Bacterial growth requirements
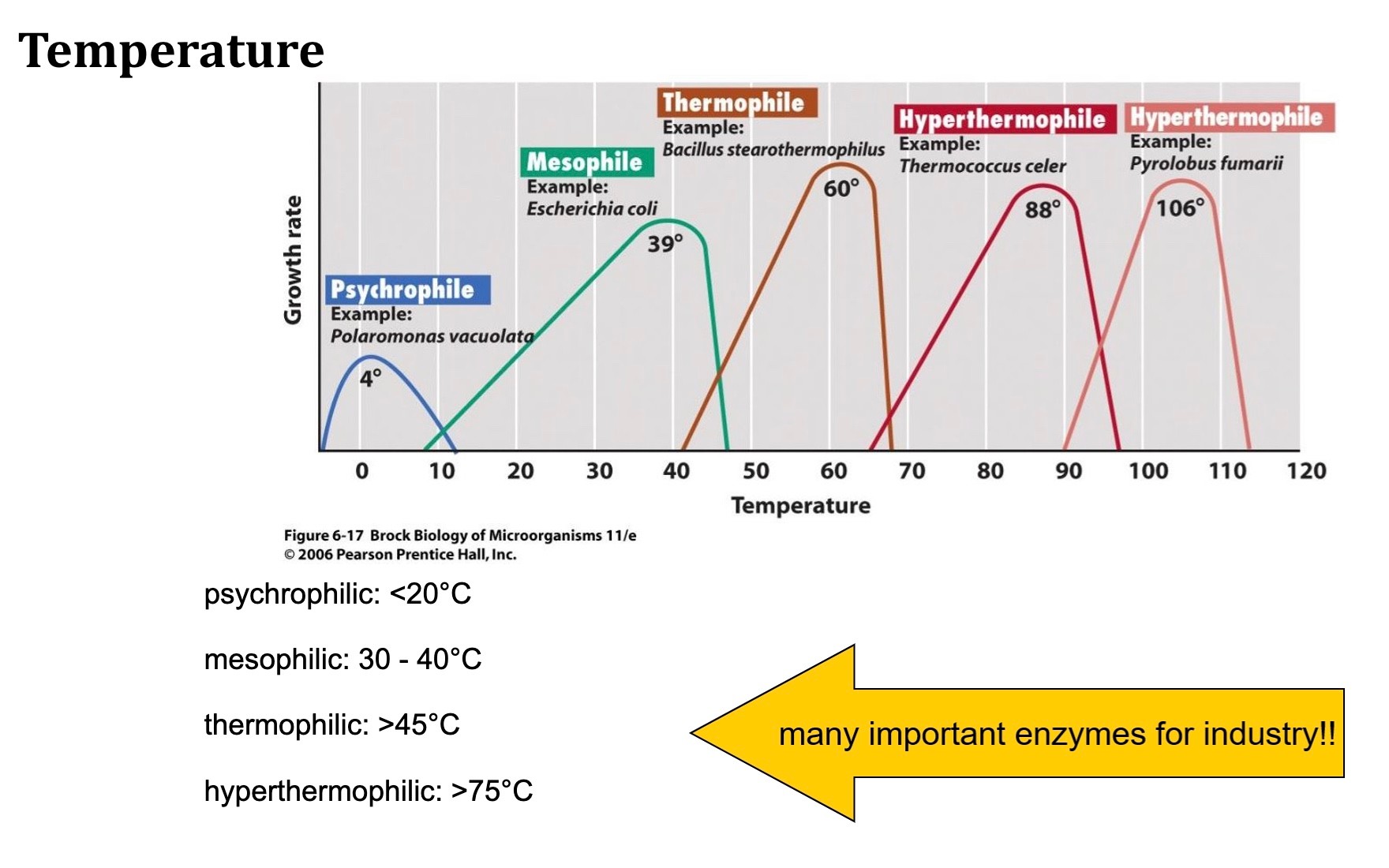
-temperature
-pH
-oxygen
-osmotic pressure
-hydrostatic pressure
-light
-nutrients
How to maintain desired temperature of medium?
incubator/shaking incubator
How to adjust the pH of the medium?
