Neurorights
h
Farahany - The Battle For Your Brain (2023)
Main Point: our brains need special protections.
Points:
restricting the flow of information is impossible and harmful
cognitive liberty
mental privacy: rights over info abour your mind
freexom of thousht:
pos: right to change mental state
neg: right not to have something happen or be protected (unwarranted search/seizure)
self determination
pos: rights to change your mental state as you wish
neg: right to not be denied determination?
neurotech could oppress or protect us we must choose
Concerns/Rebuttals:
"we should restrict" impossible
Summary:
Bublitz & Merkel - Crimes Against Minds: MEntal Manipulations, Harms, Rights to Mental Self-Determination
current legal does not acknowledge mental crimes. the law should introduce inner sphere protections.
Not covered bodily rights
Not just harm to brain
Involves brain but in diff way concussion/disease
Not a new idea
Implicit in ideas about human dignity; always assumed/intuitive
direct: on brain physically dbs
indirect: mediated.
Concerns/Rebuttals:
we alter eachothers minds all the time/free speech: how ban intervention?
consent
some interventions informed consent and can eval legally
neg mental
impair cog, alter prefs, injure, undermine self deter
what makes change negative?how do we know emotion inappropriate?
Lever - Neuro v Privacy (2012) Democratoc perspective
Main Point: new neuro tech will create new ways to harm privacy. must first address the mundane ethics as things become more advanced
Points:
we already have exposes on celebrities in biographic depictions. forefit privacy in deatht
torture violate a victim's privacy
privacy vs liberty
invasions of privacy=intrusion, disclosure
Concerns/Rebuttals:
Summary:
Farah et al. (2014) functional MRI-based Lie detection; scientific and sociaetal challenges
Main Point:
Points:
detection of deception. not always high tech. can fmri discriminate lies from truth in individual subjects with sufficient accuracy?
lying is not homogenous behavior
low accuracy
criminals vs subjects and undergrads
first: different policies considered for different fmri lie detection. not banning despite shortcoming. different restrictions different scenarios
second: publically funded research.
removal of experimental ocnfounds.
more realistic experiment conditions
third: scientists vital neuroscience law. raise questions about accuracy and provide answers
Concerns/Rebuttals:
Summary:
Jabari (2013) Brain MAchine Interface and Human Enhancement
Main Point:
Points:
Concerns/Rebuttals:
Summary:
President's Council (2003)
Main Point:
Points:
Concerns/Rebuttals:
Summary:
Kolbert (2011) Give Memory altering drugs a chance
Main Point:
Points:
Concerns/Rebuttals:
Summary:
Clark & Chakmers (1998) the extended mind
Main Point:
Points:
Concerns/Rebuttals:
Summary:
Aas (2019) prosthetic embodiment
Main Point:
Points:
Concerns/Rebuttals:
Summary:
Greene & Cohen (2004) neuroethics changes nothing and everything
Main Point:
Points:
Concerns/Rebuttals:
Summary:
Hardcastle (2017) my brain made me do it?
Main Point:
Points:
Concerns/Rebuttals:
Summary:
What is cognitive liberty?
j
Lie Detection in Neuroethics
h
Reasons for Punishment
retribution
deterrence
containment
rehabilitation
TMS
transcranial magnetic stimulation
(bbublitz and merkel propose stimulating areas of the brain during testimony to make deceit harder therefore easier to detect)
dbs
deep brain stimulation. the scientists change and monitor a patients brain activity
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves implanting electrodes within areas of the brain. The electrodes produce electrical impulses that affect brain activity to treat certain medical conditions. The electrical impulses also can affect cells and chemicals within the brain that cause medical conditions.
Parkinson's disease.
Epilepsy.
Tourette syndrome.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder.
what are some examples of self determination violations from bublitz and merkel
Investigating corruption through TMS to make lying harder
DBS for journal paper. patient altered to create mood swings
ghrelin (chemicals to cause hunger) to sell more restaurant food appetite
oxytocin to win at poker (manipulate intuation of situationa nd raise trust)
memory blockers to conceal crime (SA victims forcced to forget)
stimulants for financial trading (concstantly alert financial broker to always be ready to make quick bet
SOME WE DO NOT NEED TECH FOR:
interrogators leading witnesses to certain beliefs
stores designed for subtl purhasing
snack chemisty
subliminal web dessign cause purchase
brainwashsing: mk ultra, communism thought reform
ALL ARE: INTUITIVELY WRONG in the SAME WAY
bublitx merkel: why do we need and not have neurorights
different from bodily harm (mwntal harm not same concussion)
implicit. we take for granted. we assumed
Negative and Posiitve Neurorights
Negative: defense from unwanted intrustions
posiitv: freedome to determine one's niner realm
Normal interaction vs Violation (bublitz merkel)
consented?
negative mental effects?
