-
Where is the proteasome found and in what amount?
In cytosol and nucleus, accounts for 1% of the cellular protein
-
What does the proteasome look like?
A hollow cylinder with caps at each end and an active site in the core.
-
How does proteasome know what proteins to work on?
It only acts on proteins that have been marked with a small protein tag called ubiquitin. (several)
-
How is ubiquitin added onto other proteins?
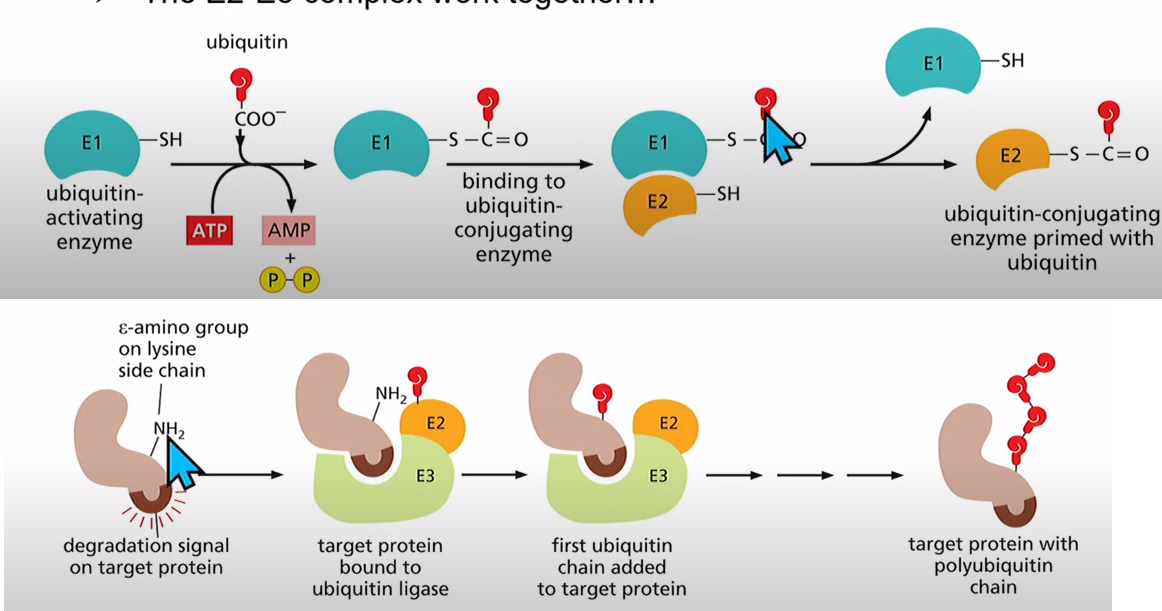
Ubiquitin-conjugating system made up of 3 enzymes
E1: an ATP-dependent ubiquitin-activating enzyme creates an activated E1-bound ubiquitin (couple types)
E2: ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme accepts ubiquitin from E1 and exists as a complex with E3, a ubiquitin ligase that selects substrates. (30 types)
E2 and E3 work together
E3: Binds to specific degradation sequences and is added onto a lysine residue, forms a polyubiquitin chain (100's of types)
They all interact with each other with different specificities
-

A
-
What are other functions of ubiquitin?
Monoubiquitylation- Histone Regulation
Multiubiquitylation- Endocytosis
Polyubiquitylation- Proteasome degradation , DNA repair (The lysine that its attached to determines it)
-
What are some of the ways you can regulate the e2, e3 complex?
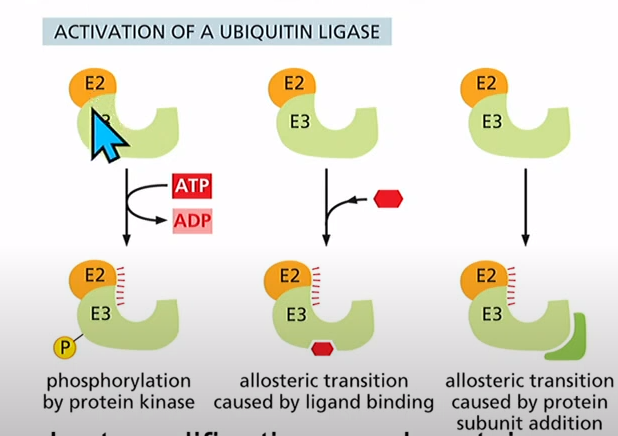
Phosphorylation using protein kinase, using a ligand, or needing another protein to activate the e2, e3 complex (covalent modifications)
-
What are some of the ways you can regulate protein degradation?
