Kinesiology
study of movement through the application of anatomy, physiology, physics and mechanics.
biomechanics
study of force exerted on an object.
Kinematics
branch of mechanics describing movement of the human body without consideration of the forces or torque needed to produce.
osteokinematics
movement of bones in space about a joint
EX: flexion and extension
arthrokinematics
movement of bone surfaces during joint movement
EX: roll and glide
kinetics
branch of mechanics describing how forces or torque affect the body
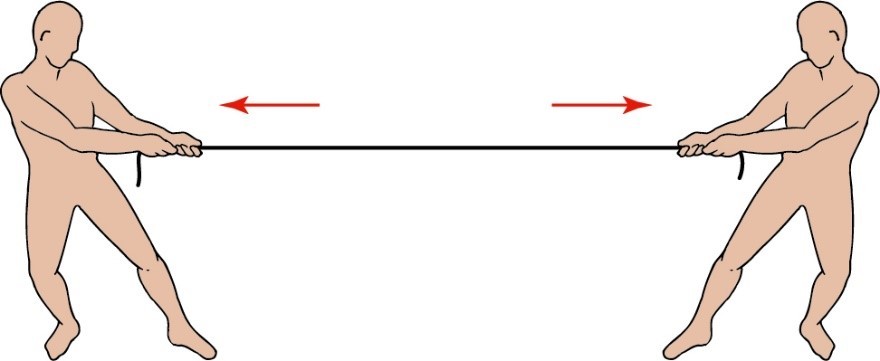
Linear Forces
Two or more forces acting along the same line
* can be in the same or opposite direction but same line
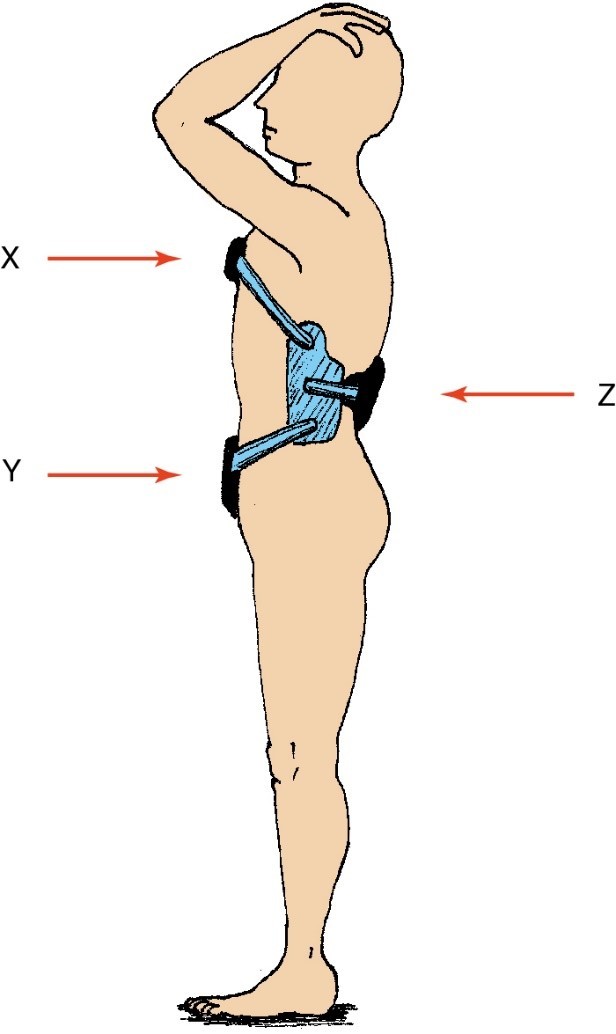
Parallel Forces
Occur in the same plane and in the same or opposite direction
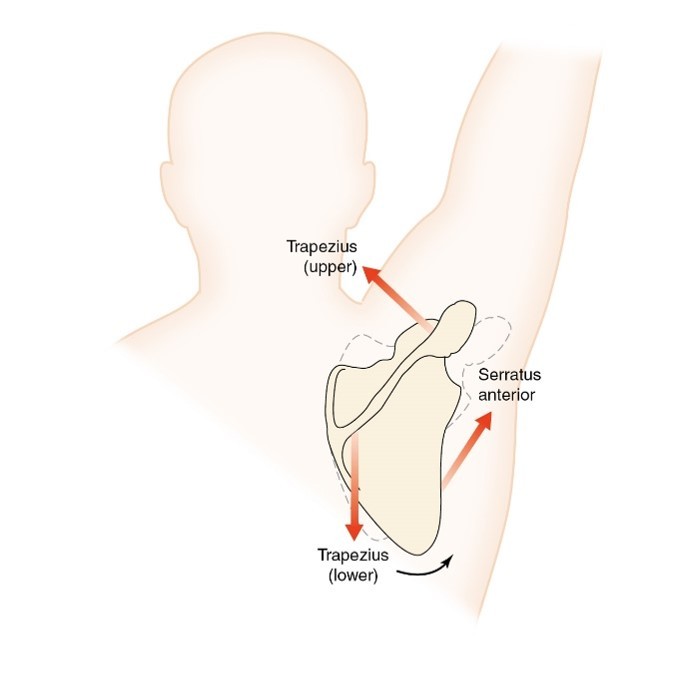
Force couple
.Specific configuration of parallel forces
.Two or more forces act in different directions
.produces clockwise or counterclockwise rotation.