● reduce or impair cognitive capacities (e.g. memory, concentration, will
● alter preferences, beliefs dispositions (e.g. implanting false memories, creating addictions),
● elicit inappropriate emotions (e.g. artificially induced appetite)
● orclinically identifiable mental injuries.”
directly or indirectly?
(I) stimuli that operate directly on the brain… bypassing mental control capacities of the addressee, causing serious negative mental consequences shall be punishable …unless consent
(II)through stimuli purposefully designed to bypass mental control capacities causing severe negative mental consequences punishable unless such stimuli are exercises of permissible conduct such as free speech….[unless consented to]
What is an invasion of mental privacy?
Tort for privacy violation: intrusion into soething pricate defined by METHOD reasonably expect privacy, disclosure public defined by CONTENT would offend reasonable person (truth is not defense but public interest is)
what if we consent? is internet data harvesting unethical?
Faranahay Tech Worries
Consumer EEG (devices (meditation aides, sleep trackers, migraine predictors, etc.) (electroencephalogram) (records the electrical activity of brain via electroedes fix to scalp. record conditions)
Neural Interfaces to connect to tech
FArahany "Last Fortress"
brain the ONE PLACE of solace.
why is brain data uuniwue?
important? not really
control? not always
WHAT TO DO?
doesn't want to restrict flow of information; impossible and limits progress. doesn't want to stop use and records
put into place clear rules and regulations
WHAT REGULATIONS?
transparent corporations
limited processing
user-based controls
(power on and off without worrying what actiity)
local process
continuous overwrite
standards against discrim use
how is farahany's approach apolitical?
Focuses on individuals (not social structures or relationships)
Treats individuals as all having the same interests (not opposed interests)
Assumes that the value of privacy is shared (opposition is just from greed etc.
Lever on the link between privacy and societies
concentrate valye of privacy compatible and implicit in democratic government. current pricacy does not always mirror democratic values
eg:
secret ballot
open voting
reinforce the entitlement to vote: “while democratic legislators may be more vulnerable to intimidation than citizens [...] it is the former, not the latter, who must vote openly, not secretly"
(reinforcing different ppls rights!)
privacy can create domination (shielded domestic violence because "private")
parents controlling what children see online? is critixizing them an invasion of their privacy? is discussing parenting protecting the child's privact?
value judgement!
Lie detection
OLD:
dry mouth (rice in mouth. after questions if dry then called liar)
polygraph "lie detectors"
sodium pentothal (truth serum)
now untrustworthy. false confessions. anxiety, impairm compel
Functional MRI (fMRI)- lie detection
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is a class of imaging methods developed in order to demonstrate regional, time-varying changes in brain metabolism. mri using magnets creates magnetic field
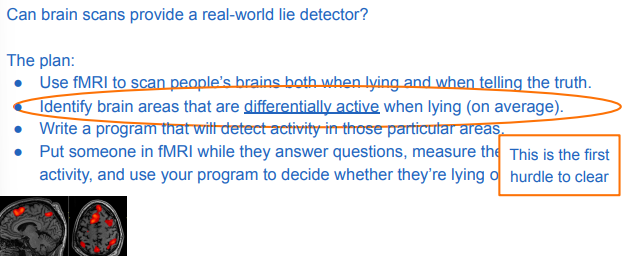
PLAN:
use fmri to scan when lying and telling trusth
identifying areas different active when lying (FIRST HURDLE)
CLEARED we know brain areas active in deception
write program to detect those areas
use fmri to detect activity during interrogation
Hurdles for fMRI lie detecion
confounds (picking up lying or something else?)
base rates (if lying rate, then even accurate etest may give false results) (false positives. 67% in studies)
individual variation (everyone different)
task variation (what different sorts lies have different neural signatures)
countermeasures (tech widely used, way to trick?)
Lever's main claim
how we codify privacy reflects what kind of society we want to make
“Truth” is a good goal when everyone’s interests line up; when people’s interests are in conflict, truth helps some people and hurts others.
E.g. In war, both sides want their information about the enemy to be true, and want their enemy’s information about them to be false.
COOPERATIVE vs ANTAGONISTIC when interests align
No Lie MRI
introduce lie detection to courts.
rules out epxplicit coercion. but doesnt guaruntee implicit coercian.
