Forming
Uncertainty about purpose, structure, and leadership
Storming
Intragroup conflict as members resist constraints
Performing
Group is cohesive with strong group identity
Norming
Group fully functional and working toward goals
Adjourning
For temporary groups: breaking up
Role identity
alignment of attitudes andbehavior with given role
Role perception
our view of how we’resupposed to act in a given situation
Role expectations
how others believe youshould act in a given situation
Role conflict
conflict experienced whenmultiple roles are incompatible
Norms
Acceptable standards of behavior within agroup that are shared by the group’s members
Deviant Workplace Behavior
Voluntarybehavior that violates significantorganizational norms and, in doing so,threatens the well-being of the organization orits members
Cohesiveness
The degree to which membersof the group are attracted to each other andmotivated to stay in the group
Effectiveness
.Accuracy – group is better than average individualbut worse than most accurate group member.Creativity – groups are better.Speed – individuals are faster
Efficiency
Groups are generally less efficient
Groupthink
A deterioration of individual’smental efficiency and moral judgments as aresult of group pressures
Groupshift
Groupdiscussions leadmembers to assumemore extreme positions
Brainstorming
Generates a list of creative alternatives whilewithholding criticism
Nominal Group Technique
Restricts discussion during the decision-makingprocess to encourage independent thinking
Task Conflict
Helps team perform better (good)
Interpersonal conflict
I don't like you you don't like me (bad)
Problem solving
solving problems
Self managed
everyone in charge of everyone else
Cross Functional
team comprised of people from different departments
Virtual Teams
Connected through technology
Traditional View
All conflict is harmful and mustbe avoided
Interactionist View
Conflict is encouraged to preventgroup from becoming stale
Managed Conflict View
Conflict is inevitable but weshould focus on productiveconflict resolution
Intentions
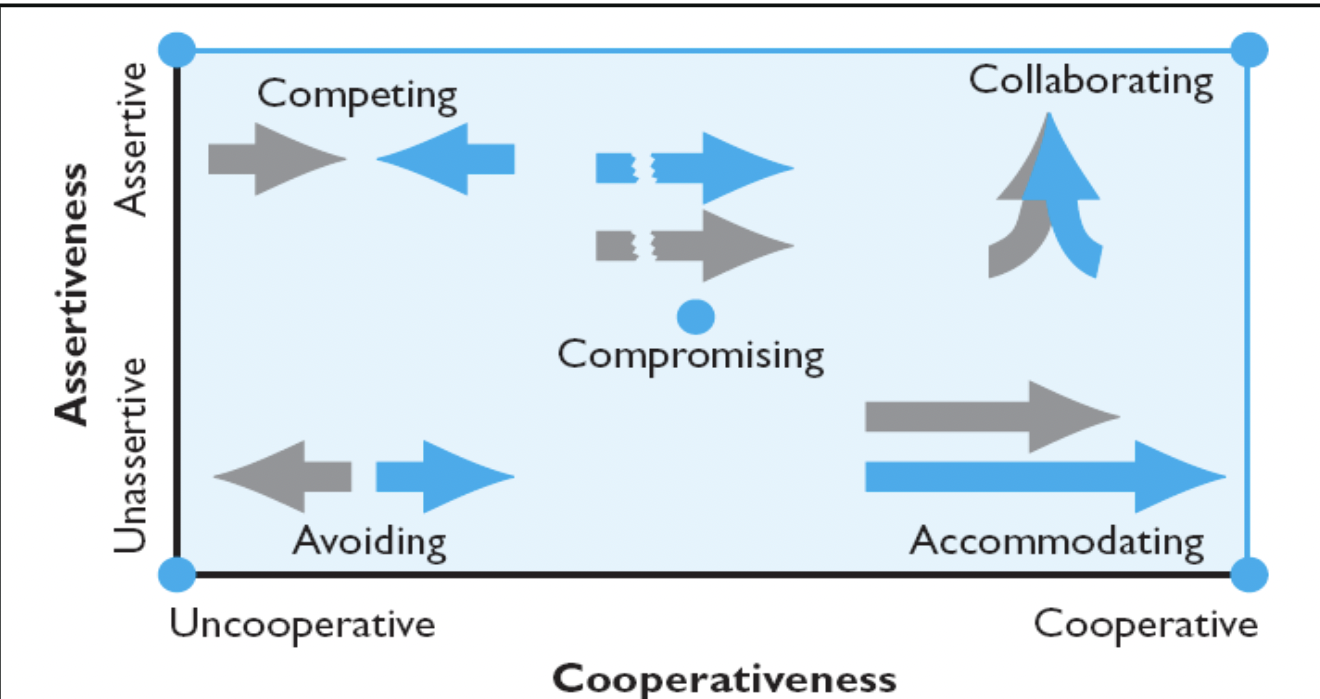
The decision to act in a given way
Leadership
The ability to influence a grouptoward the achievement of a vision or a set ofgoals
Trait theory
focuses on personal qualities andcharacteristics
Initiating Structure
Attempts to organizework, assign roles, andgoals (productivity
Consideration
Concern for followers’comfort, well-being,status, and satisfaction
Contingency theories
attempt to match leadershipstyle with work contextbecause one leadership styledoes not work in everysituation
Transformational leaders
Inspire followers to transcend their own self-interests for the good of the organization
Dependency
Based on the available alternatives(control) and their desirability (significance)
Coercive Power
Complies from fear of the negative results
Reward Power
Complies due to desire for positive benefits
Legitimate Power
From the formal authority to control and useorganizational resources
Expert
Influence wieldedas a result of expertise,special skill, or knowledge
Referent
Based onidentification with a personwho has desirable resourcesor personal traits
Politicking
Twisting facts to support one’sown goals and interests
Impression Management
The process by which individualsattempt to control the impression othersform of them