buffers
oxygen classes of microorganisms
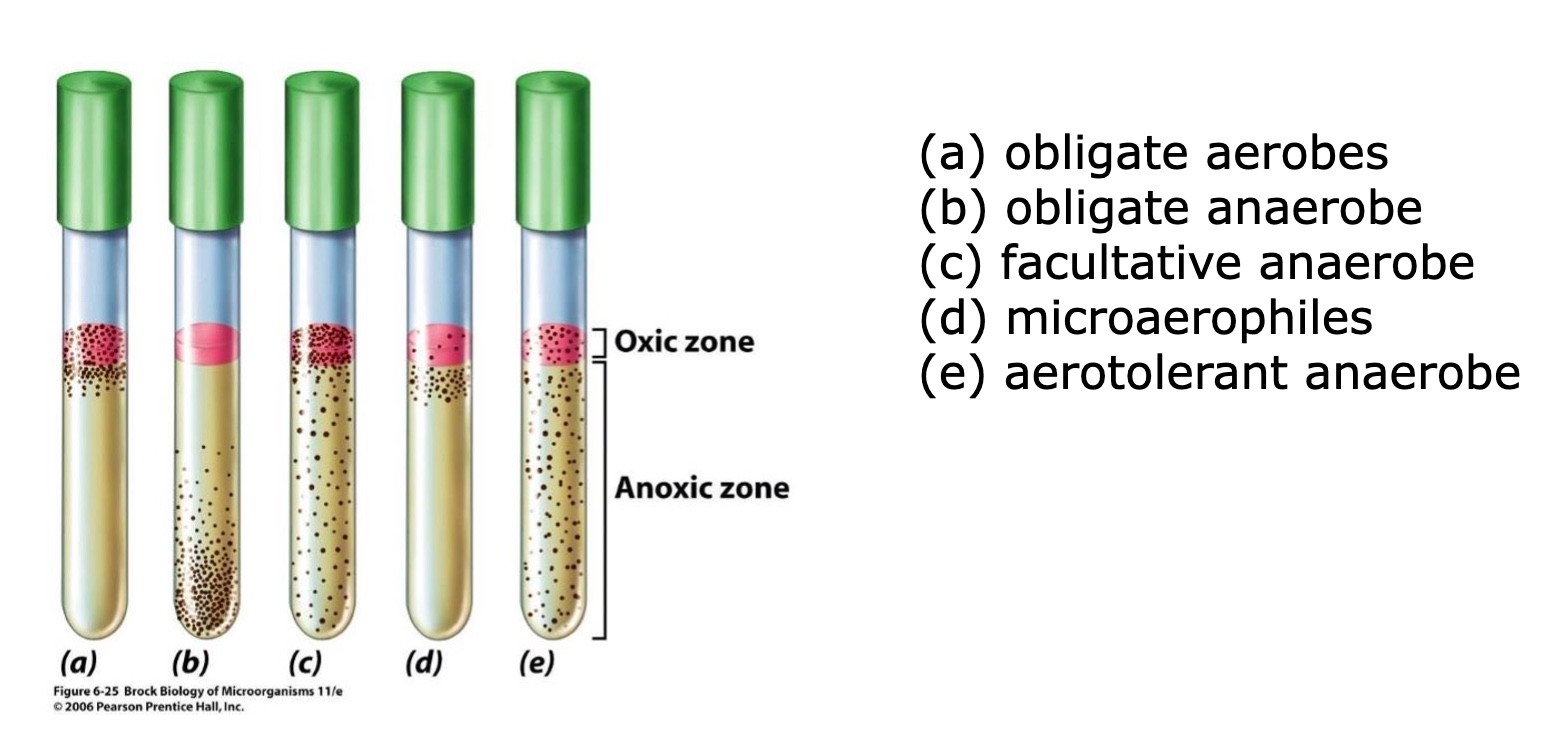
-obligate aerobe
-obligate anaerobe
-facultative anaerobe
-microaerophiles
-aerotolerant anaerobe
obligate aerobe
an organism that can use O2 in respiration, require O2 some
anaerobe
an organism that cannot use O2 in respiration and whose growth is typically inhibited by O2
facultative anaerobe
with respect to O2, an organism that can grow in either its presence or absence
microaerophiles
an aerobic organism that can grow only when O2 tensions are reduced from that present in air
aerotolerant anaerobe
a microorganism unable to respire O2, but whose growth is unaffected by it
temperature classes of microorganisms
pasteurisation
the heat treatment of milk or other liquids to reduce its total number of microorganisms
where do you grow anaerobes?
CO2 incubators
obligate anaerobe
an organisms that cannot grow in the presence of O2
osmotic pressure
the minimum pressure applied to a solution to stop the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane
bacterial growth factors
-vitamins
-amino acids
-purines and pyrimidines and their precursors
medium (plural: media)
any solid or liquid specially prepared for bacterial growth
media state of matter
liquid:
-broth
solid:
-plates
-tubes
-slants
what can be used for solidification of media?