terms for implants/ tech connecting to nervous system (via electrodes to machine.) communication between brain and machine
Brain Machine Interface (BMI)
Brain-Computer Interface (BCI)
neural interface
Extracting info from brain
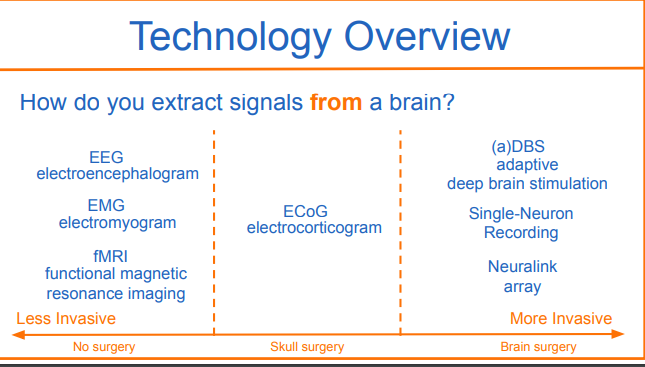
methods
Electrocorticography (ECoG), a type of intracranial electroencephalography (iEEG), is a type of electrophysiological monitoring that uses electrodes placed
how do you send sisgnals into a brain
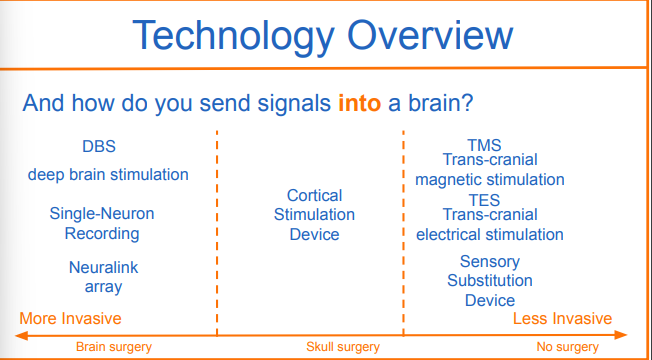
sending in
applications for BCI
sensory prostheses (link camera to cortical stim. sub sense), motor prostheses (robo limb), Brain to Brain (silent talk, eeg user to user communication on battlefield)
Jebari on autonomy
as DBS becomes more widespread, as this paper has concluded is to be expected, costs and risks will plunge and in a longer perspective, productivity-enhancing DBS seems like a real prospect.
An Autonomy Comparison
A cashier could be made happier and more friendly, a police officer could have his aggressions blocked, a doctor could be made more caring and empathetic, and a soldier could be transformed into a callous and detached person.”
(addicted police officer?) (arm-matic 3000)
Low/MEdium tech memory modification
TYPES OF MEMMORY:
Short-term memory
Long-term memory
Implicit memory
■ Procedural memory
■ Associative memory
○ Explicit memory
■ Semantic memory
■ Episodic memor
LTP long term potentiation
Rehearsal (to solidify the memory) ● Mnemonics (to make something easier to remember) ● Revisiting with a different mood (to moderate emotional tone) ● Suggestive prompting (to implant false memories) ● ‘Externalizing’ memories in the form of notes, writing diaries, photographs, stories, etc. We also have familiar drugs that can interrupt long-term potentiation by disrupting brain activity generally (e.g. ‘getting blackout drunk’). This stops any memory being formed at all, and has severe side-effects.
LTP
long term potentiation, processing long term memory.
move from short to long term.
neuron connections strengthened (one fire will usually acivate others)
relies on hippocampus and strengthened by amygdala aka emotional arousal area
low/medium memory modification
rehearsal (solidify)
mnemonics
revisitng
suggestive prompting
exterbalizineg (writing diaries, notes, photos, stories)
alcohol/intoxication
propanolol
propanolol
heart nedication
interfere with emotion effects and LTP
doesnt affect recall but affects emotion response
emotive intensity can improve recall
USE:
PTSD
dampen flashbacks
cptsd (complex ptsd without single focal event long term)
Prez council bioethcis worries about memory mod. (beyond therapy: pursuit of happiness)
(no proposals, just worries)
clinical use: make prospective judgement that event is sufficiently terrible to warrant in-the-moment blunting?
non-clinical: (could also apply to research)
prepare soldier to kill,
dull sting of shame,
criminal numb victims memory
societal: obligation to remember
obligation on those who experience directly
victims/witnesses numb themselves and protect perpetrators? testimony?
(value of emotional pain? psychic pain unnecessary.....become inhuman....remove difficult)
Discuss in pairs which of the PCB’s worries seem the most reasonable or serious.
Judging when to administer propranolol clinically
● Making soldiers callous and unfeeling ●
Blocking guilt from wrongdoing ●
Numbing victims and witness’s memories of wrongdoing ●
Victims and witnesses numbing their own memories
Life Should have pain? memory modification worries
human life should incorporate pain:
plausible: life without pain sounds weird
paradoxical: when we feel pain we try to reduce it
what sorts of pain?
failure: life without failure impoverished?
torture: good life without this?
loss/lovehurt:unclear??? love entails pain but we may never feel pain in love
What sorts of emotional pain seem like important parts of a full life, and which don’t? (What makes the difference?)
value of emotional pain. contemplate answer
Kolber thinks the worries raised by the PCB are:
not concerned enough
important/reasonable
overblown
overblown
(but recent discoverries more radical ways. overblown concerns in 2001 could be reasonable in 31)
Value of Self Knowledge
kolber: pcb overblown fears. unjustified aversion to pharmaceutical managing trauma
Self-knowledge is valuable
(maybe also: “personal growth”?)