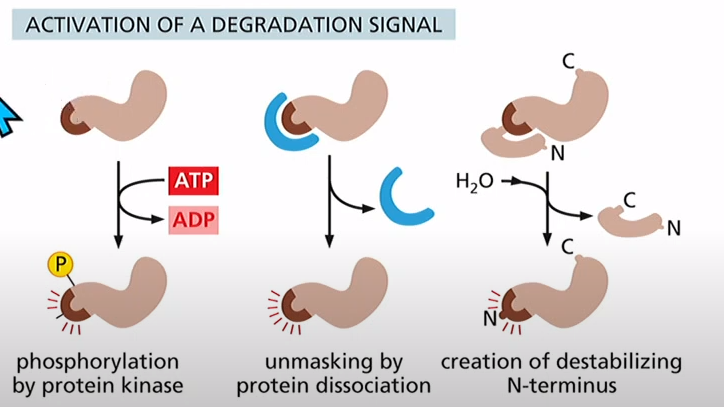
Phosphorylation using protein kinase, Dissociating protein reveals signal, cleavage of some blocker
-
What are some ways you can regulate the activation of proteins?
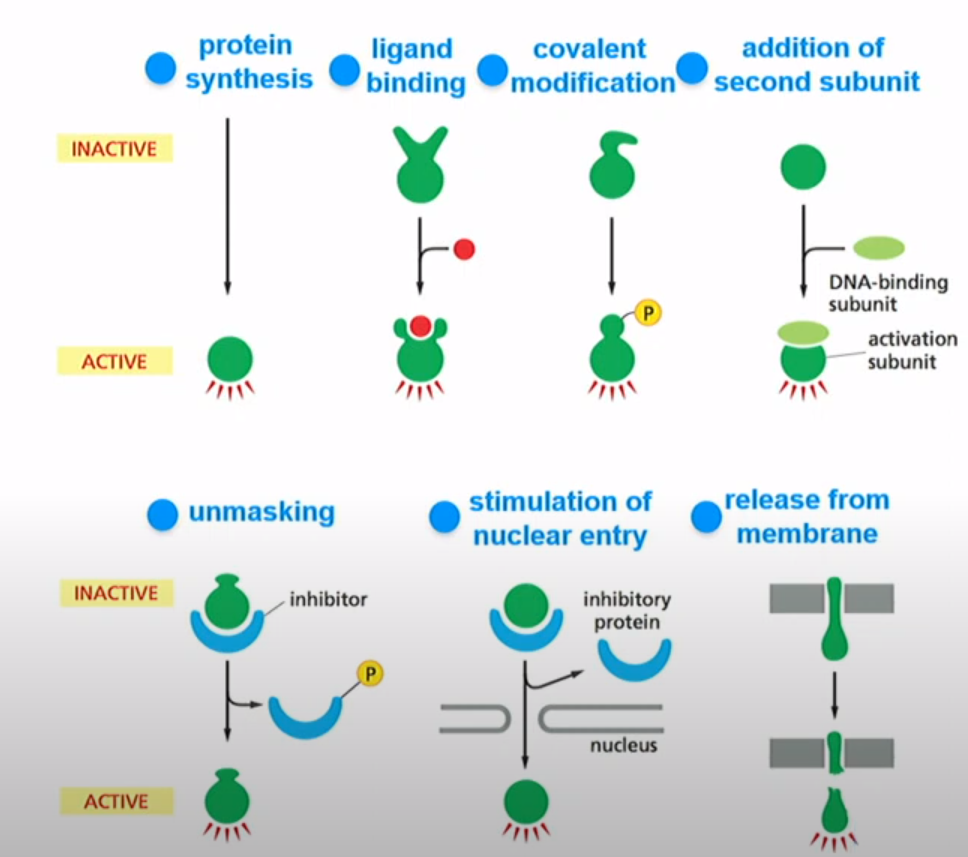
-
What does Protein Kinase A (PKA) do?
Uses ATP phosphorylates other proteins (hence "kinase"). Can regulate gene expression and is activated by cyclic AMP
-
What is PKA made of?
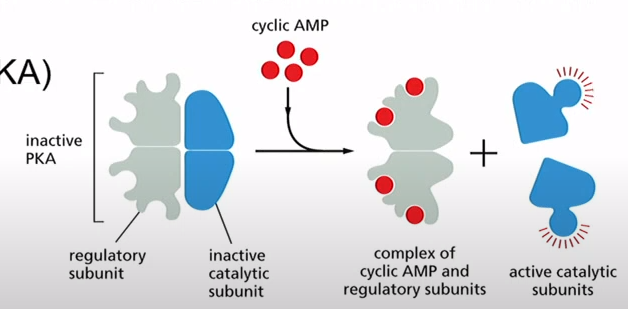
Two Regulatory Subunits
Two Catalytic Subunits
-
What are some examples of what PKA is used in?
Enzymes involved in glycogen metabolism in skeletal muscle and liver
-
What is an example of PKA and its effect?