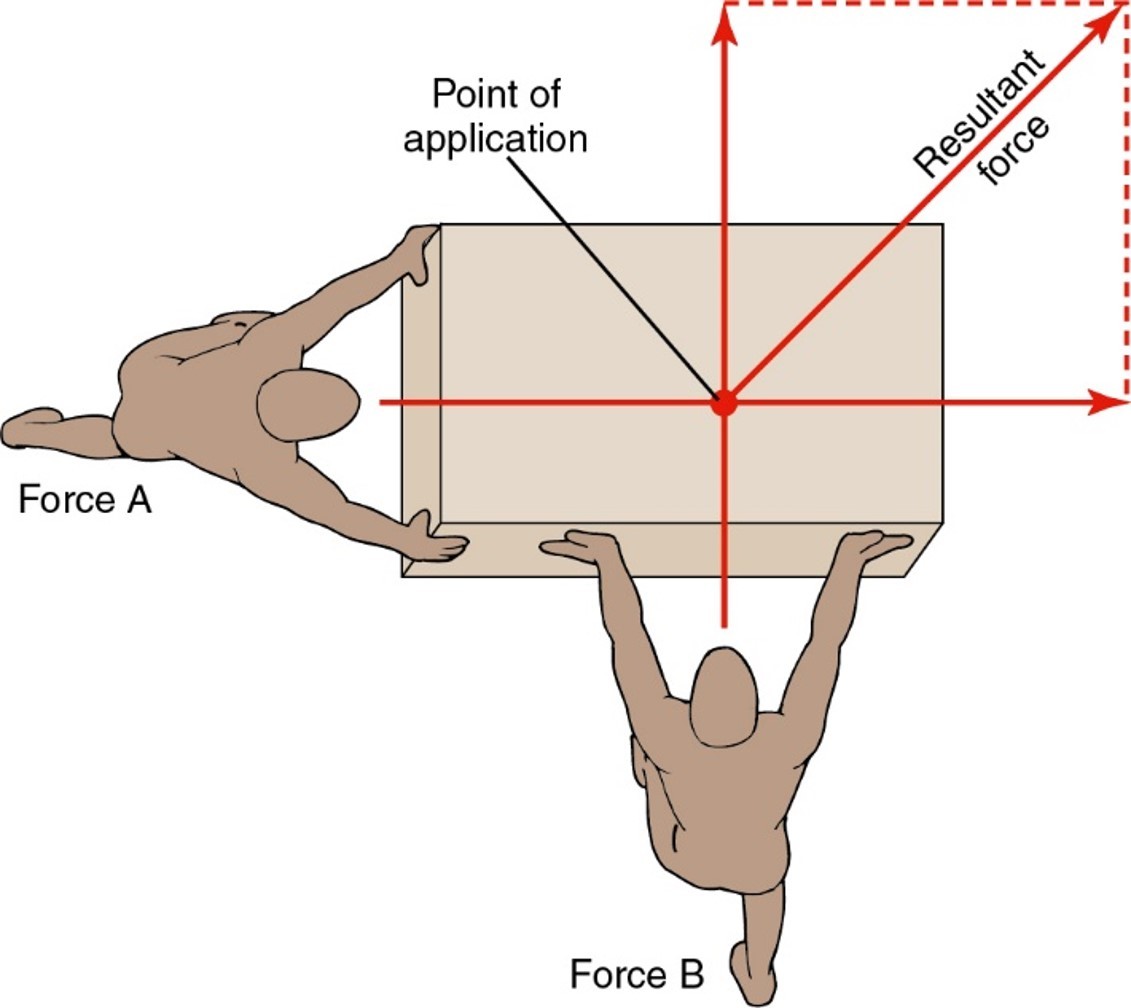
Concurrent forces
.Two or more forces acting on an object
.Push or pull in different directions
.Resultant force vector
-Represents the sum of the magnitudes and directions of each individual force vector
-Indicts the magnitude and direction of the movement