Direct methods work independently of self-knowledge.
Indirect methods change our minds by means of giving us self-knowledge.
➔ Therefore We should prefer indirect methods when possible
“some bioethicists argue that instead of seeking a solution in a pill bottle, we should do the difficult but rewarding emotional work"
levy accepts first two and says third is true in SOME cases. some indirect methods work through self knowledge. but direct methods may still facilitate self knowledge. self knowledge is just one good among many not an obligation.
ZIP
Zera-inhibitory Peptide
blocks PKC-Zeta, protein involved in LTP
(rat taught where to get cocaine, ZIP injected, rat lost behavior related to finding the cocaine, but no brain damage)
(BUT: rat memory diff from human, not clear how selective or how to make it selective,)
Hypothetical ZIP uses
ERASE
1
find neurons with certain memory.
injext ZIP to block those neurons and erase that memory
hopefully does not erase all memories associated with those neurons
2
actibating memory to re-encode with LTP
ZIP blocks LTP
activating memory and injecting ZIP = erasure
CREATE
3
what does opposite of ZIP? (PKC-Zeta?)
patient imagines event
inject anti-Zip
imagined event feels real
would be COMPLEX
Lacuna-eternal sunshine. removes emotional charge AND factual knowledge (would anyone choose to remove instead of just "numbing". is it ethically diff?)
arm-matic 3000
define
Individual & Social Knowledge
most of what we know we learn from others. removing info from your mind might make it less available to others
Honesty andDemocracy
do others have a right to know info
are you making democratic society worse
is removing a factual memory lying to yourself?
is lying to self as bad, or worse than to others
SELF DECEPTION:
exceptions for honesty:
deceive enemies in conflict
trivial matters
private matters when others have no right to know
where is the mind
where is my mind? why do we think it is there?
immediate experiene- eyes and ears in front brain (contingent
soul is? cannot detect?
biology? nothing special about brain-tissue
philosophers think key is function. mind is in brain because of what it does
functionalism
: Mentality is a matter of performing certain information-processing functions.
The mind is software, the brain is hardware
You can run the same software on any sufficiently complex hardware ● Hence microchips, if they can perform the same function, are just as good as neurons. ● Hence aliens or robots might have minds just like ours, but implemented in a different sort of materia
parity principles
If an internal process and an external process perform the exact same function, they’re on a par for being part of the mind. But obviously
There are some functional differences between a notebook and biological memory.
(E.g. A notebook requires light: it stops functioning in darkness, where biological memory continues to function.) So we have to spell out which aspects of what something does matter.
specifically thinking about STORAGE
inga and otto
can otto's notebook be part o his mind
“playing the same role.”
clark and chalmers four key functional featuures of otto's notebook
constant presence. rarely take action if re;evant
available without difficulty
autpmatically endorses
consciously endorse some point in the past
(but notebook not always, still interface, doubt or distrust (what if someone else write) perfectly track)
what biological brain functions which also fail to meet features
Your mind and body both seems like constituents of you ➔
Whatever is part of your mind is also part of you)
coupled system
..
what defines the body?

should crimes against a person include intimate inorganic items? artificial limb stolen is theft or battery?
bodily wrongs like assault are simply wrongs that involve the body where what counts as the body is a question for science
Aas:
body is all things and only things which
PSYCHOLOGICAL ACCOUNT:
feel like part of my body when using skillfully
feel part of my body alll the time (ownership?)
are part of my extended mind
BIOLOGICAL ACCOUNT:
work like body part (organic/functional integration?)
grew from same zygore v(ontogenetic?)(biology of being)
evolved in tandem with other parts (evolutionary)
accepted by my immune system (immunology?)
critical to our functioning as equals

Aas body vs Levy treatment/enhancement
levy/aas
body moral def
“to the extent that a kind of inorganic item meets the following conditions, it is hard to imagine how any institutions that treat disabled people as equals could resist affording items of this kind bodily protection [...]
(1) Functionally replace a ‘missing’ organic item (whether, in terms of relevant phenomenology or matching self-representation; or in terms of maintaining the integrated functioning of a system needed to support action and experience); and
(2) Are themselves not significantly easier to replace than the organic item they replace
Justifications for Punishment
If P kills someone. should they b punished? why
types of justice
retribution: only fair for guilty people to suffer in proportion to their guilt (backward) (free will)
deterrence: seeing an act punished will deter people from further in the future (free will)
rehabilitation: make them better in future (because not in control)
restitution: some punishments rectify harm doneto victims (regardless free will)
containment: some punishments make an offender physically less able to offend again (because not in control)
consequentalists
right thiung to do is whatever will bring about the best overall consequencces (utilitarianism is form of consequentialism)
retributivism
punishment should be given "As deserved"
mens rea vs actus reus
guilty mind vs guilty act
(criminal punishment presupposes free will )
acting intentionally or negligently not autoamtic
understand what you are doing
understand moral status
being in control and able to do otherwise
mr puppet, boys from brazil
Greene and Cohen argue as follows:
Premise 1: The planned external causes of Mr. Puppet’s actions mean that he doesn’t have free will. (Responsibility for Mr. Puppet’s actions lies with the scientists, not him: he’s just “a pawn”.)
