-
What does the autonomic nervous system regulate?
- heart muscle
- actions of glands
-
Activities of the ANS is made without conscious awareness. True or false?
True
-
What are the two motor neurons that are connected in an autonomic pathway?
Preganglionic; spinal cord > ganglion
Postganglionic; ganglion > effector
-
Where are the cell bodies of somatic motor neurons located?
The anterior gray horns
-
In the SNS, how many synapses are there?
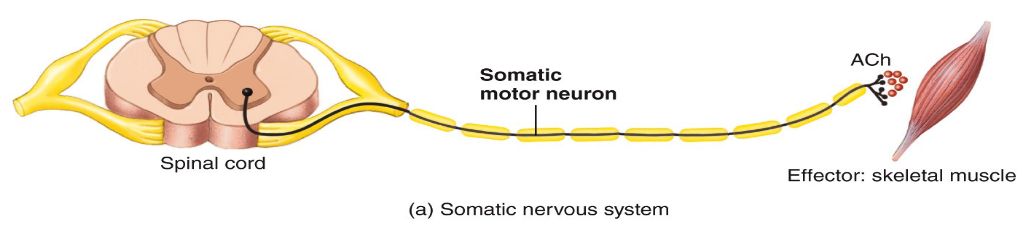
Only 1; it's uninterrrupted.
-
Epinephrine and norepinephrine are both ___ and ___.
neurotransmitters and hormones.
-
Both of them have an effect on the heart and blood vessels. However, epinephrine has more of an effect on the ___ and norepinephrine on the ___.
epinephrine - the heart
norepinephrine - bv
-
Where are the autonomic motor neurons located?
In the lateral gray horns.
-
What is the difference in the preganglionic fibers in the sympathetic and parasympathetic system?
>length in the sympathetic than in the parasympathetic, thus they have less schwann cells, and vice versa.
-
What gland produces nor/epinephrine as hormones?
The adrenal gland.
-
What hormone is released in the parasympathetic neuron?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
-
What hormones are released in the sympathetic neuron?
ACh and nor/epinephrine
-
What does the sympathetic nervous system do?
Increases alertness; the flight-or-fight division.
-
What does the parasympathetic nervous system do?
Slows down most body activity; the rest-and-digest division.
-
What is another name for the sympathetic nervous system and why is it called that?
Thoracolumbar; because the preganglionic neurons are found in the lateral gray horns of the thoracic and lumbar segments.
-
In the ANS, the axon of the preganglion is always ___ and the postganglion is ___.
myelinated, unmyelinated
-
___ form the sympathetic chains.
Sympathetic ganglia (cell bodies).
-
What does adrenergic mean and division of the ANS is described as that?
- When epinephrine/norepinephrine (adrenaline or noradrenaline) are released to their effectors. "Activated by adrenaline".
- The sympathetic nervous system because it releases those hormones and neurotransmitters.
-
What is another name for the parasympathetic nervous system and why is it called that?
Craniosacral; because the cell bodies of the preganglionic neurons originate in the cranial nerves and some in the sacrum (2-4).
-
What are the 4 cranial nerves that house the preganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic nervous system.
- Occulomotor III (eye movement)
- Facial VII
- Glossopharyngeal IX
- Vagus X
-
What does cholinergic mean and what division in the ANS is described as using that?
Releasing only ACh; the parasympathetic system.
-
After neurotransmitters have been docked, what channels open and what other events occurs?
Na+ channels open, the postsynaptic end bulbs will be excited and an AP begins.
-
What is docking site?
Docking station of neurostransmitters on postsynaptic cell membranes.
-
Why does ACh stimulate digestive organs but inhibit the heart?
Because it is what activates the effectors of the parasympathetic nervous system; rest-and-digest division. Whereas the heart is only stimulated in stressful situations controlled by the sympathetic nervous system.
-
Sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous systems can be described as ___ to one another. The sympathetic excites the heart and rate of respiration while inhibiting digestion and vice versa.
antagonistic
-
What does the pupillary light reflex do to our eyes and when does it occur?
It constricts our pupil when it is hit with light.
-
How does the pupillary light reflex occur?
When the retina of the eye is stimulated by light > nerve impulses from CNII > integrating centers o the brain > interneurons send impulses to motor neurons in midbrain > axons receive info. > travel through CNIII > synapse with postganglionic motor neurons to constrict the pupils
-
What are the four times (four Es) the sympathetic nervous system is activated?
- Times of emergency
- Excitement
- Embarrassment
- Exercise
-
The parasympathetic system can cause (SLUDD) ___.
- salivation
- lacrimation
- urination
- digestion
- defecation
-
Which system innervates the sweat glands of the skin?
The sympathetic system