-Results from the application of all the forces acting on the object
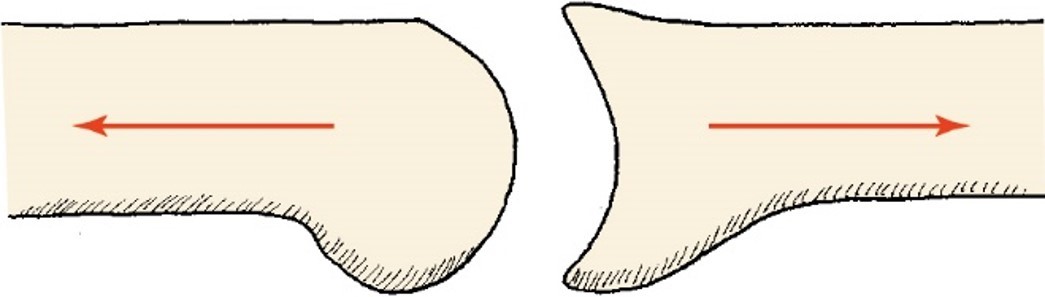
Traction
joint surfaces pull apart
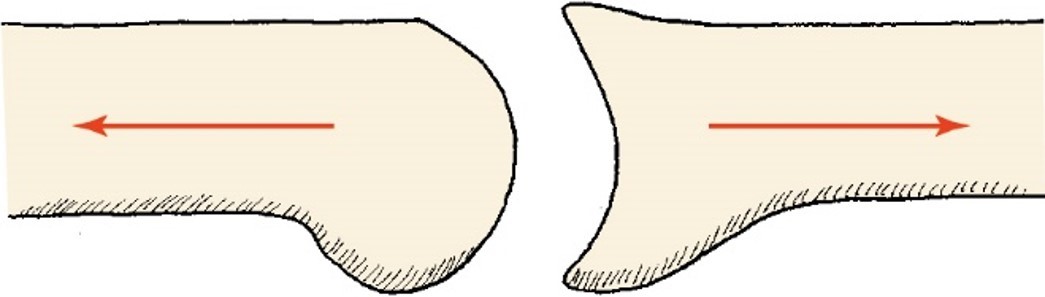
Compression
joint surfaces push closer tg
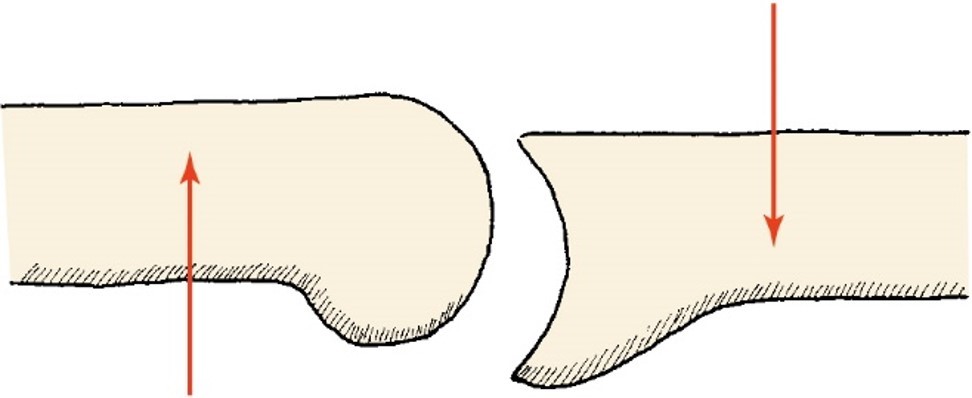
Shear
gliding motion of the joint surfaces
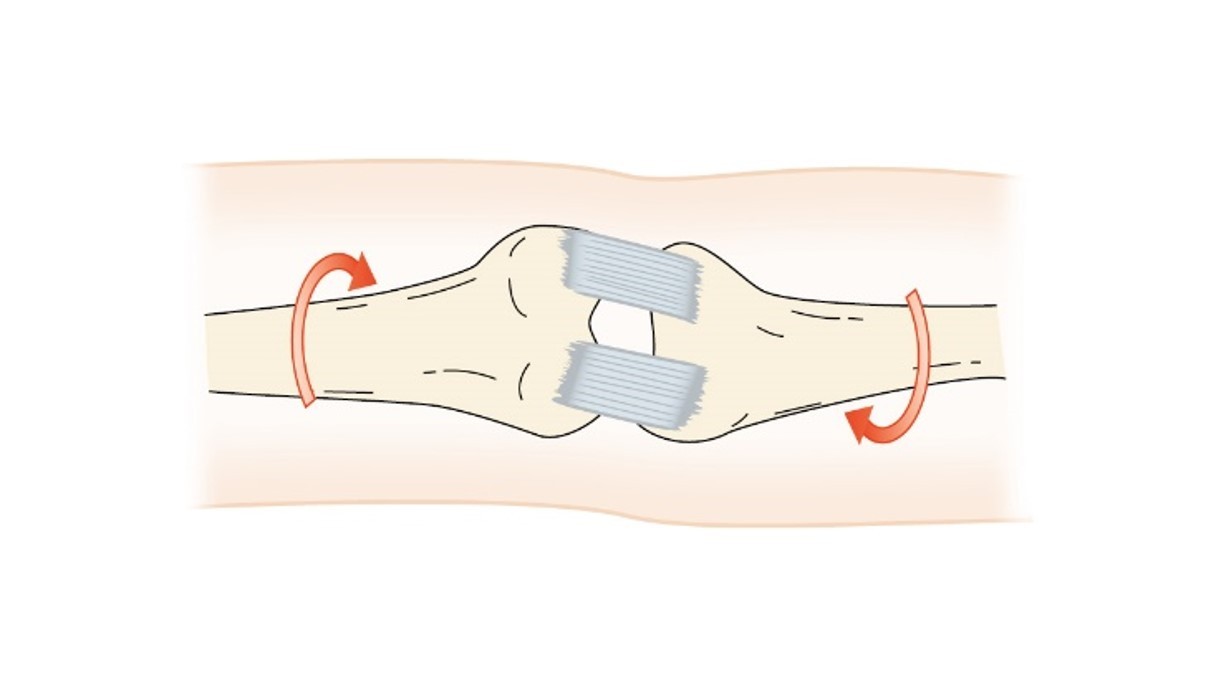