Premise 2: If Mr. Puppet is unfree, then someone whose actions are equally determined by unplanned external influences also doesn’t have free will.
Premise 3: Our actions are determined by unplanned external influences, just as much as Mr. Puppet’s are determined by planned ones.
Conclusion: We don’t have free will. (“what is the difference between Mr Puppet and anyone else accused of a crime?”)
hard determinism, soft determinism, libertarianism
hard determinism: everything we do product of prior, no free will
soft determinism: even tho everything we do is a product of prior casual influences. free will
libertarianism: free will because actions NOT product casual actions
what if we do not have free will?
since the law presupposes free will can we never punish? greene and cohen say we can punish just it will not be based on deserts
roels neuroscientific data could play
Absolve of guilt altogether (NGRI)
not guilty reason of insanity
not know nature, not know what doing wrong, could not appreciate criminality, could not conform, act product of degect (dont deserve then shorter cant control then longer double edge)x
get someone lighter sentence (mitigation)
shift how we think about justifications
(diversion courts for ngri defenders?) neuroscience?)
bub and merkel 3 key factors differentiating violation from social interaction
does the affected conset
does it bring negative mental effects
is it direct or indirect?
EEG

electroencephalogram
less invasice-no surgery
extract signals from brain
a test that measures electrical activity in the brain using small, metal discs (electrodes) attached to the scalp. Brain cells communicate via electrical impulses and are active all the time, even during asleep. This activity shows up as wavy lines on an EEG recording.
emg

electromyogram
less invasive- no surgery
extract signals from brain
measures muscle response or electrical activity in response to a nerve's stimulation of the muscle. The test is used to help detect neuromuscular abnormalities. During the test, one or more small needles (also called electrodes) are inserted through the skin into the muscle.
fMRI

functional magnetic resonance imaging
signals from brain
less invasive-no surgery
measures the small changes in blood flow that occur with brain activity. It may be used to examine which parts of the brain are handling critical functions, evaluate the effects of stroke or other disease, or to guide brain treatment.
ECoG
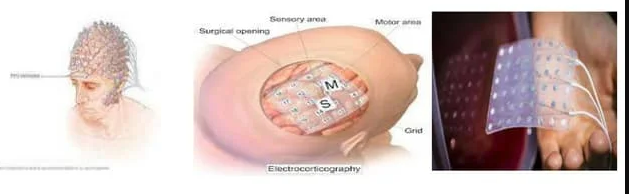
electrocorticogram
signals from brain
moderately invasive- skull surgery
An electrocorticogram (ECOG) is the tracing of the brain waves made by an apparatus used for detecting and recording brain waves made with the electrodes in direct contact with the brain.
a(DBS)
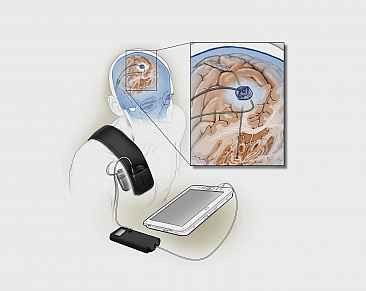
adaptive Deep Brain Stimulation
more invasive
signals to the brain/from the brain
The procedure involves implanting electrodes in the brain to deliver electrical stimulation using an implanted battery source called an impulse generator. It uses feedback from the brain itself to fine-tune its signaling.