-Agar
-Gelatine
colony
millions of bacteria formed from one bacterium
types of growth media

special growth media types
- selective media
- enrichment media
- differential media
selective media
suppression of unwanted bacteria and encouraging desired microbes
enrichment media
similar to selective media but designed to increase numbers of desired bacteria to detectable levels
differential media
allows the differentiation of desired microbes from others eg:by color reaction
How many cells will I have after certain number of generations?
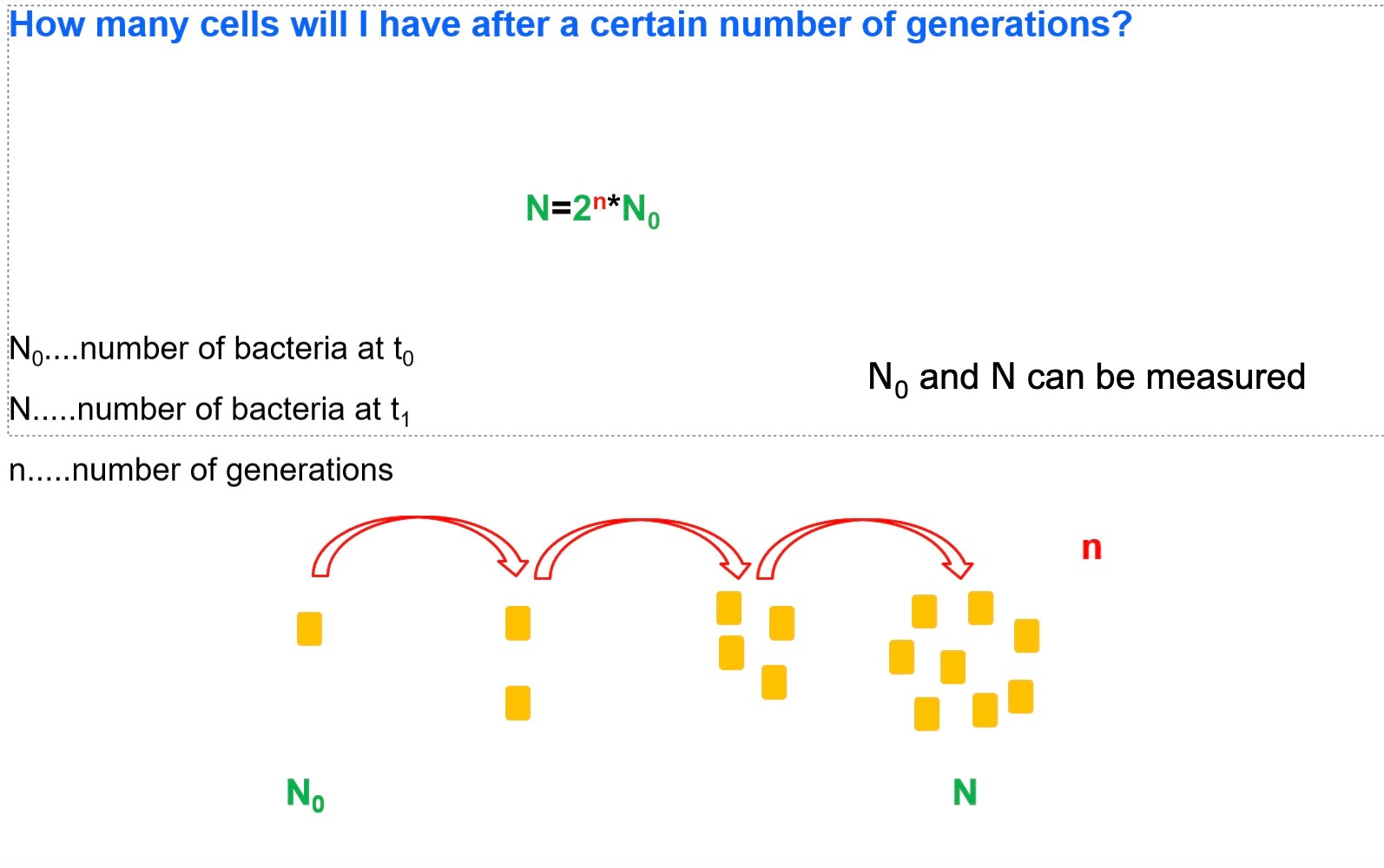
How many generations did I haven this time?