Torsion
two opposing forces twisting within an object in opposite directions
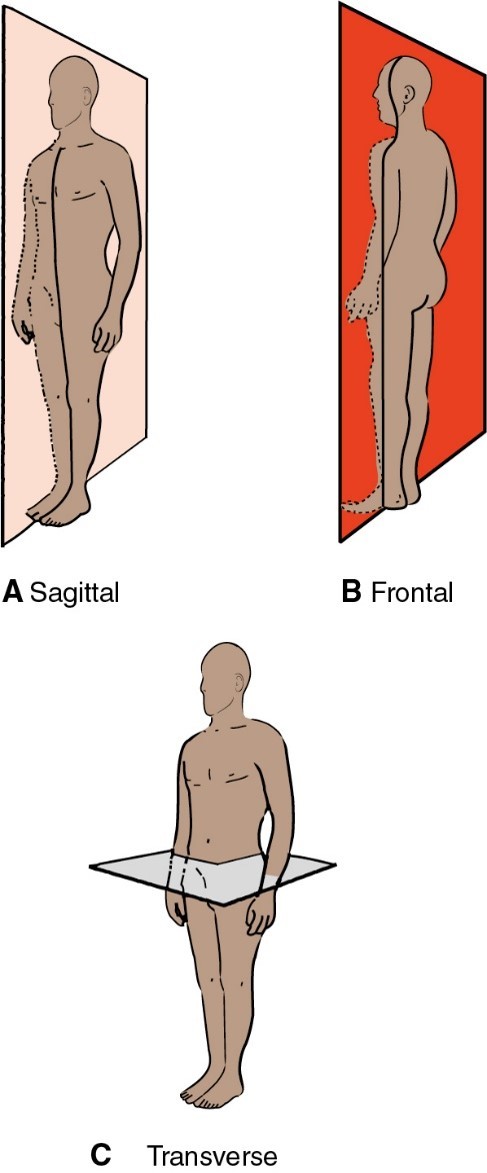
Planes
Sagittal
•vertically anterior to posterior
•divides body into right and left
Frontal
•vertically side to side divides
•body into anterior and posterior
Horizontal
