How many different proteins make up the G-Protein coupled receptor?
1
What is the abbreviation for G-Protein Coupled Receptors?
GPCRS
What are other names for GPCRS? And why are they called this?
Heptahelical Receptor and 7TM receptor
Why?
Because the amino acid chain goes in and out of the membrane, 7 times
How many different GCPRS are there on the Human genome?
830 and they are the major target of pharmaceutical developed treatment
What is the structure of the GCPRS?
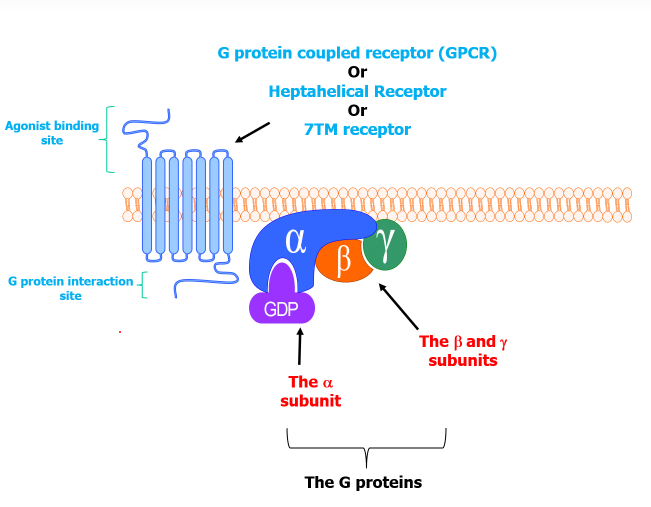
GTP bound to ford GDP
Cell signalling is caused by what in GPCRS?
By the separation of the a (alpha) and b (beta) subunits
Specific Enzyme signalling is determined how in GPCRS?
Enzyme signalling is determined by the different forms of the a (alpha) subunit
What forms of the alpha subunit are there?
4 forms:
as- (stimulation)
ai- (inhibition)
aq-
a12/13-
What do each of the alpha forms stimulate?
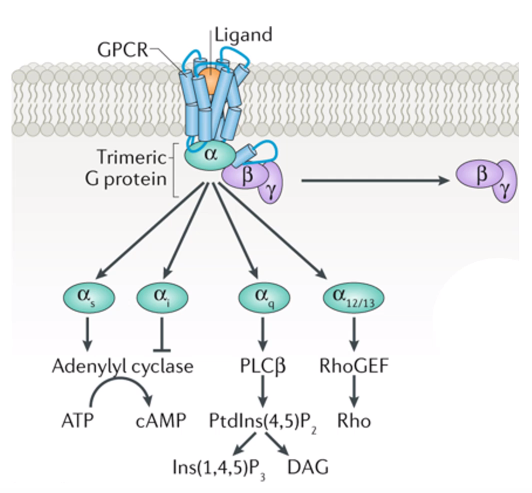
(Adenylyl is another name for Adenylate)
How are GPCRS activated?
Via binding of an agonist
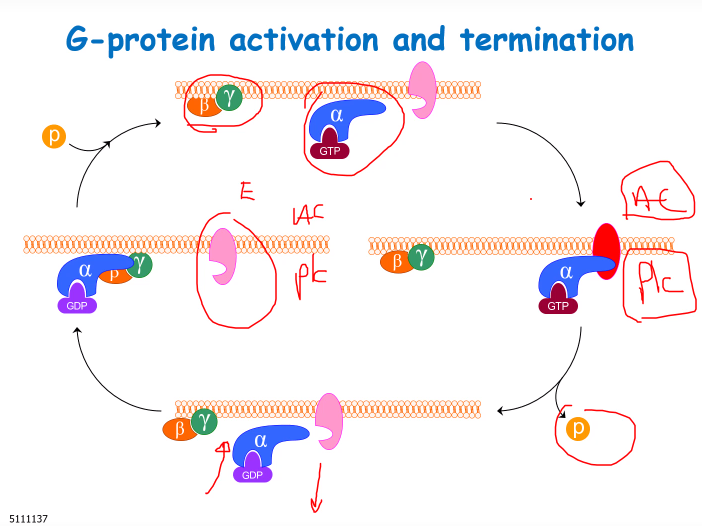
Picture summary of the G-protein activation and termination
What the series of reactions that occurs after GPCR binds with adenylate cyclase?