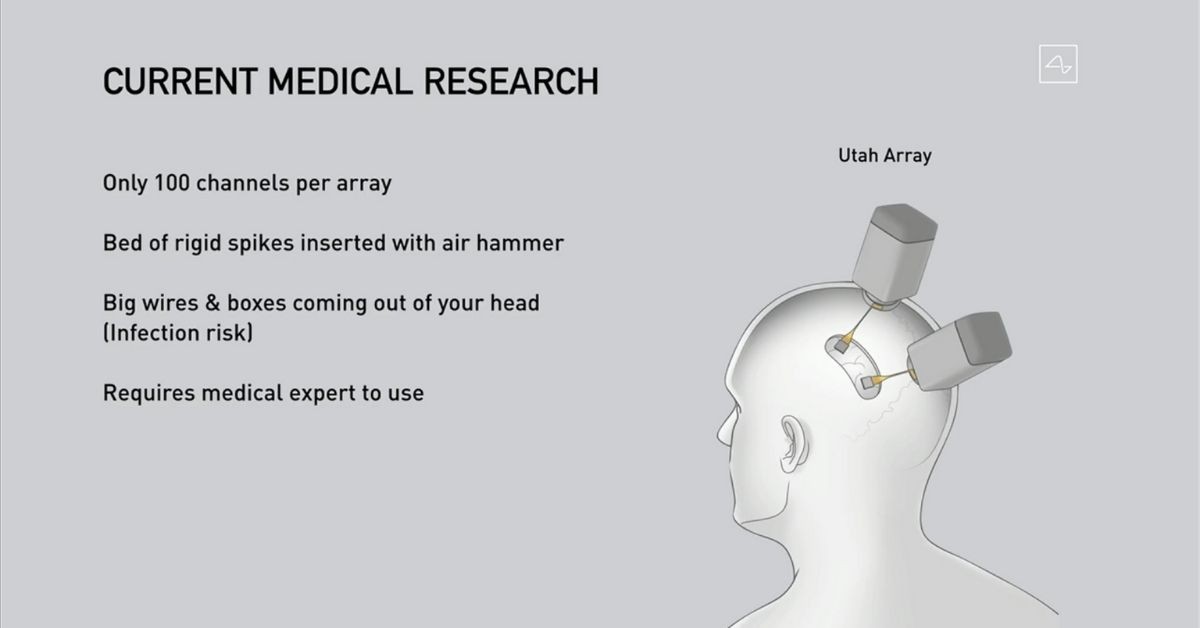
Single Neuron Recording
![<p>more invasive-brain surgery</p><p>extract signals from brain/send into brain</p><p></p><p><em>In neuroscience, single-unit recordings (also, single-neuron recordings) provide a method of measuring the electro-physiological responses of a single neuron using a microelectrode system. When a neuron generates an action potential, the signal propagates down the neuron as a current which flows in and out of the cell through excitable membrane regions in the soma and axon. A microelectrode is inserted into the brain, where it can record the rate of change in voltage with respect to time. These microelectrodes must be fine-tipped, impedance matching;<sup>[1]</sup> they are primarily glass micro-pipettes, metal microelectrodes made of platinum, tungsten, iridium or even iridium oxide.<sup>[2][3][4]</sup> Microelectrodes can be carefully placed close to the cell membrane, allowing the ability to record extracellularly.</em></p>](/flashcards/cardimage2/dbd3e92/264/8264842_back.jpeg)
more invasive-brain surgery
extract signals from brain/send into brain
In neuroscience, single-unit recordings (also, single-neuron recordings) provide a method of measuring the electro-physiological responses of a single neuron using a microelectrode system. When a neuron generates an action potential, the signal propagates down the neuron as a current which flows in and out of the cell through excitable membrane regions in the soma and axon. A microelectrode is inserted into the brain, where it can record the rate of change in voltage with respect to time. These microelectrodes must be fine-tipped, impedance matching;[1] they are primarily glass micro-pipettes, metal microelectrodes made of platinum, tungsten, iridium or even iridium oxide.[2][3][4] Microelectrodes can be carefully placed close to the cell membrane, allowing the ability to record extracellularly.
neuralink array
more invasice-brain surgery
extract signals from brain/send to brain
Neuralink device contains a chip and electrode arrays of more than 1,000 superthin, flexible conductors that a surgical robot threads into the cerebral cortex. There the electrodes are designed to register thoughts related to moti
negative neurorights
degensive wall against unwanted intrusions (faranahay calls them mental selfdetermination. zuk calls them mental integrity)
what distinguishes a violation of your mind from normal social interraction according to bublitz and merkel?
consent -how much understanding? when tacit consent asumed? what are default expectations? what if interventioin makes future consent more likely??
negative mental effects-where is
boundary between changing or impairing? what makes change negative? how do we determine when emotuon is innappropriate? what if intervenor thinks its appropriate?
direct or indirect/-why are direct impermissible (prima facie, against levy's idea that effects matter over form) direct violate demands of dignity.
five factors from bublitz and merkel specifying negative neurorights
(in)direct?
negative mental consequences?
consent?
designed to bypass control?
oritected by other rights?
bublitz and merkel define negative mental consequences:
reduce or impair cog capabilities
alter preferences, beliegs, behavioral dispositions, erasing memories, creating addictions
elicit inappropriate emotions
elicit clinicially identifiable mental injury
what is an invasion of privacy?
intrusion (form)
disclosure (content)
truth not defense but public interest is
(based on jurisprudence's evaluation of reasonable)
for your private information: what protects it?
do you rely on expectation people who know it will not shre it?
do you conceal it so snoopers must use intrusove methods?
do you hope?
answer
how do tech companies violate privacy
INTRUSIVE: hack phone, computer, email
DISCLOSE: share location, purchase, personal data etc
why can we not sue? because we conseneted (if we consented why do we still feel uneasy?)
why are we uneasy at the idea of tech companies using our data in ways we consent to?
we dont understand agreements
would we choose diff?
we dont have control over details of data use?
what would we choose if we did?
internet use non optional
whose fualt?