• horizontally divides body into
• superior and inferior
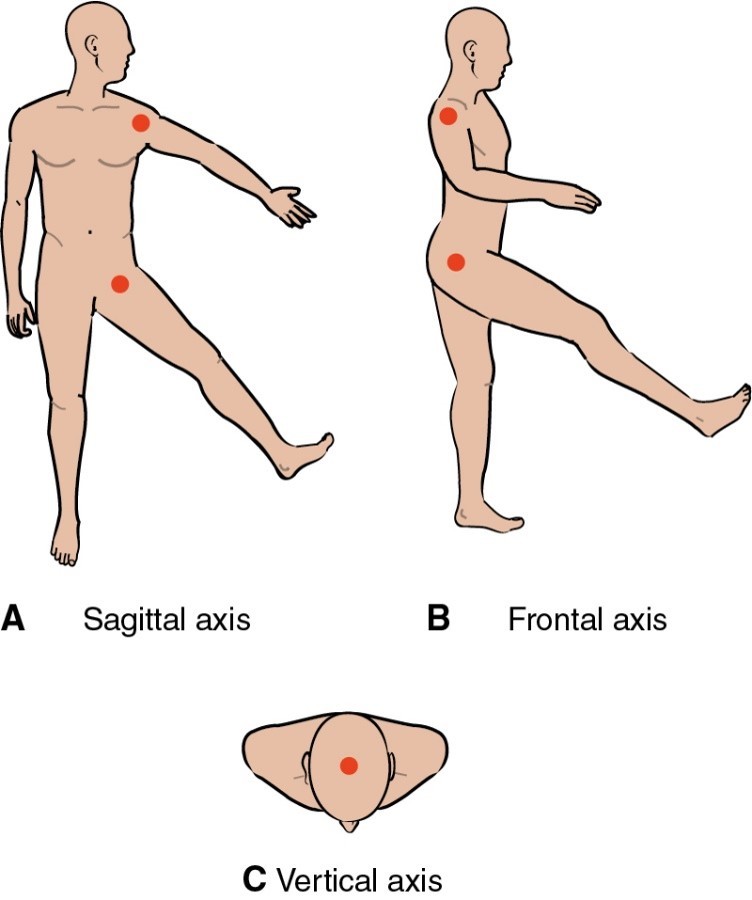
Axes
Sagittal
•anterior to posterior
Frontal
•side to side
Vertical
•superior to inferior
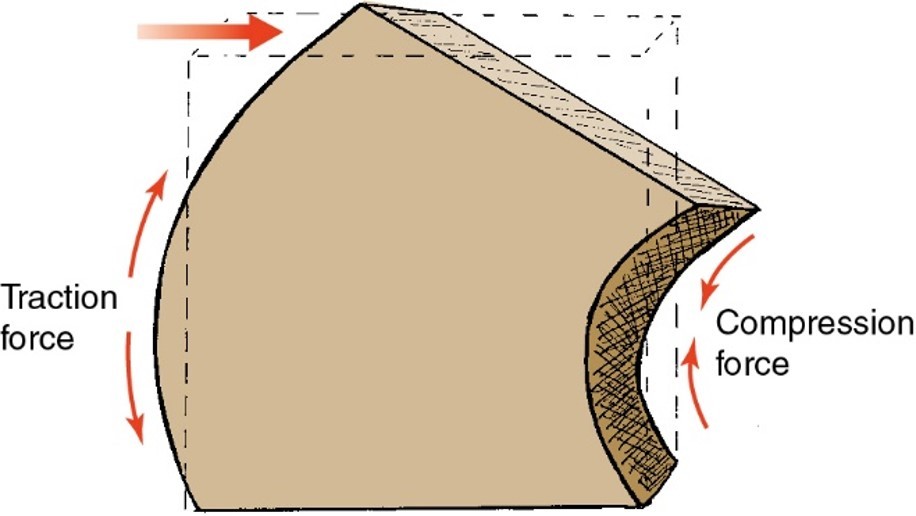
Bending
.force is not applied at the central axis of an elongated object, causing the object to bend.