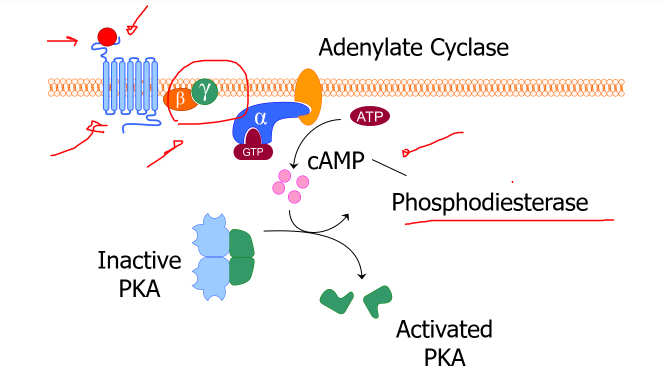
Adenylate cyclase converts ATP into cAMP,
cAMP will activate a kinase (Kinases put phosphate groups onto targets), which allows long-lasting cellular effects. cAMP levels are broken down by phosphodiesterases
What do the Gq and G11 alpha subunits do?
Increase phospholipase C activity
What the series of reactions that occurs after GPCRs Gq/G11 subunits have been activated? (9)
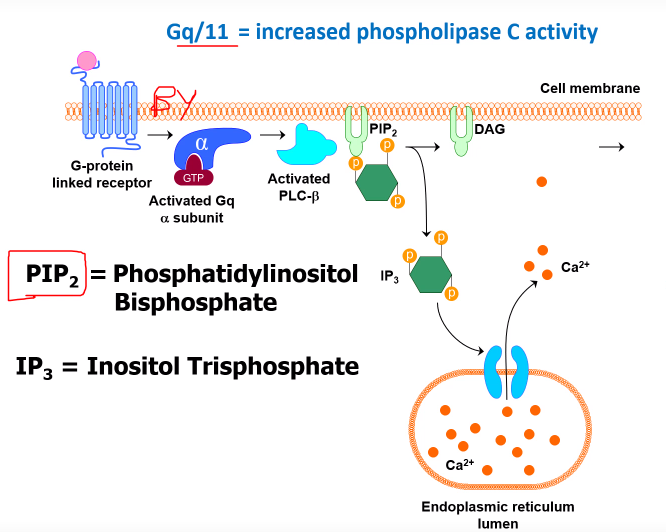
1)Agonist binds
2)Affinity of the a subunit for GTP goes up
3)Causes a dissociation of the b and y subunits (they stay in the lipid phase)
4)The activated Gq a subunit leads to the activation of PLC-b (Phospholipase C (beta)
5)Which interacts with PIP2
6)PLC-b cleaves the inositol group of PIP2, which converts it to IP3
7)Which leads DAG (diacylglycerol) to remain in the cellular membrane
8)IP3 will bind to its own receptor found in intracellular calcium stores
9)DAG will usually stay in the cellular membrane but can activate its own protein kinases
General summary of the different a (alpha) subunits
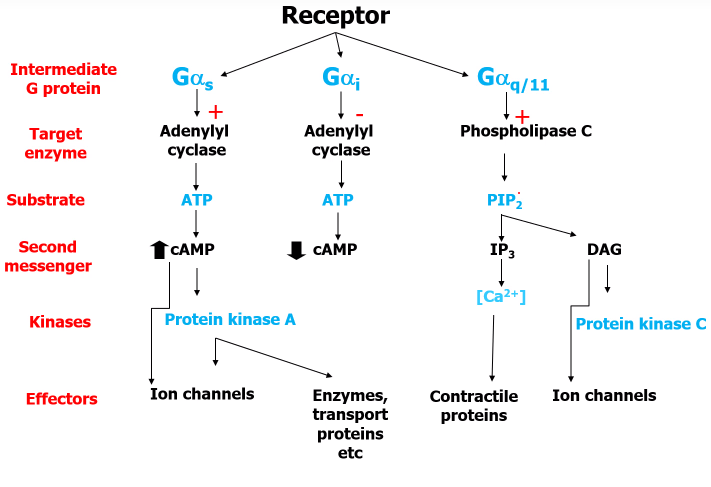
What a subunit does the different Muscarinic and Adrenergic receptors stimulate? What increases/decreases? And what happens after that?