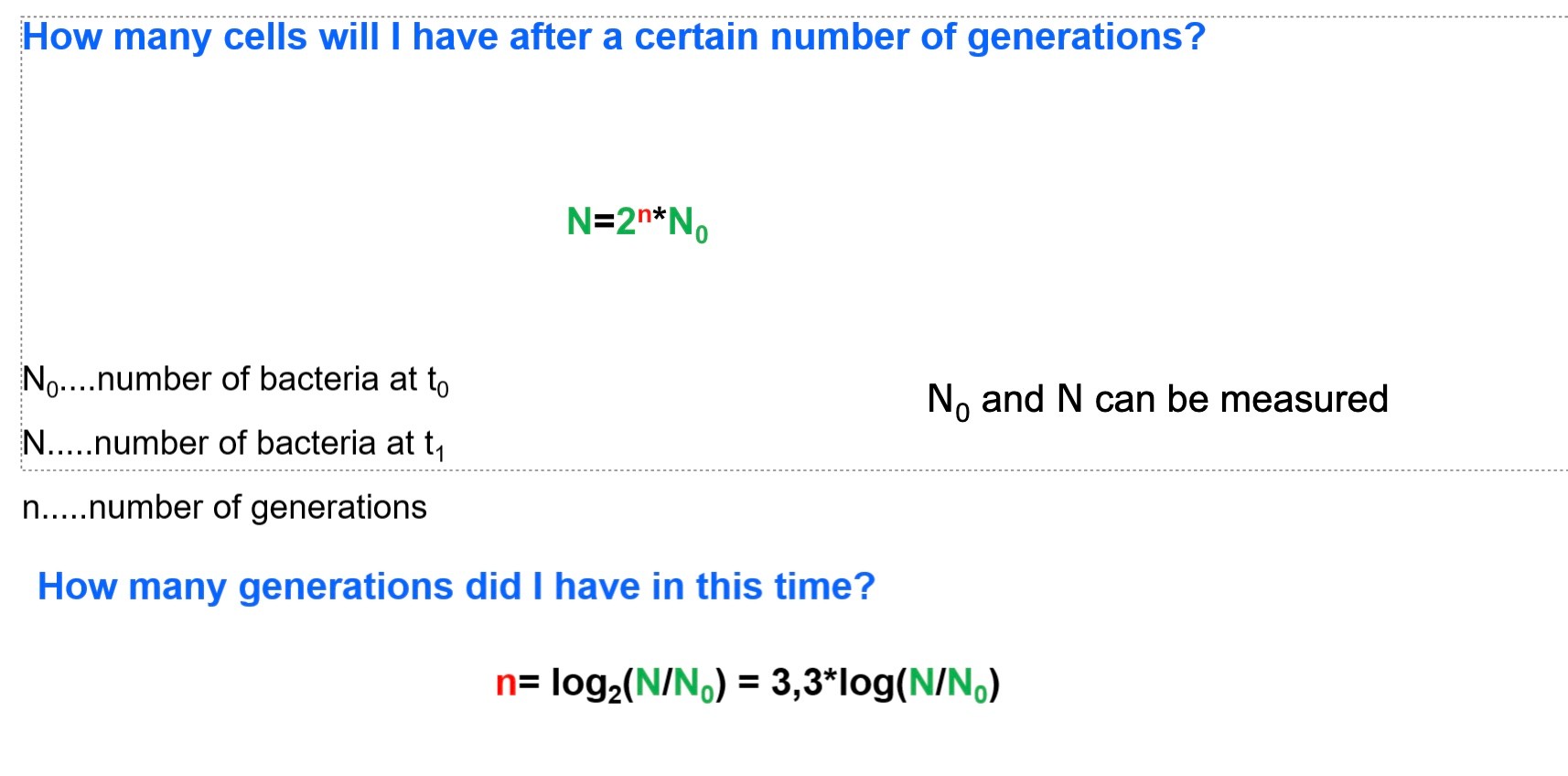
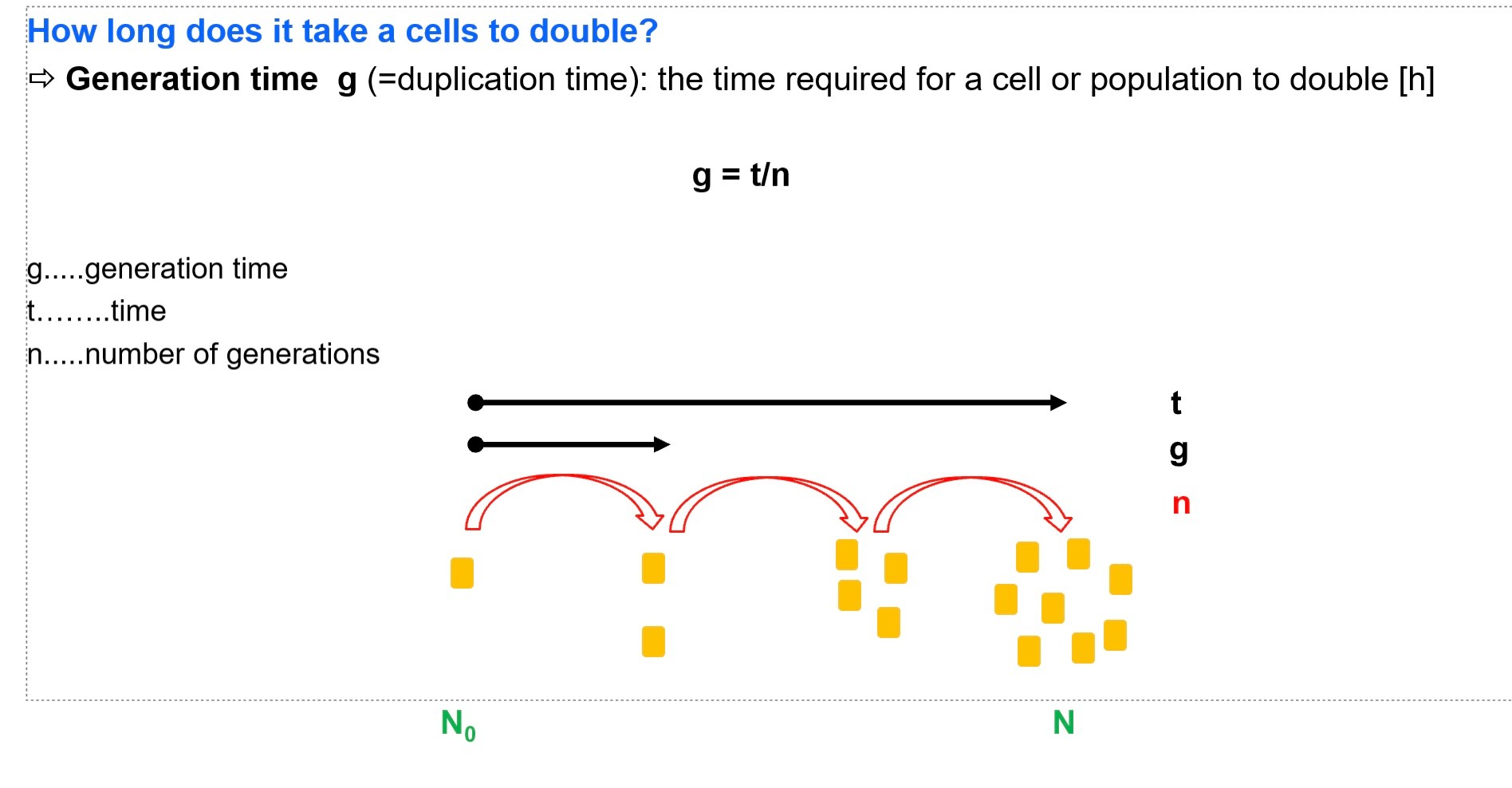
How long does it take