-Concave surface one side and convex surface on other side
-Compression on concave side and traction on convex side
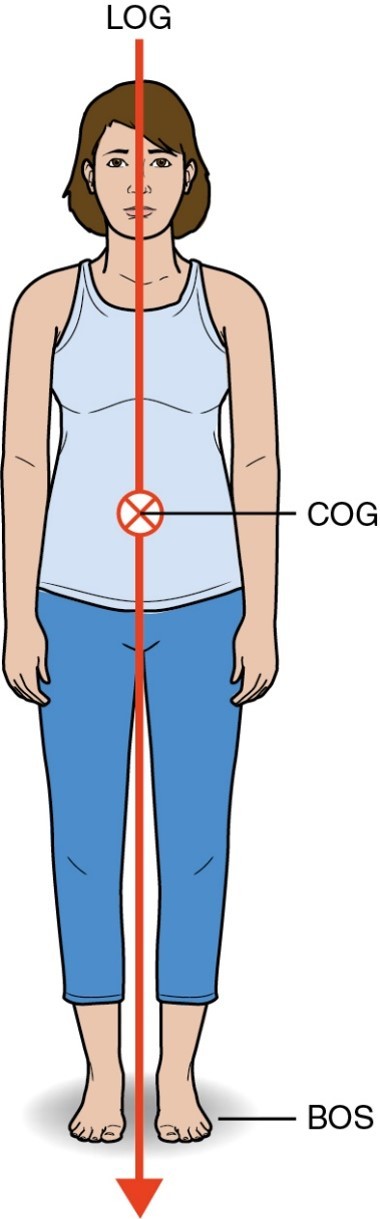
What makes an individual more or less stable?
More stable
Large BOS
Wide BOS in direction of disturbance
COG lower to BOS
COG centered in BOS
Greater mass
Greater friction between object and BOS
Less stable
Small BOS
Narrow BOS in direction of disturbance
COG higher to BOS
COG close to margin in BOS
Lesser mass
Lesser friction between object and BOS
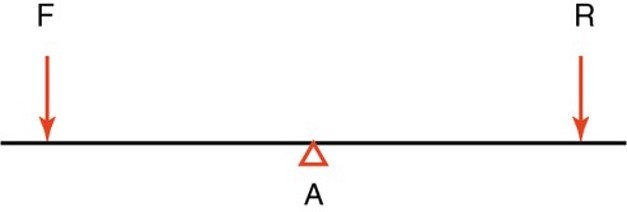
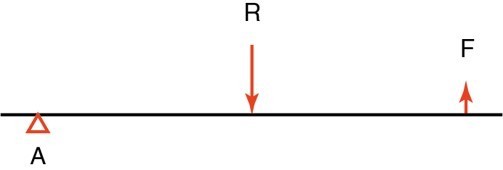
First class lever
.Axis is between force and resistance
.F – A – R or R – A – F
.ex: cervical flexion and extension
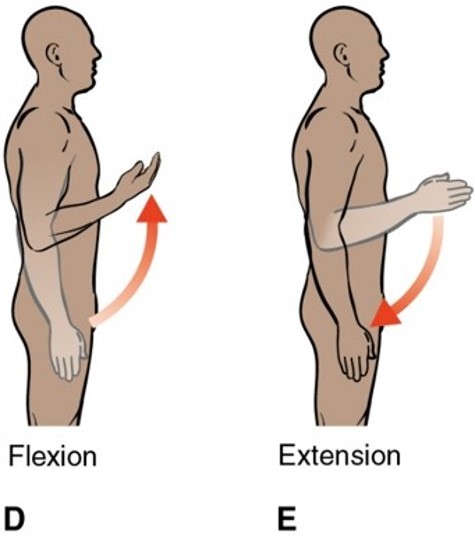
What plane and axis does flexion/extension occur in?
