-
Subphylum Urochordata
Sea squirts or tunicates
-
Subphylum Cephalochordata
Lancelets
-
Subphylum Vertebrata
Fishes, Amphibians, Non avian reptiles, Reptiles, Mammals
Have a brain surrounded by a skull made of bone or cartilage
must have a backbone column that replaces the notocord
-
What are the 5 Chordate characteristics
1. A supportive Notocord
2. A dorsal hollow nerve cord laying dorsal to the notochord
3. Pharyngeal slits or pouches in the pharynx (anterior region of the gut)
4. A Tail posterior to the anus
5. Endostyle or thyroid gland
-
Describe Urochordata
have a single-chambered heart, are marine filter feeders, can be solitary or colonial and are sessile except during a free-living "tadpole-like" larval stage
They have all 5 chordate characteristics during the larval stage
In adult form they have
1. Endostyle (Produces mucus for feeding)
2. Pharyngeal basket (modified slits)
-
Describe Cephalochordate
Retain all 5 chordate characteristics throughout the entire lifecycle
have a single-chambered heart, filter feed using cilia and mucus in their pharyngeal slits
Buccal cirri and wheel organ in the pharynx create water currents
Animal of Great evolutionary significance
-
what is Buccal cirri?
Buccal cirri are feeding structures found in the oral hood of primitive jawless organisms called amphioxus, also known as lancelets. They are small filaments that are used for mechanical sorting.
-
What is the wheel organ?
the wheel organ is a series of ciliated cells that create water currents to help draw food particles into the mouth for feeding
-
