-
A _________ __________ is a combination of physiological and chemical systems that control ___ by regulating the amount of ____ or _____ in the body
buffer system
pH
acid
base
-
First line of defense and act within a fraction of a second to resist pH changes
chemical buffers
-
Changes in respiratory rate and depth occur to compensate for acidosis or alkalosis within 1-3 minutes
brain stem respiratory centers
-
Most potent buffer system but require hours to a day or more to alter blood pH
renal mechanisms
-
brain stem respiratory centers and renal mechanisms are forms of _____________ __________
physiological buffers
-
chemical buffer systems work by binding __________ ___ whenever the pH ____ and releasing them when the pH _____
hydrogen ions
drops
rises
-
The chemical buffer system is the result of three major chemical buffer systems in the body including the
1. ______________________
2. ______________________
3. ______________________
Anything that cause a shift in ___________ concentration in one fluid compartment causes a change in others, this allows the entire buffer system to _______ any drifts in ___
bicarbonate buffer system
phosphate buffer system
protein buffer system
hydrogen
resist
pH
-
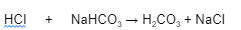
How the BBS prevents the pH from becoming too acidic
The most important ECF buffer is the ______________ ______ ________
1. It is a mixture of ___________ _____ and its salt, _________ ____________
2. Carbonic acid is a _____ ____ and does not dissociate to any great extent in _______ or ________ solutions and remains intact when a ________ _______ like hydrochloric acid (HCI) is added to the buffer system
3. _____________ ____ of sodium bicarbonate act as a ______ _______ to take the __________ (H+) released by the stronger acid (HCI) to form more _______ _______
4. Because HCI is converted into the weaker ____________ _____, HCI lowers the ___ of the solution only ________
bicarbonate buffer system
carbonic acid
sodium bicarbonate
weak acid
neutral
acidic
strong acid
bicarbonate ions
weak base
hydrogen
carbonic acid
carbonic acid
pH
slightly
-
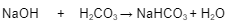
How the BBS prevents the pH from becoming too alkaline
The most important ECF buffer is the ______________ ______ ________
1. It is a mixture of ___________ _____ and its salt, _________ ____________
2. Any ________ _________ (NaOH) added to the buffer solution does not cause the ______ ______ of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) to dissociate any further despite the _________ conditions
3. The added base forces from the sodium hydroxide causes the ________ ____ to dissociate further donating more __________ to tie up the ____________ (OH-) released by the sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
4. The net result is the ______ ______ (NaHCO3) replaces the _____ _____ (NaOH) preventing the ___ from majorly _______
bicarbonate buffer system
carbonic acid
sodium bicarbonate
sodium hydroxide
weak base
alkaline
carbonic acid
hydrogen
hydroxide
weak base
strong base
pH
rising
-
The __________ _____ _________ is identical to the bicarbonate buffer system except salts of _____________ __________ (NaH2PO4) acts as the weak acid and _______________ ________ (Na2HPO4) acts as the weak base
phosphate buffer system
dihydrogen phosphate
monohydrogen phosphate
-
The __________ _______ _______ is relatively unimportant for buffering blood plasma, it is more effect as a buffer in the _______ and ______ where ___________ concentrations are usually higher
phosphate buffer system
urine
ICF
phosphate
-
The __________ ______ ________ is formed from proteins in plasma and in cells, it has 3/4 of all the buffering power of ____ due to the buffering power of _________ _______
protein buffer system
ICF
intracellular proteins
-
Protein buffer system (1)
Proteins are polymers of linked _______ _____, some of them have exposed side chains of atoms called ___________ _______ (⎻COOH) which are organic acid groups that release _______________ when the ___ rises to prevent the solution from becoming too ________
amino acids
carboxyl groups
hydrogen
pH
alkaline
-
Protein buffer system (2)
Other ________ _____ have exposed groups like ⎻NH2 that can act as _____ and accept __________ to prevent the solution from becoming too _______
amino acids
bases
hydrogen
acidic
-
Protein buffer system (3)
Both exposed groups that accept and release _____________ allow a single protein molecule to function as either an ____ or a _____ depending on the ___ of its environment, this is known as an _______________ __________
hydrogen
acid
base
pH
amphoteric molecule
-
_________ is whenever the pH of arterial blood drops below _____
acidosis
7.35
-
________ is whenever the pH of arterial blood rises above ______
alkalosis
7.45
-
Shallow breathing (hypoventilation) or when gas exchange is hampered leading to falling blood pH and rising Pco2
respiratory acidosis
-
Low blood pH and HCO3⁻ levels
metabolic acidosis
-
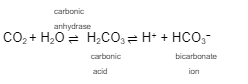
This formula represents the ___________ ____________ __ ____________
The goal of the respiratory system is to eliminate the acid, _____ from the blood while replenishing ____
carbon dioxide enters _______________ in the circulation and is converted to ___________ ___ for transport in the ________
respiratory regulation of hydrogen
co2
o2
erythrocytes
bicarbonate ions
plasma
-
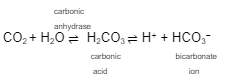
Because of the __________ any increase in any of these chemicals pushes the reaction to the __________ direction
equilibriums
opposite
-
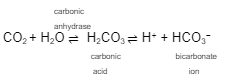
Decreases in blood pH
1. an increase in ______ within the blood activate medullary ___________ via cerebral acidosis and rising plasma ____ concentration excites the __________ _______ indirectly via ____________ _____________
2. This leads to an increase in __________ ____ and _______ ________
3. The increased ___________ leads to more ____ being removed from the blood pushing the reaction to the ______ and reducing __________ concentration
PCO2
chemoreceptors
H+
respiratory centers
peripheral chemoreceptors
respiratory rate
tidal volume
ventilation
CO2
left
hydrogen
-
Increases in blood pH
1. _____________ in blood ___ leads to respiratory centers becoming depressed
2. This decreases ___________ ____ and _______ ____________
3. This causes ____ to accumulate and the _____________ is pushed to the _______ as _____________ increases to restore blood pH to the normal range
increases
pH
respiratory rate
tidal volume
CO2
equilibrium
right
hydrogen