Sagittal plane in frontal axis
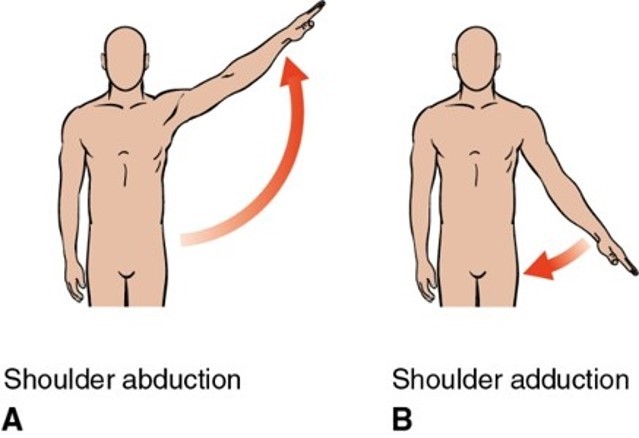
What plane and axis does adduction/abduction occur?
Frontal plane on the sagittal axis
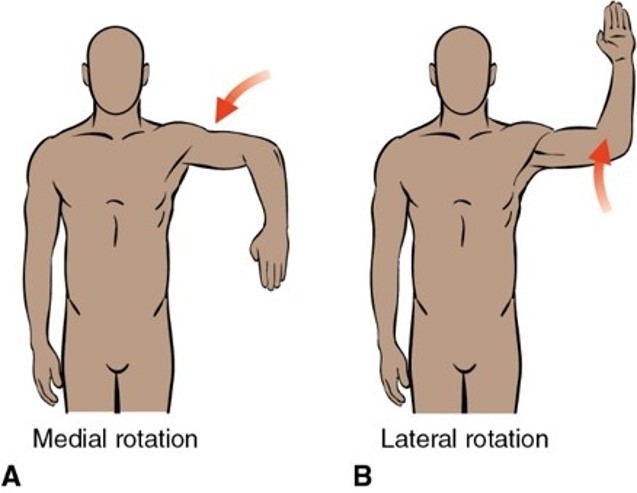
What plane and axis does Medial/lateral rotation occur?
in the horizontal plane about the vertical axis
Second class lever
.Resistance is between the axis and the force.
.A – R – F or F – R – A
.Mechanical advantage: FA always longer than RA
.ex:calf raise
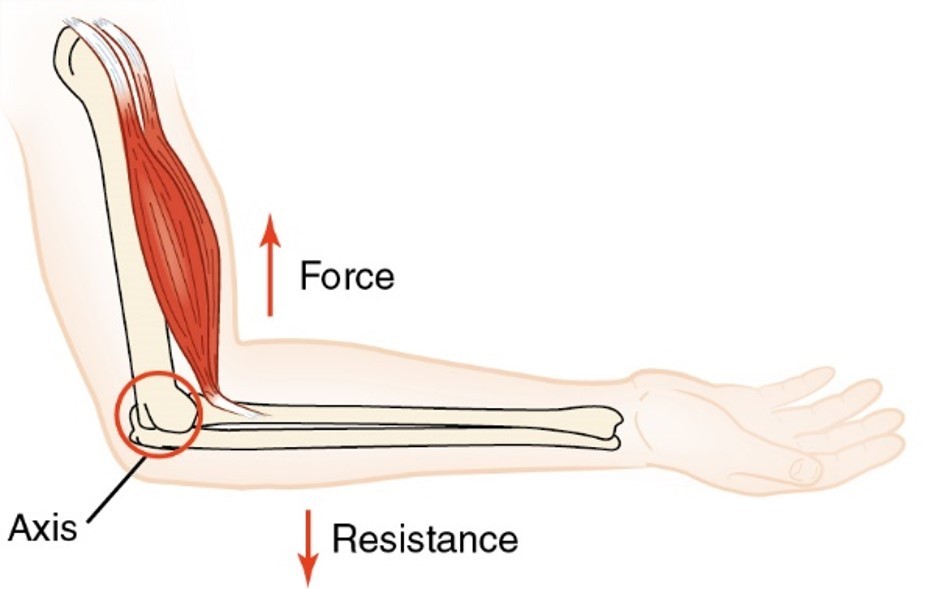
Third class lever
.Force is between the axis and resistance.
.A – F – R or R – F – A
.Mechanical advantage: RA always longer than FA
ex: biceps muscle flexion/extension
What is the purpose of the skeletal system?
.support the body
.protect organs
.serve as anatomical landmark
.enable movement
.store minerals
.produce red blood cells
How many vertebrae in the cervical spine?
7
how many vertebrae in the thoracic spine?
12
how many vertebrae in the lumbar?
5
How many vertebrae are in the axial skeleton?