What is an Amphioxus and how is it similar to a urochordate tadpole larvae?
The Amphioxus is a lancelet
like the urochordate larvae, it filter feeds and has all 5 of the chordate characteristics
-
what is the Ammocoetes and how are they different to Amphioxus
They are Lamprey larvae, have a heart with an atrium and a ventricle (like all fish) as well as 2 eyes and a 3 part brain.
It has all 5 chordate characteristics and appears very similar to Amphioxus
Amphioxus has: Buccal cirri, wheel organ
-
What is the pineal organ
The pineal gland, often referred to as the "third eye", senses light and is responsible for regulating circadian rhythms and the production of melatonin.
-
What do sharks use for buoyancy
squalene in the liver and heterocercal tail
-
What is the spiracle
allows water to enter and flow over the gill filaments
-
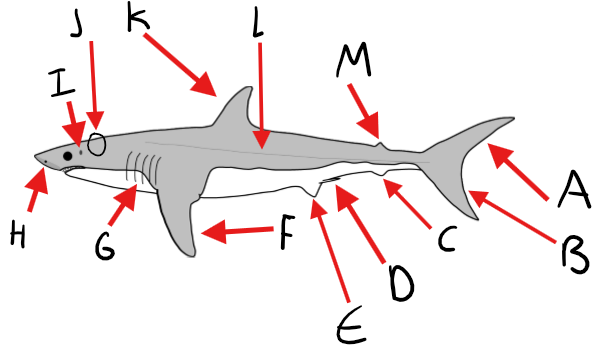
Label the shark diagram
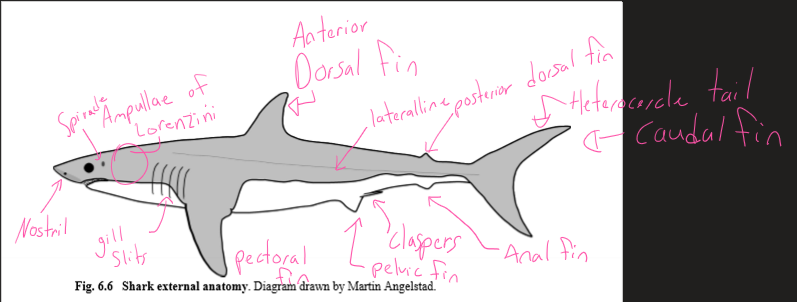
-
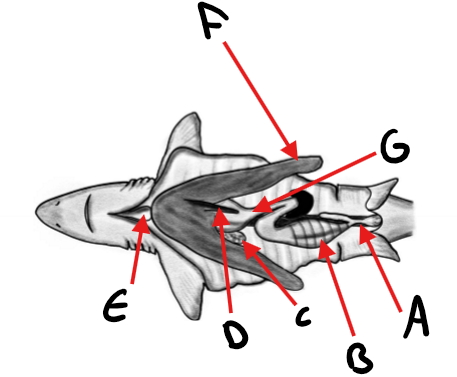
Label the shark diagram
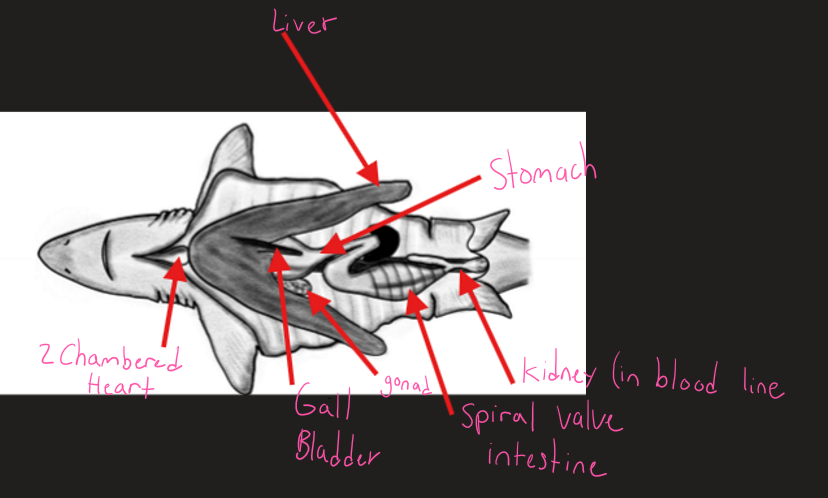
-
What is Actinopterygii
Ray-finned bony fish
-
What is Chondrichthyes
Cartilaginous fishes
Large toothed jaws
Paired fins
Powerful tail muscles
-
What is the ecological significance of evolving jaws?
The evolution of jaws allows the diversification of diets and environments. by being able to grasp, tear and chew food they could grow larger as well as inhabit new environments (like in fish 115 where salmon that eat fish grow larger by being more predatory early vertebrates could grow larger)
-
What are placoderms
