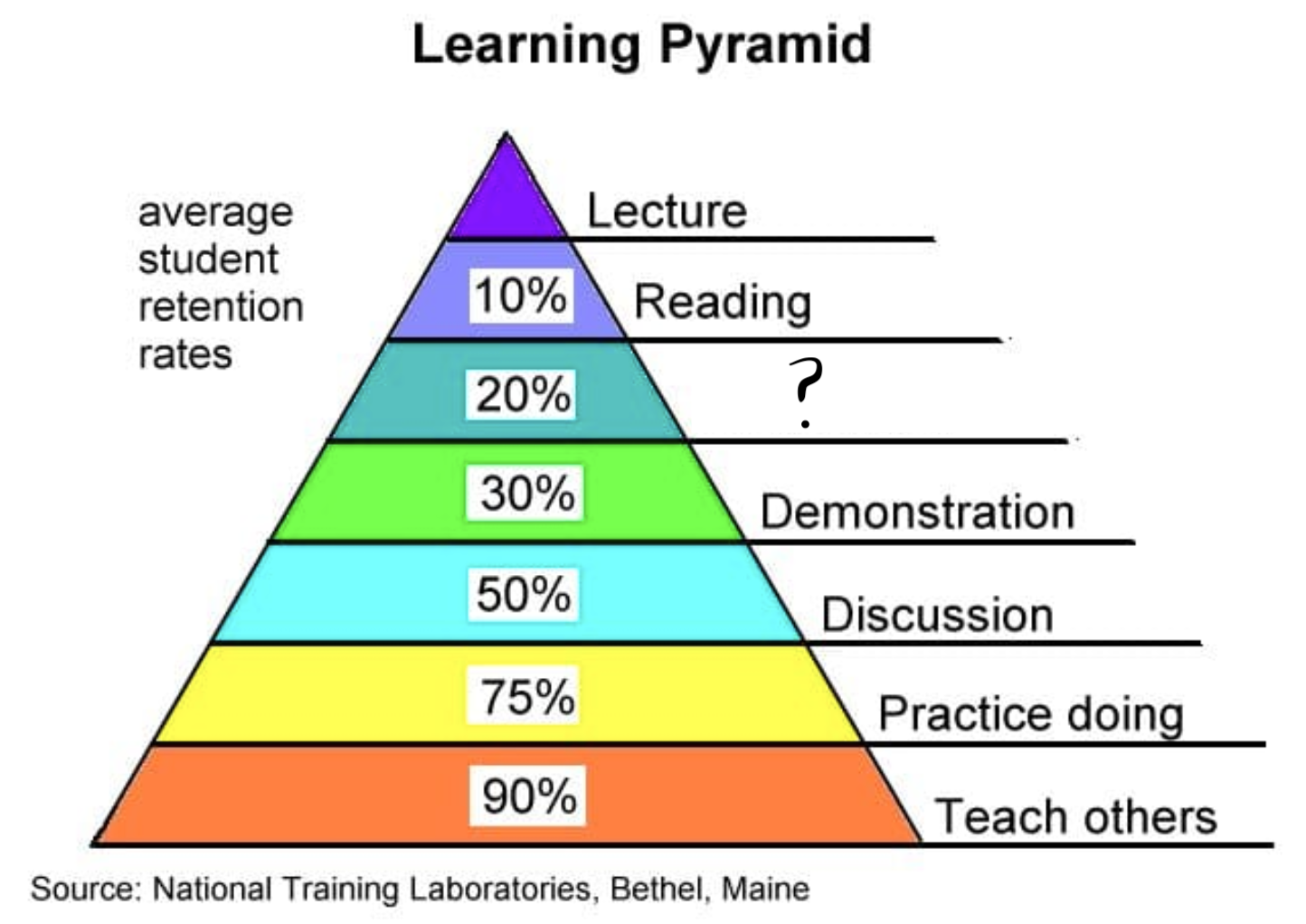
Audiovisual
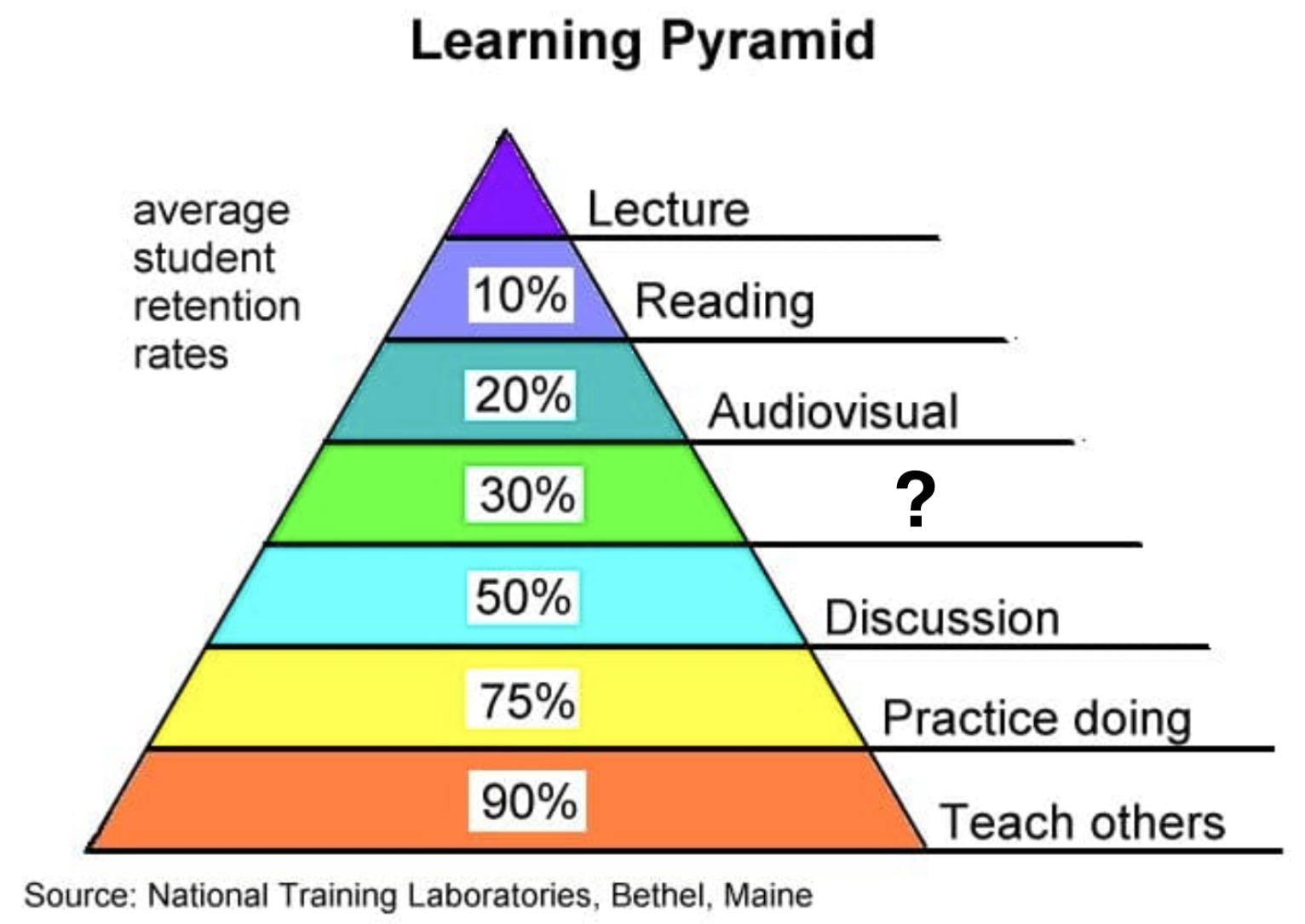
Demonstration
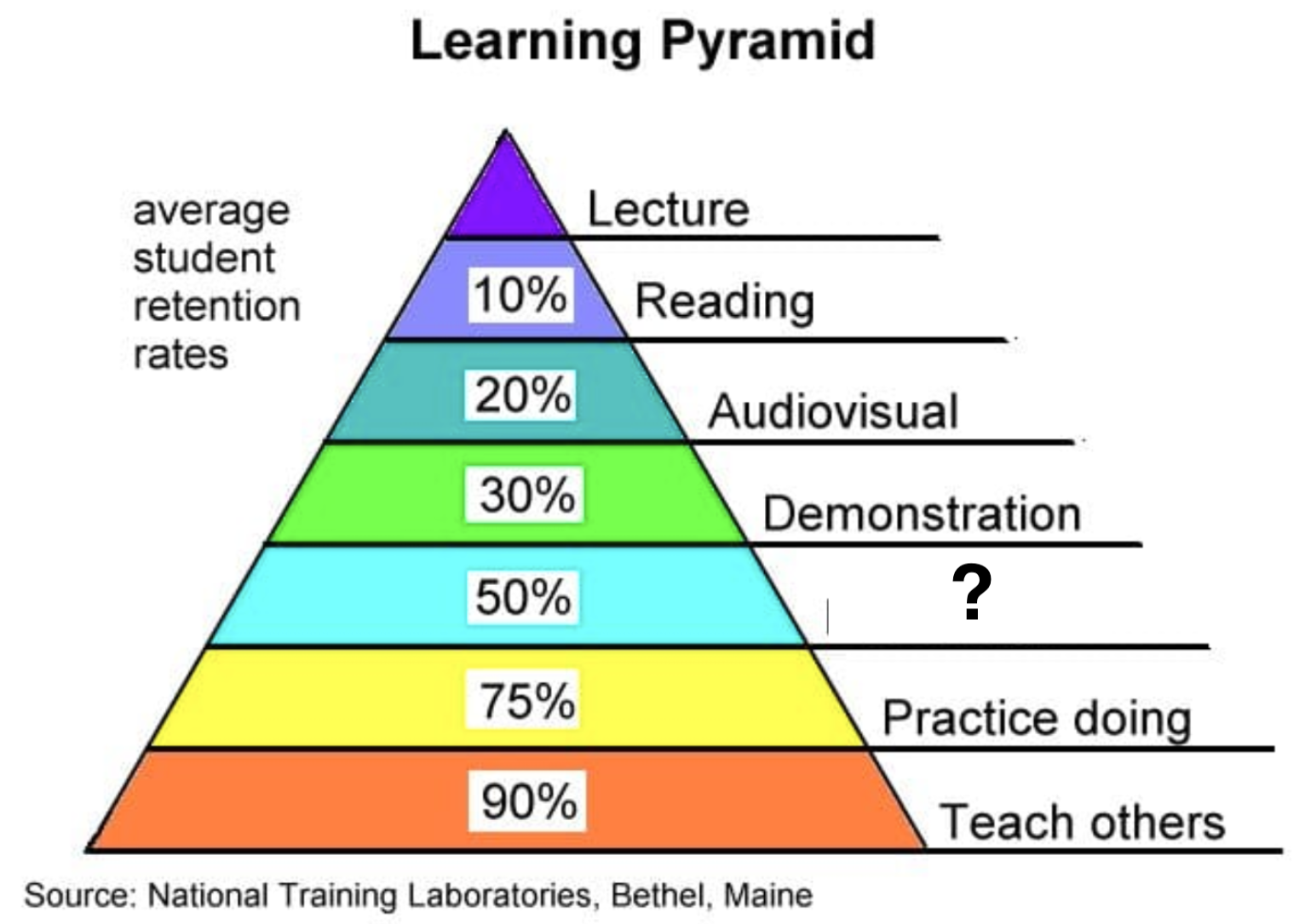
Discussion

Practice Doing
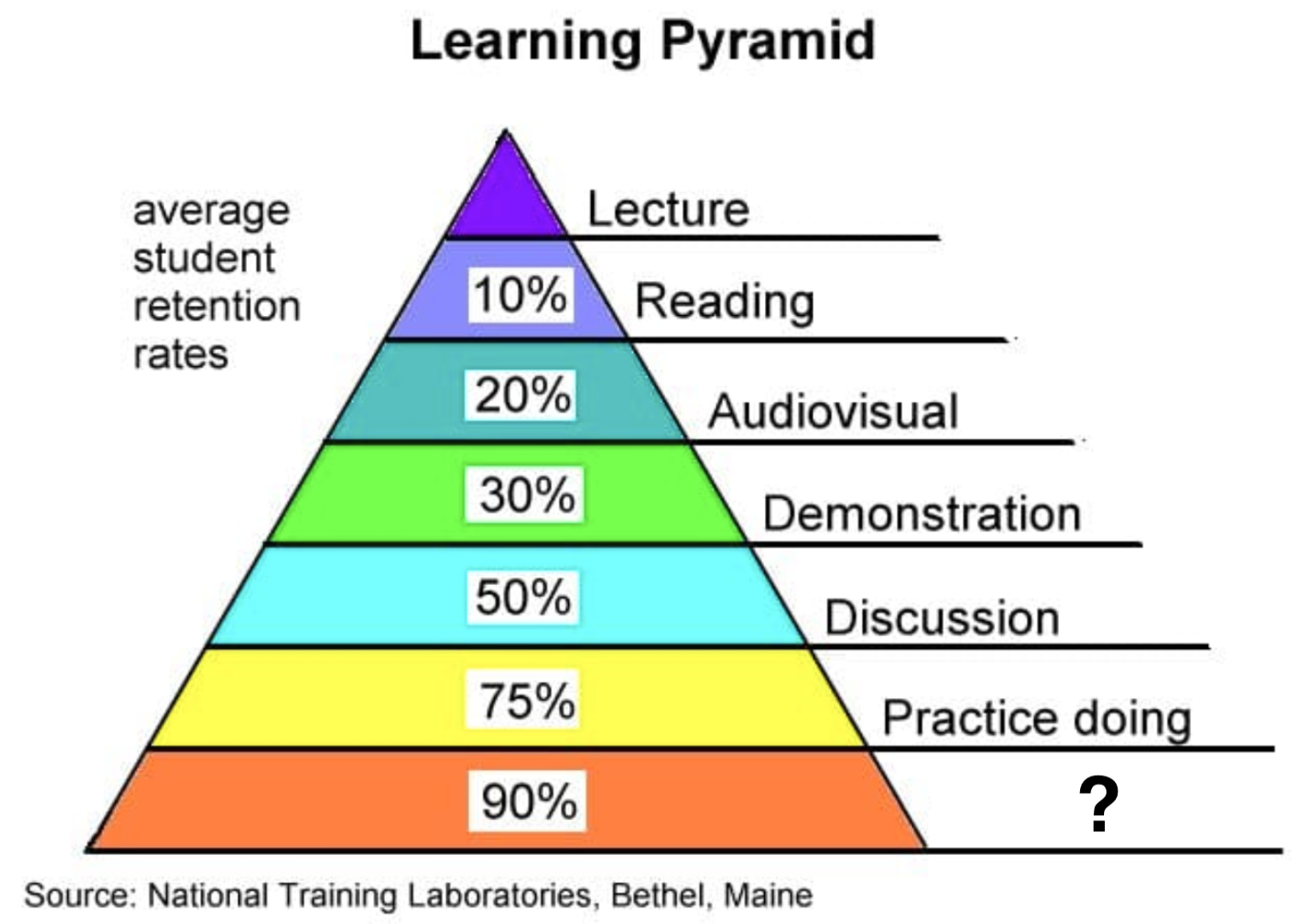
Teach Others
Classical Conditioning (Pavlov)
a reflexive or automatic type of learning in which a stimulus acquires the capacity to evoke a response that was originally evoked by another stimulus. (Pavlov's dogs)
Operant Conditioning (Skinner)
a method of learning that uses rewards and punishments to modify behavior
Social Learning Theory (Bandura)
observation and modeling play a primary role in how and why people learn
Attribution Theory (Weiner)
an individual's causal attributions of achievement affect subsequent behaviors and motivation
Cognitive Load Theory (Sweller)
explains how people learn and store new information by examining the relationship between working memory and long-term memory. There's only so much info that can be stored in working memory.
Cognitive Development Theory (Piaget)
Children move through 4 stages of learning: Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operational, and Formal Operational
Discovery Learning (Bruner)
implies that students construct their own knowledge for themselves (also known as a constructivist approach)
Social Development Theory (Vgotsky)
learning is a social process that occurs through interactions with others
Problem-based learning
a student-centered approach in which students learn about a subject by working in groups to solve an open-ended problem
situated learning
students are more inclined to learn by actively participating in the learning experience
Inquiry-based learning
encourages students to be active participants in their learning by asking questions, generating data, and applying knowledge
Elaboration Theory (Reigeluth)
instruction should be offered to learners in increasing order of difficulty.
Experiential learning (Kolb)
the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience in 4 stages: Concrete Experience (CE): feeling
Reflective Observation (RO): watching
Abstract Conceptualization (AC): thinking
Active Experimentation (AE): doing