for cells to double?
How long does my culture grow?
How many cells will I have after a certain time?
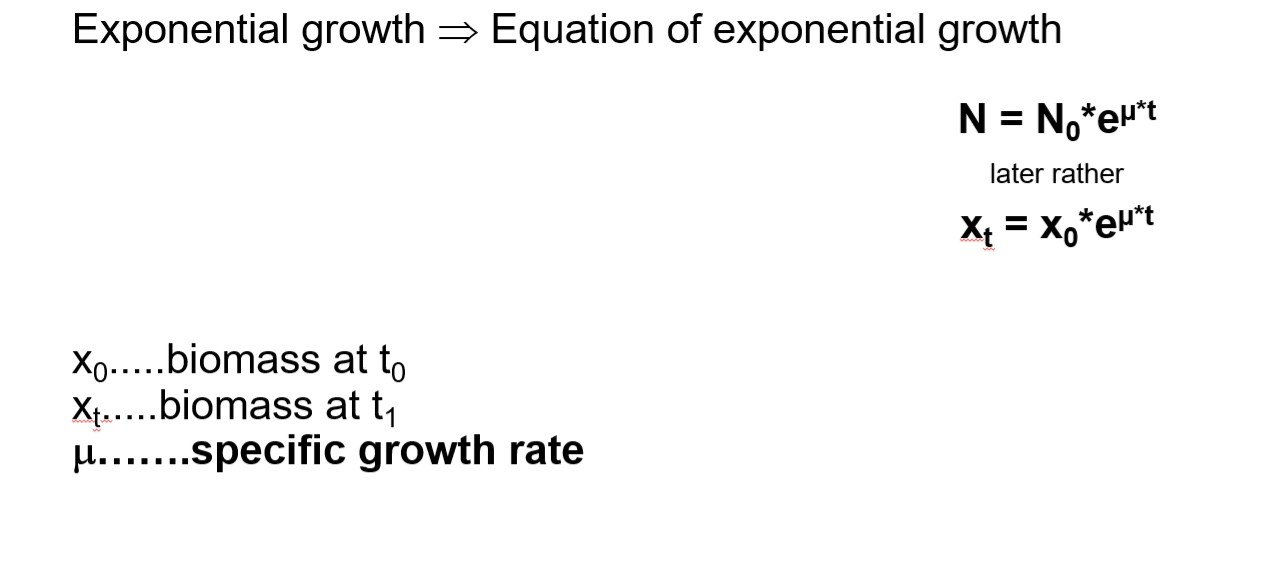
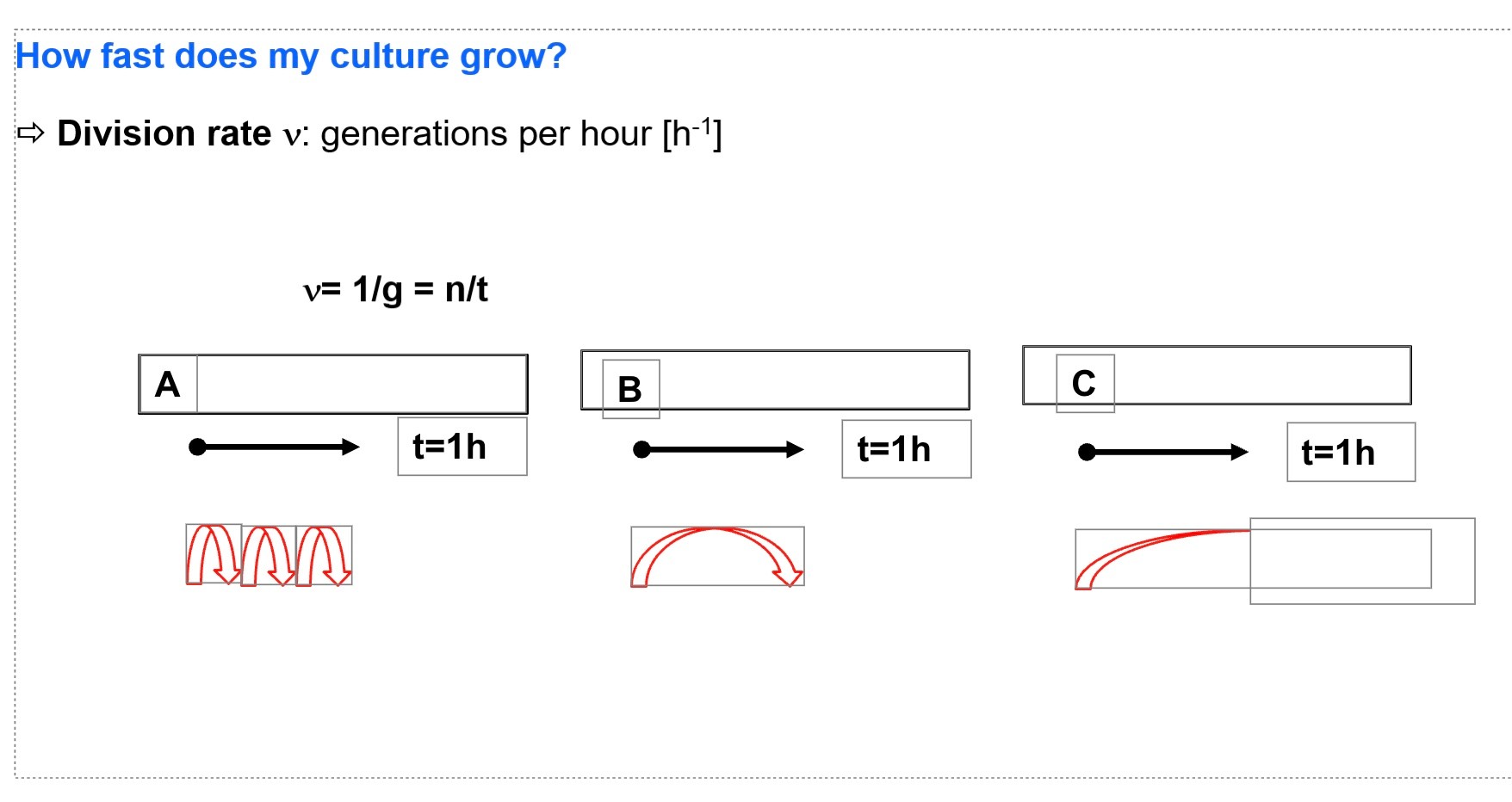
How fast does my culture grow?