Extinct group of jawed fish that likely gave to the rise of condrichthyes
-
What type of scales do sharks have
Placoid
-
What type of tail do sharks have
heterocercle
-
what is the lateral line
fluid filled canals containing sensory cells (Neuromast cells)
can detect low frequency vibrations and currents in water
-
What are claspers
a male appendage used in copulation
-
What are some adaptations of Actinopterygii
Bony skeleton, Operculum, Swim bladder
-
What is a swim bladder
and a gas filled structure used to maintain neutral buoyancy
-
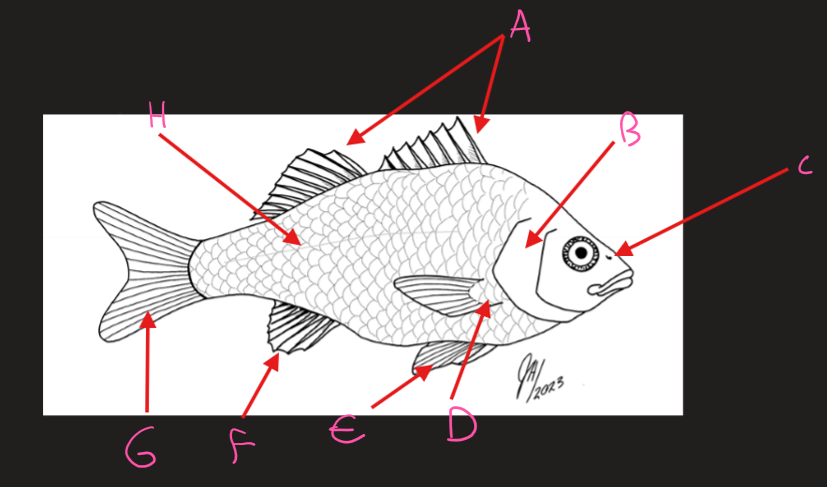
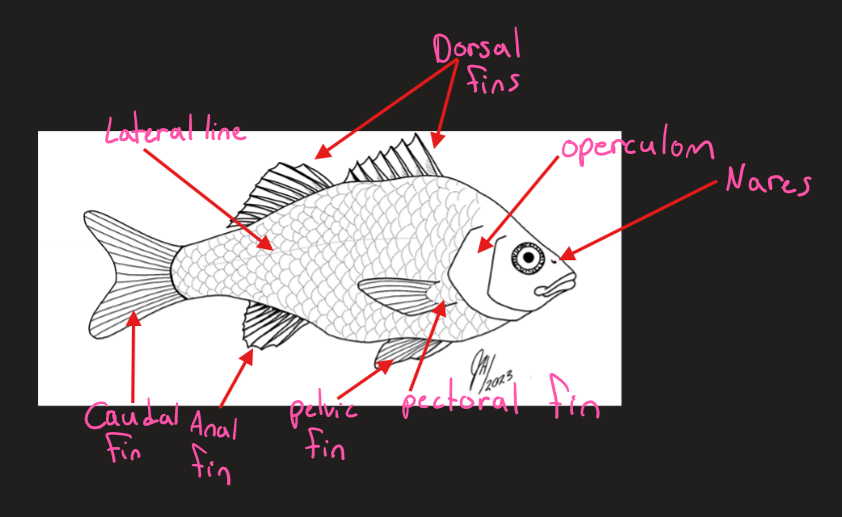
Label the fish diagram
-
Why is the operculum an important adaptation
improved the ability of a fish to aerate the gills
helps pump water through the gills
-
What types of scales do fish have (2types)
Cycloid and Ctenoid
-
What do pyloric ceca do
Expands to surface area of the stomach
similar to the spiral valve intestine in the sharks
-
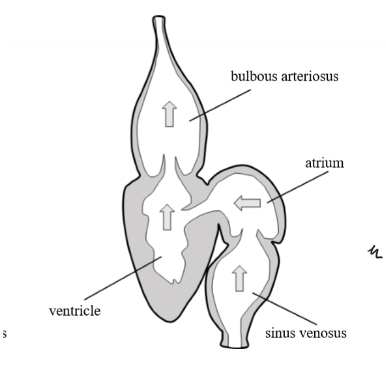
What chambers are in a fish heart?
Sinus venosus
Atrium
Ventricle
Bulbous arteriosus
-
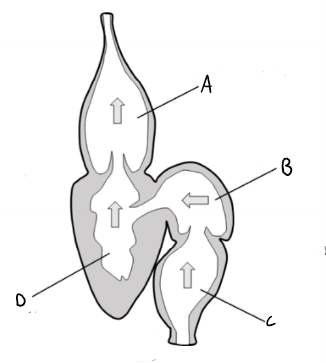
Label this fish heart
-
Explain a counter current exchanger
The counter-current exchange process allows for efficient oxygen extraction. Water flows over the gill filaments in one direction, while blood flows in the opposite direction. This maintains a gradient that maximizes oxygen diffusion from water to blood.
-> oxygen levels want to balance out between the water and blood
-
What are the parts of the gill, explain their purpose?