Is internet data harvesting:
unethical by companies
social problem but no companies fault
fair price for free internet?
answawer
faranahay worries about two main sorts of tech:
consumer EEG
neural interfaces
why is brain data uniwye? is it uniquely sensitive? just because it is new?
control
important
does farahany want to restrict research into neurotech for fear of pribacy info?
NO! She wants regulations, not restrictive bans
"impossible and limits insights to end suffering"
transparency
limit further processing
user-based controls
data processed locally
data continuously overwritten
standards against discriminatory use
what sort of privacy supports a democratic society?
lever
what sort of privacy are humans entitled to
s
if we're so worried about brain data. what do we do?
?
in waht ways does faranahay consider privacy apolitical
individuals, not structures/relationships
treats individuals as having the same interests
assumes value of privacy is shared (opposition is just greed)
lever feels that definitions of privacy reflect
different forms of society
“we have to concentrate on the value of privacy that is implicit in, or compatible with, democratic rather than undemocratic forms of government, and cannot assume that current forms of privacy adequately reflect the former.”
example of different privacy forms in voting
secret ballot
open voting
how can overexpansive privacy make oppression? how can limited privacy create oppression?
-rape, assault,
mackinnon on feminism
MacKinnon thus argues that fighting sexism requires willingness to openly discuss or intrude into “private” matters like sex, domestic violence or who does the dishes.
child controls as indicator of value judgement in privacy
private matter: parents authority. otherwise invading.
publis: in
what sort of privacy we prioritize is a _
value judgement
What sort of society do you want to live in?
(E.g. what sorts of power relations do you want between different groups of people?)
What conceptions of privacy support that sort of society?
How might rival conceptions of privacy disagree about how to regulate brain data
talk with
old lie detection methods
too useful at getting a FALSE confession
100% accurate lie detector. when should be used?
● When they consent?
● When they are an enemy?
● When they are under arrest?
● When a judge issues a warrant? \
● Never?
answer
cleared hurdle fMRI
identify brain areas differentialy active when lying
issues to fMRI brain
confounds: about lying or something similar. does it just affect effor? something concomitatn to lying but not indicatove or cuasal
base rates: if lying is rare, tests may be innacurate with proper creto. false positives.
individual variation: every brain diffenr'. changed with age and psychiatric conditions
task variation (what sorts of lies have different neural signatures)
countermeasures-s=the stayhe oeioke look for howuo. subjects lie as instructed on interpersonal things
biggest hurdle to making fMRI lie-detection useful
detecting confounds instead of lying
base rates throwing off numbers- false
individual variation
task variation between training lies and irl lies
countermeasuers being developed
truth is a good goal ehwn everyone's interests __; when people's interests are __, truth helps some and hurts others
line up (cooperate)
innocent and the police want to know who did it
in conflict (antagonistic)
innocent but police want to pin it on someone and go home
there have been _ attempts to introduce fmri detection data into us courts. all have been _ byjudges
3
rejected
in what situations should we permit a (an assumed high reliability) lie detector be used?
● Insurance claims?
● Job interviews?
● Police interrogation?
● Court cases?
● Romantic relationships?
DBS

deep brain stimulation
more invasive-brain surgery
send signals into brain
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves implanting electrodes within areas of the brain. The electrodes produce electrical impulses that affect brain activity to treat certain medical conditions. The electrical impulses also can affect cells and chemicals within the brain that cause medical conditions.
The amount of stimulation in deep brain stimulation is controlled by a pacemaker-like device placed under the skin in the upper chest. A wire that travels under the skin connects this device to the electrodes in the brain.
Cortical Stimulation Device
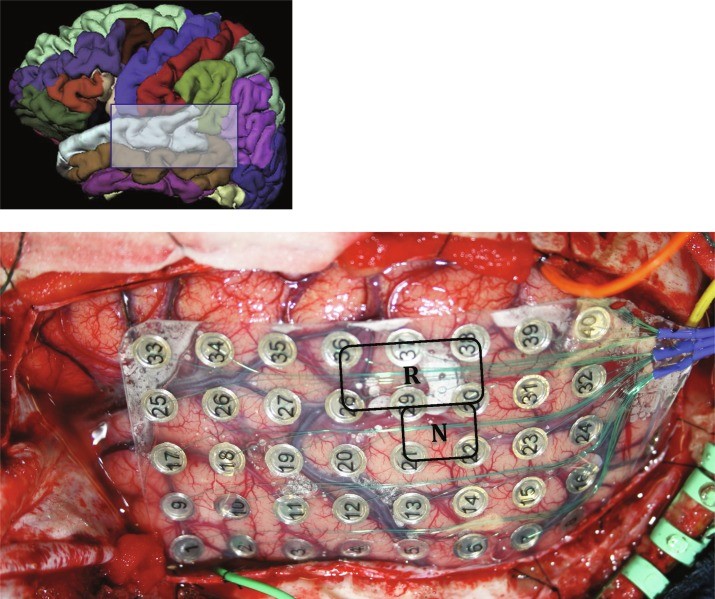
moderately invasice (skull surgery)
send signals into brain
Cortical stimulation is an emerging treatment option for a variety of neurological disorders. In contrast to deep brain stimulation where electrodes are implanted deep in the brain, cortical stimulation uses electrodes that are placed on the surface of the brain.