Phases of growth
-lag phase: little or no cell division, cells are accommodating to the new environment
-log phase: exponential growth
-stationary phase: a nutrient runs outer waste products accumulate
-death phase: exponential death rate
batch culture
a closed-system microbial culture of fixed volume
batch culture types
-fed-batch culture
-continuous culture
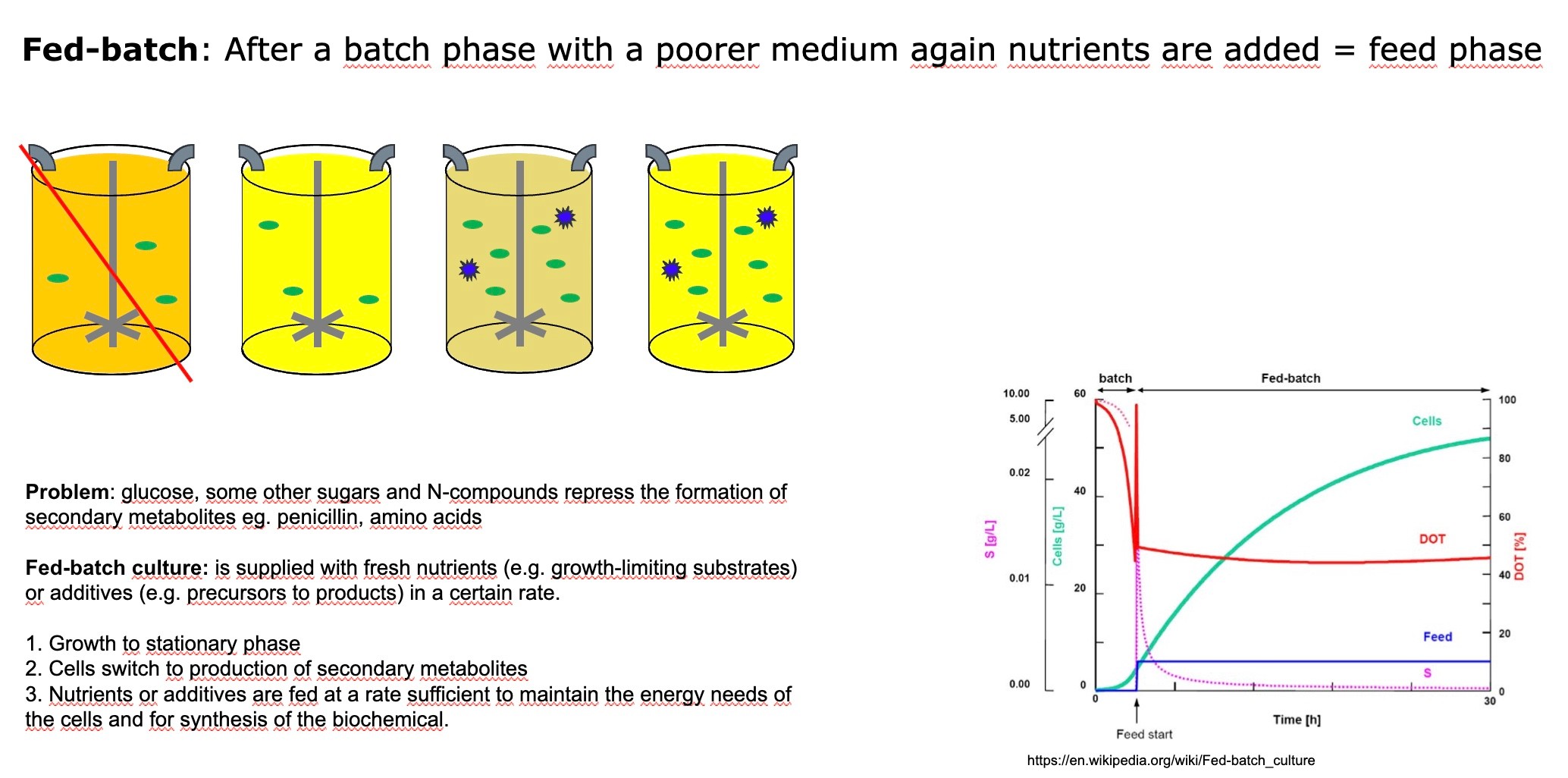
Fed-batch
continuous culture
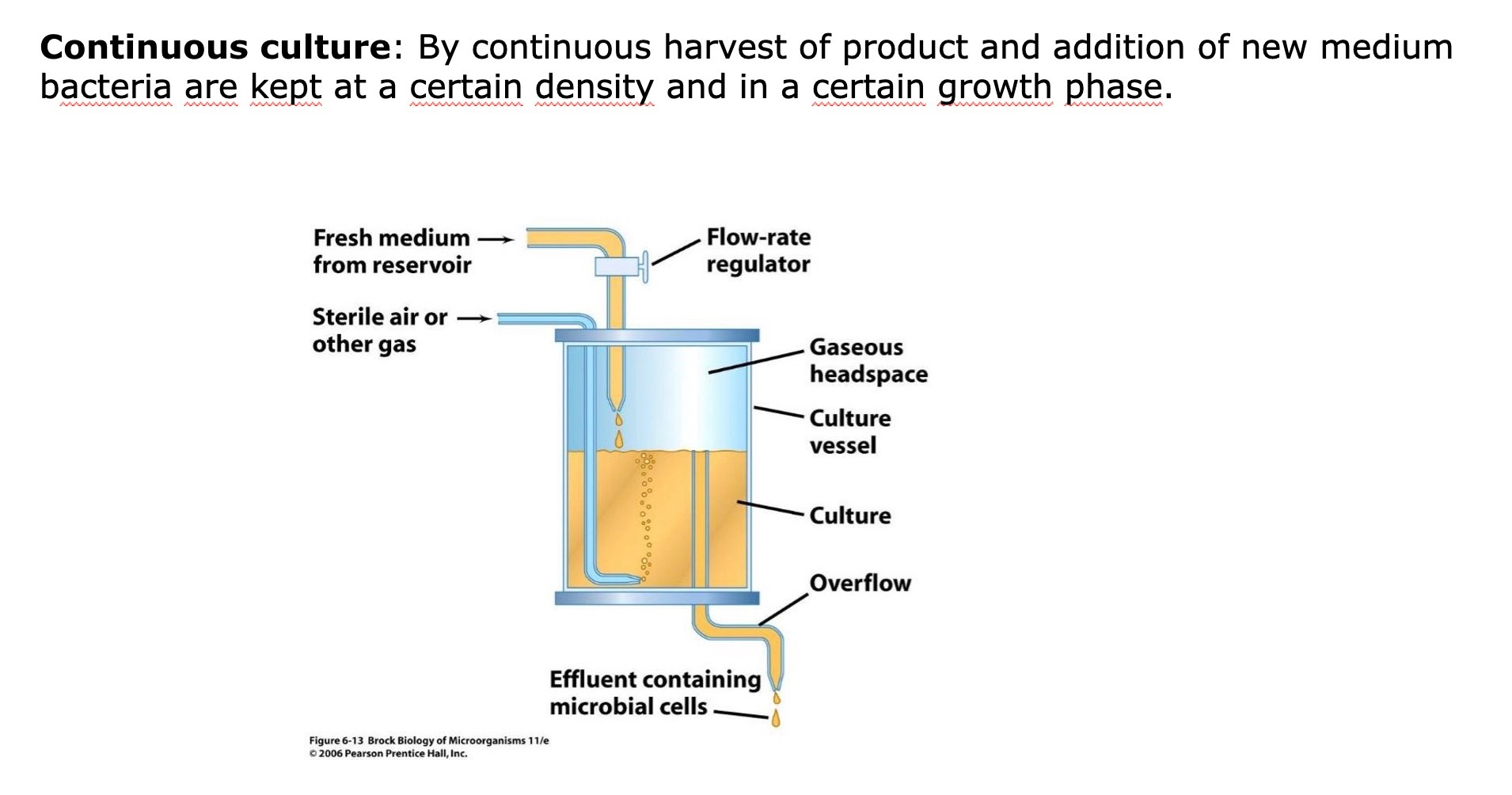
chemostat
a device that allows for the continuous culture of microorganisms with independent control of both growth rate and cell number
autoclave
a sealed heating device that destroys microorganisms with temperature and steam under pressure
bactericidal agent
an agent that kills bacteria
bacteriostatic agent
an agent that inhibits bacterial growth
biofilm
an attached polysaccharide matrix containing bacterial cells
exponential growth
growth of a microbial population in which cell numbers double within a specific time
generation time
the time required for a population of microbial cells to double
growth
an increase in cell numbers
MIC
minimum inhibitory concentration: the minimum concentration of a substance necessary to prevent microbial growth
plate count
a method of counting viable cells, the number of colonies on a plate is used as a measure of cell numbers