Gill arch
- Provides support to the gill
Gill raker
-Direct food to the esophagus
- strain food from water
Primary lamella (Gill Filament)
- protrude from gill arch and are made up of secondary lamella
Secondary lamella
- extract O2 from the water using counter current exchange
-
What is the Pharyngeal mill
tooth like structures in the esophagus of some fish that help grind food (similar to chewing food in mouths of mammals)
-
Explain the blood flow in fish
Single circuit system
Body-> Heart (Sinus venosus -> Atrium -> Ventricle -> Bulbous arteriosus) ->Gills -> Body
-
What Clade contains Sharks, Rays, Skates and Chimaeras
Chondrichtheys
-
What Clade contains Ray finned fishes
Actinopterygii
-
What Clade contains Lobe finned fishes
Sarcopterygii
-
What clade contains the hagfish and lampreys
Cyclostomata
-
What is Myxini
Hagfish
-
What is petromyzontidae
lamprey
-
What is Agnatha
Extinct jawless fishes (Maybe some living?)
-
What is Cutaneous respiration
Gas exchange through the skin
-
What is the axial skeleton
Skull, Vertebrate collumn (spinal cord) and Sternum
-
what is the appendicular skeleton
Pectoral girdle (Forelimbs, scapula, etc) and the pelvic girdle (includes hindlimbs and pelvis)
-
What is the pectoral girdle
Includes scapula coracoid process and acromial process - Shulders and where the upper limbs attach
-
what is the pelvic girdle
Includes the Ischium, Ilium and pubis - Hips and pelvis
-
what is the atlas
The first cervical vertebra in the spine supports the head and allows the nodding movement
-
What are transverse processes
Bony projection of the vertebra that serve as attachment points for muscles and ligaments
-
What is the urostyle
A long rod loke bone found in the pelvic region of frogs and toads formed by the fusion of several vertebrae and allows the hind legs in their powerful jumping abilities
-
What Skeletal adaptations have adapted frogs to a hopping mode of transport
Long hind legs and the fused bones that make up the urostyle allow the frogs to have greater leverage when they jump
-
What is the nicitating membrane
Transparent membrane on frogs eyes that provide additional protection for the eye
-
What are the ID traits to determine if a frog is male or female
males have larger Tympanum sizes and vocal sacs
-
What are the maxillary teeth
The frog teeth on the upper jaw
-
what are the vomerine teeth
Teeth on the vomer bone (the middle portion of the upper jaw
-
what is the glottis
Protects the airway preventing food and liquid to enter during swallowing
-
what are the vocal sacs
Resonators that amplify the frogs mating sounds located in the larynx
-
What is the fuction of the liver in frogs
Bile production and detoxification of the blood
-
What is the gallbladder
stores bile produced by the liver and releases it into the small intestine
-
what is the pancreas
Regulates endocrine/blood sugar through hormone secretion
Secretes digestive enzymes into small intestine to help breakdown food
-
What is a cloaca
Last chamber of the digestive tract of many vertebrates except mammals
Receives feces form intestine as well and Urine and Sperm from the urogenital system
-
Expalin how frogs breath
Frogs use positive pressure meaning they have to gulp and swallow air to push it into their lungs
-
What is the function of the urogenital system
Urine production and excretion as well as reproduction
-
what is the adrenal gland
small triangluaar gland on top of the kidneys that produce hormones
-
Label this diagram of a frogs Urogenital system
?
-
Lable the following aphibian hearts blood flow
?
-
How many chambers are in an aphibian heart
3
-
Describe Frog circulatory system
Double circuit
Systemic (Blood to the body) and pulmonary (blood from the heart to the lungs)
Three chambered heart
2 atrium and 1 ventricle
Some mixing of the blood
-
What order contains frogs and toads
Anura
-
What Order contains Salamanders
Caudata
-
What are the important adaptations that lead to tetrapod
Legs and Lungs
-
What is a Amniote
Reptiles, Birds, Mammals
Do not need water for reproduction because they have a AMNIOTIC EGG which has a shell to maintain moisture within the egg while allowing Gas exchange between the egg and the enviornment
-
what is differnet about an amniote egg to a amphibian egg
It has a external shell which protects the egg
-
What skin layer are Reptile scales derived from
the epidermis which is the outermost layer of skin
-
What skin layer are fish and shark scales derived from
fish and shark scales are derived from the dermis layer which is the middle layer of skin
-
What is a temporal fenestrae
A temporal fenestra is an opening in the skull behind the eyes found in some vertebrates. It allows for the attachment of muscles
-
How many Temporal fenestrae does this specimen have
?