TMS
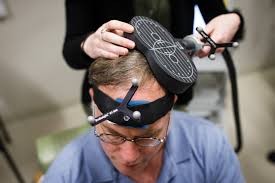
trans-cranial magnetic stimulation
send signals into brain
less invasive, no surgery
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain to improve symptoms of major depression. It's called a "noninvasive" procedure because it's done without using surgery or cutting the skin. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), TMS usually is used only when other depression treatments haven't been effective.
TES
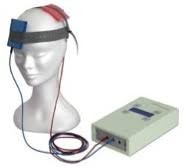
transcranial electrical stimulation
less invasice no surgery
send signals into brain
noninvasive brain stimulation technique that passes an electrical current through the cortex of the brain in to alter brain function
sensory substitution device
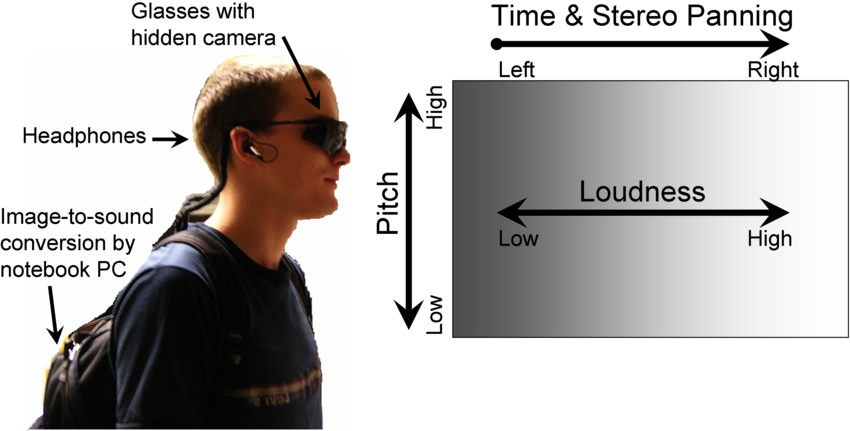
less invasive no surgery
send signals into brain
Generally, a camera or a microphone is used to collect visual or auditory stimuli that are used to replace lost sight and hearing, respectively. The visual or auditory data collected from the sensors is transformed into tactile stimuli that are then relayed to the brain for visual and auditory perception.
3 applications for BCI
sensory prostheses
link camera
motor prosthesses
robot arm
brain to brain
link input with an output in another brain
DARPA
jebari autonomy argument
happier workers, transformation.
]as DBS becomes more widespread, as this paper has concluded is to be expected, costs and risks will plunge and in a longer perspective, productivity-enhancing DBS seems like a real prospect.
if using BCIs to transform employees how does this differe from other ways of acquiring or eliminating some psychological trait?
structure of the addicted police argument-jebari. which premise most vulnerable to obkection? how persuasive?
the idea that dbs is equivalent to conventional therapy and antidepressents?
arm matic bionic police
he loses his job if he does not accept the arm matic. was he coerced into giving up part of his autonomy?
what do we think of this ethics scenario?
How does LTP work?
connections strengthened between neurons that fire together, strenghten long term memory
depends on hippocampus
strengthened by emotional arousal
What does proponal do?
effects emotion on LTP
reduced emotional impact of memory. doesn't directly affect recall but could on balance affect recall more likely to forget without emotional anchor
usually used for PTSD
are there any memories you'd change if you could?
s
How do clinicians or patients or first responders make the prospective judgement that an event warrants preemptive memory blinting? risks of wrong?
d
blublitz and merkels crimes against minds and the presidents councils worries about memory mods
criminal erase victims memories
societal value of memory defined by pcb
do we have an obligation to remember things? as victims? perpetrators? leanring from mistakes?
which of PCB's worries is most reasonable or seriosu?
●Judging when to administer propranolol clinically
● Making soldiers callous and unfeeling
● Blocking guilt from wrongdoing
● Numbing victims and witness’s memories of wrongdoing
● Victims and witnesses numbing their own memories
What sorts of emotional pain seem like important parts of a full life, and which don’t? Is pain essential? is PCB right that pain is important?
failure
torture
love
what about emotional pain is PCB worried about
numbing, being empty, not alive
kolber thinks the pcb worries are
unjustified aversion to managing trauma
do you value self knowledge?
d