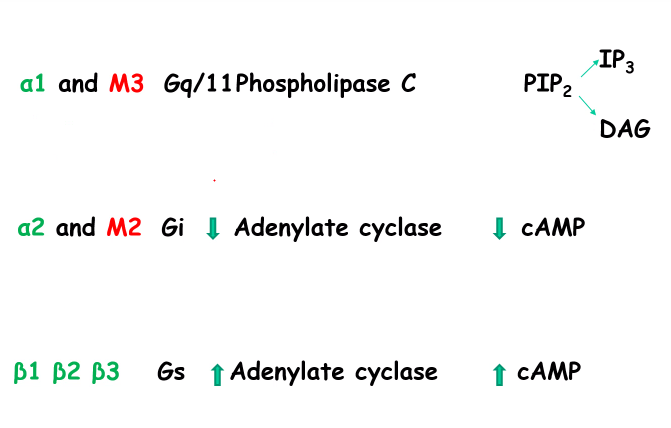
What are the Receptors (adrenergic/muscarinic?) which are stimulated by the Gas and Gai subunits?
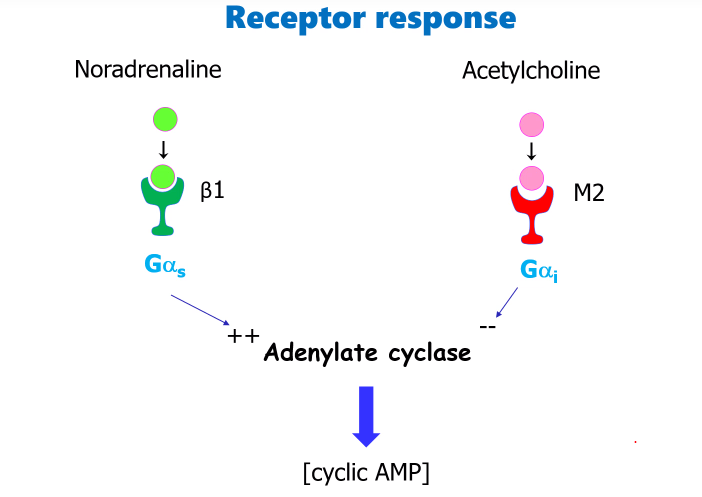
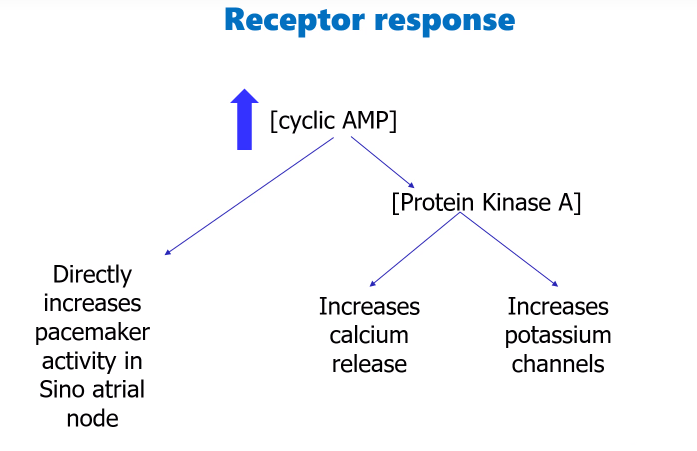
General summary of the receptor responses from increased cAMP