What are the structural features of the eye?
- fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, nervous (sensory) tunic (retina), lens, anterior segment, and posterior segment
What is the eye in terms of shape alone?
3 layered sphere filled with fluid
What is the posterior segment of the eye?
posterior to lens
contains vitreous humor (gel-like)
What is the anterior segment of the eye?
anterior to lens
contains aqueous humor (fluid similar to plasma)
What are characteristics of the lens of the eye?
avascular, transparent
What is cataracts?
clouding of lens on the eye
What are the parts of the nervous (sensory) tunic, i.e. the retina?
- outer pigmented layer
- inner neural layer (3 layers of neurons)
- fovea centralis
- optic disc
What are the 3 layers of neurons in the inner neural layer of the retina?
- Photoreceptors (2 types): Rods (black and white) and Cones (colour)
- Bipolar Cells
- Ganglion Cells: axons from optic nerve (= Cranial Nerve II)
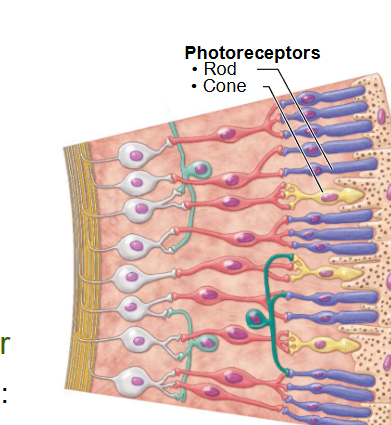
Name the 3 layers of neurons in the inner neural layer of the retina?
- Bipolar Cells (pink in pic)
- Ganglion Cells (white in pic)
What is the fovea centralis in the inner neural layer of the retina?
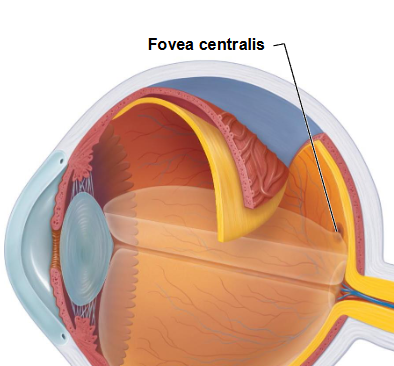
where light is focused
= area of greatest visual acuity
no rods, just cones
What is the optic disc in the inner neural layer of the retina?
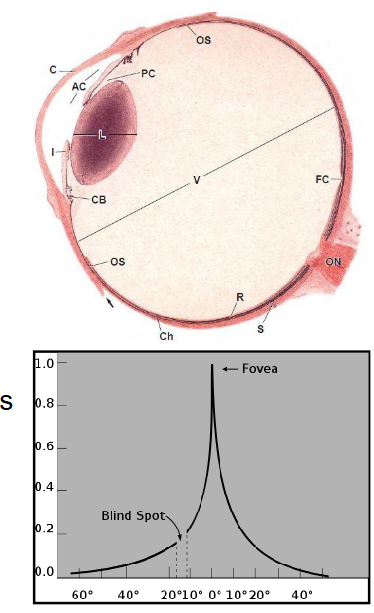
blind spot where blood vessels + optic nerve exit eye
no rods or cones
What are the parts of the fibrous tunic?
- sclera (white): avascular connective tissue (CT)
- cornea (transparent): avascular CT
- conjunctiva (covers anterior sclera, vascular mucous membrane, when vessels dilate = bloodshot eyes)
What are the structural features of the ear?
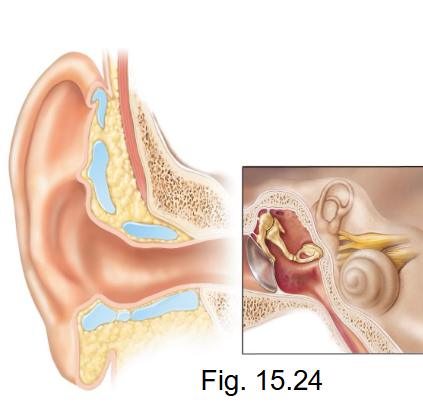
- external ear, middle ear, inner ear (labyrinth), cochlea, receptors in inner ear
What does the external ear do? What are the parts?
- conducts sound
- parts:
auricle (pinna, elastic cartilage, covered with skin)
external auditory canal (meatus)
tympanic membrane (eardrum)
What does the middle ear do? What are the parts?
- conducts sound
- parts: Eustachian tube (also called pharyngotympanic tube) and ear ossicles
What are the parts of ear ossicles in the middle ear?
- malleus (secured to tympanic membrane)
- incus
- stapes (transmits sound to inner ear via oval window)
What does the inner ear (labyrinth) do? What are the parts?
- conducts sound
- parts: bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth
What is the bony labyrinth in the inner ear?
- tunnels in temporal bone (contain perilymph)
- parts:
- semicircular canals: equilibrium
- vestibule: equilibrium
- cochlea: hearing
What is the membranous labyrinth in the inner ear?
surrounded and protected by bony labyrinth
contains endolymph
What are the parts of the membranous labyrinth in the inner ear?
parts:
- semicircular duct (inside canals)
- utricle and saccule (inside vestibule)
- cochlear duct (inside cochlea)
What is the cochlea?
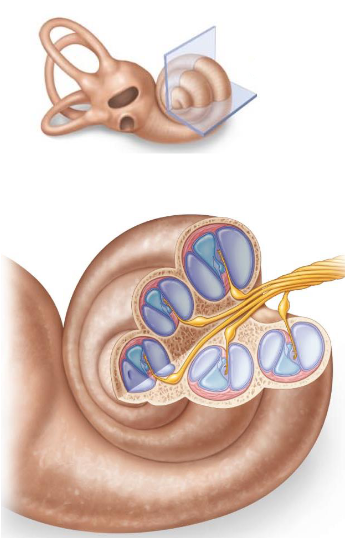
- coiled (and each coil has 3 channels)
- has 3 membranes
What are the 3 membranes of the cochlea?
- vestibular membrane: between cochlear duct + scala vestibuli
- basilar membrane: between cochlear duct + scala tympani
- tectorial membrane: covers hair cells (= receptor cells)
What are the 3 channels each coil of the cochlea has?
- scala vestibuli: upper; perilymph
- scala tympani: lower; perilymph
- cochlear duct: middle; endolymph
What are the receptors in the inner ear?
- called hair cells that synapse with neurons (send impulses to brain via cranial nerve VIII)
- hairs are cilia that extend into endolymph, the tips of cilia embedded in tectorial membrane (stability)