-
what does Diapsid mean
Two temporal fenestrae
ex. Lizards, snakes, crocodiles
-
What does Anapsid mean
No temporal fenestrae
-
what does synapsid mean
One temporal fenestrae, mammals came from synapsid lineage
-
What is the Foramen magnum
Large hole that the spinal cord passes through, located above the occipital condyle
-
What is the occipital condyle
A bony bump that articulates with the first cervical vertebra
Atlas
Birds= 1
Reptiles= 1
Amphibians=2
Mammals=2
-
What does homodont mean
All the teeth are the same
found in reptiles
-
what are otic notches
Indentation in the back of the skull near the ears that allows muscle attachment
(Looks like a spike out the back of the Turtle skull)
-
What is the carapace
Dorsal shell
-
What is the plaston
Ventral shell
-
what are scutes
Turtle scales - combine to make up the carapace and Plaston
-
what are cervial vertebrae
the neck vertebras
-
What is special about turtle ribs
they are fused
-
what is the sacral vertebrae
The vertebras located below the lumbar
Allow the pelvic girdle to articulate
-
What are palates
Flat plates made of bone
-
What is the Humerus
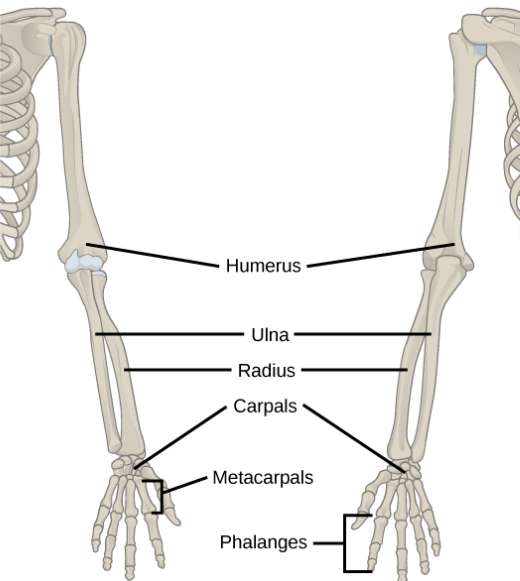
The humerus is the long bone in the upper arm or forelimb. It runs from the shoulder to the elbow, connecting the scapula (shoulder blade) to the radius and ulna (forearm bones).
-
what is the radius
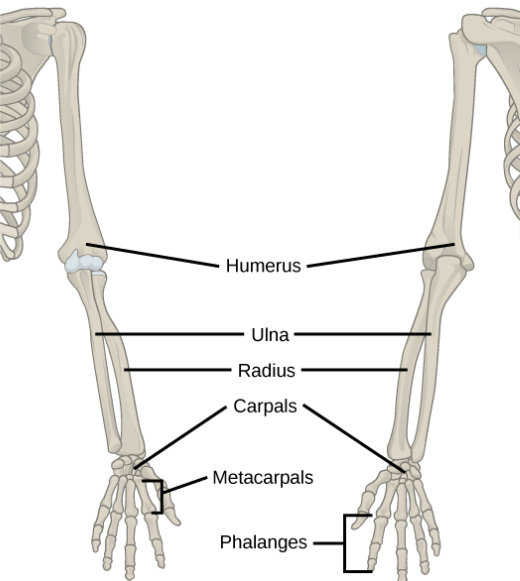
The radius is one of the two long bones in the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist.
-
What type of wing is this?
elliptical
-
What type of wing is this?
Highspeed
-
What type of wing is this?
soaring
-
What type of wing is this?
High lift
-
what is the central shaft
Main stem section of a feather
-
what is the quill
tip of a feather that penetrates the feather pollicle of a bird
-
What are the barbs
Projection off central shaft that form the large surface area called the vane