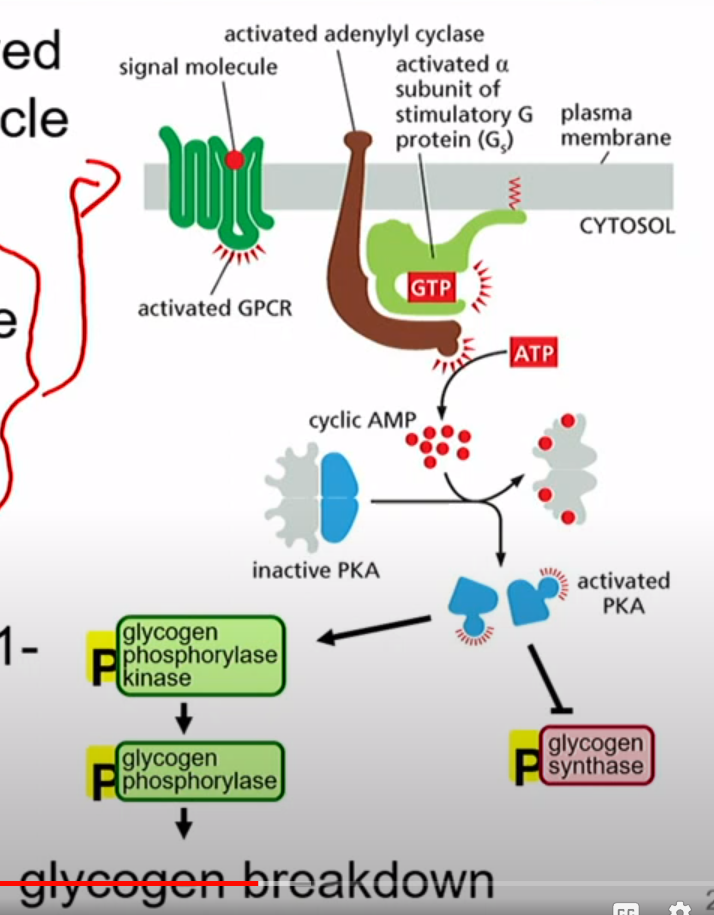
Ligand(signal molecule) = Adrenaline
1. Promotes Breakdown of Glycogen
2. Inhibits glycogen synthesis
-
Where is PKA found?
Inactive PKA usually cytosol while active PKA translocated to nucleus
-
What is CRE?
cAMP Responsive Elements
-
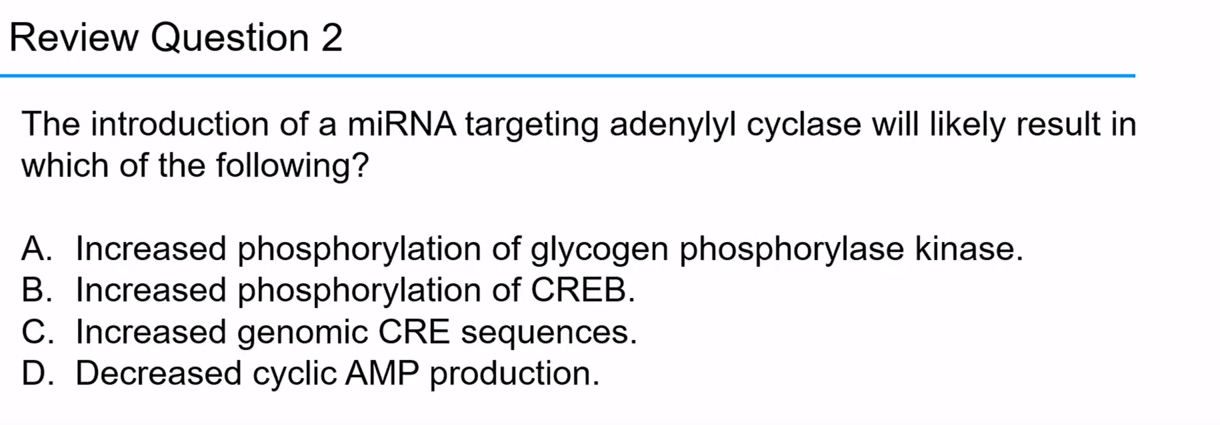
D
-
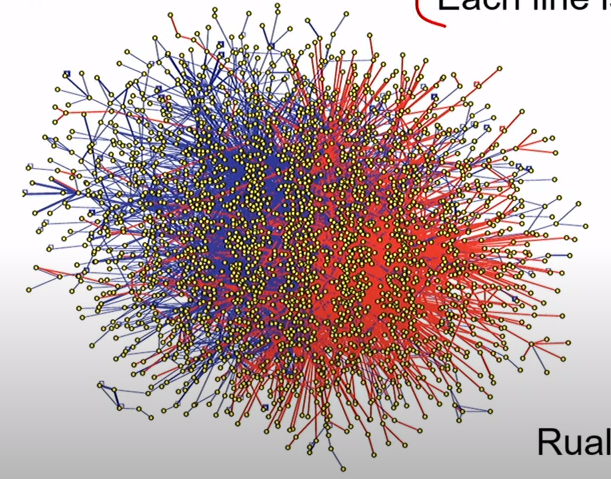
How do you read an interactome?
Each dot is a protein node
Each line is an interaction edge