26
*hint*
think breakfast, lunch and dinner
cervical- 7 am
thoracic- 12pm
lumbar-5pm
Bones of the axial skeleton (cranium)
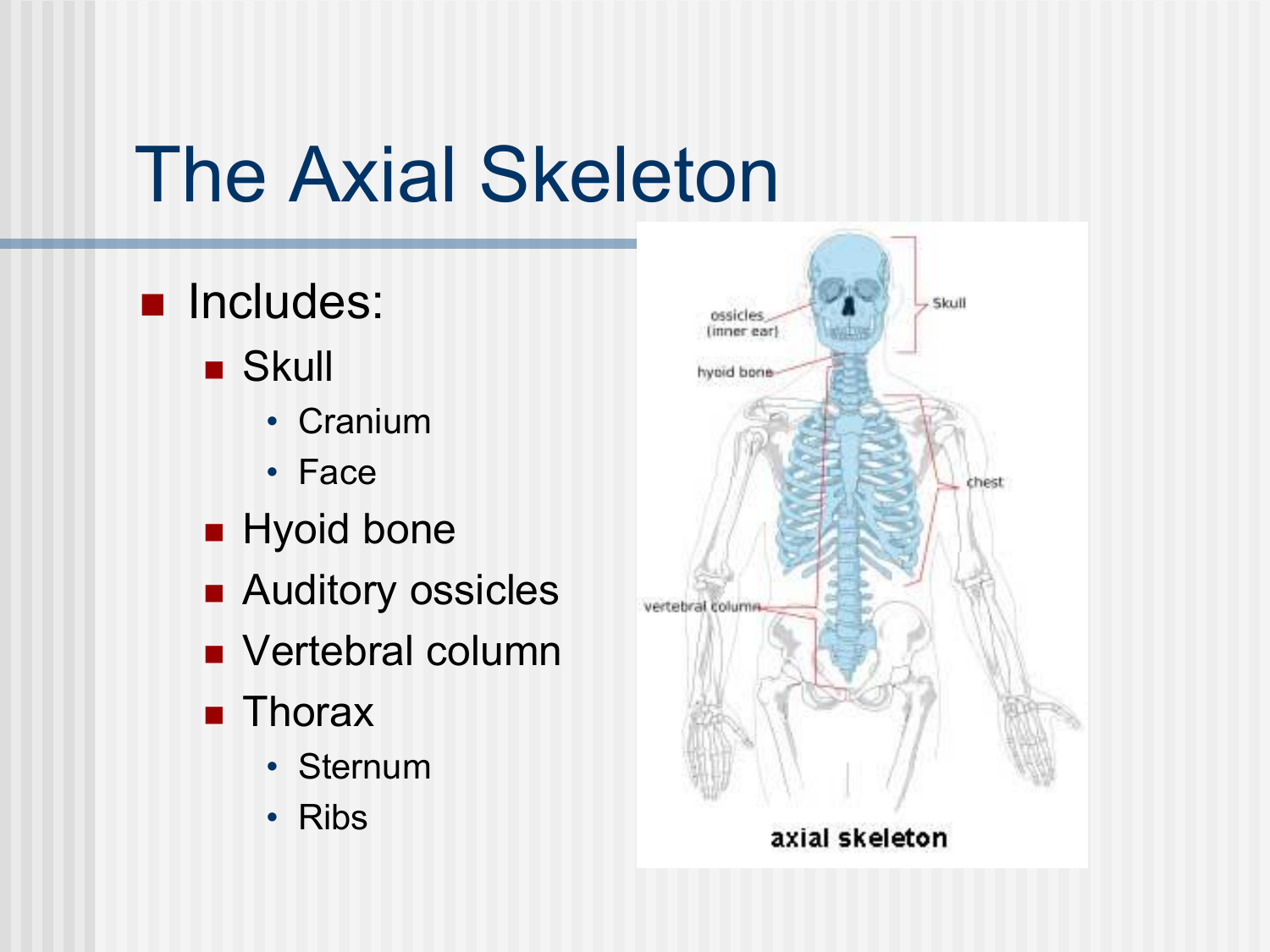
Cranuim(8)
frontal
sphenoid
ethmoid
occipital
parietal and temporal (paired)
Bones of the axial skeleton (face)
Face(14)
mandible
vomer
maxilla
zygomatic
lacrimal
inferior concha
palatine
Nasal
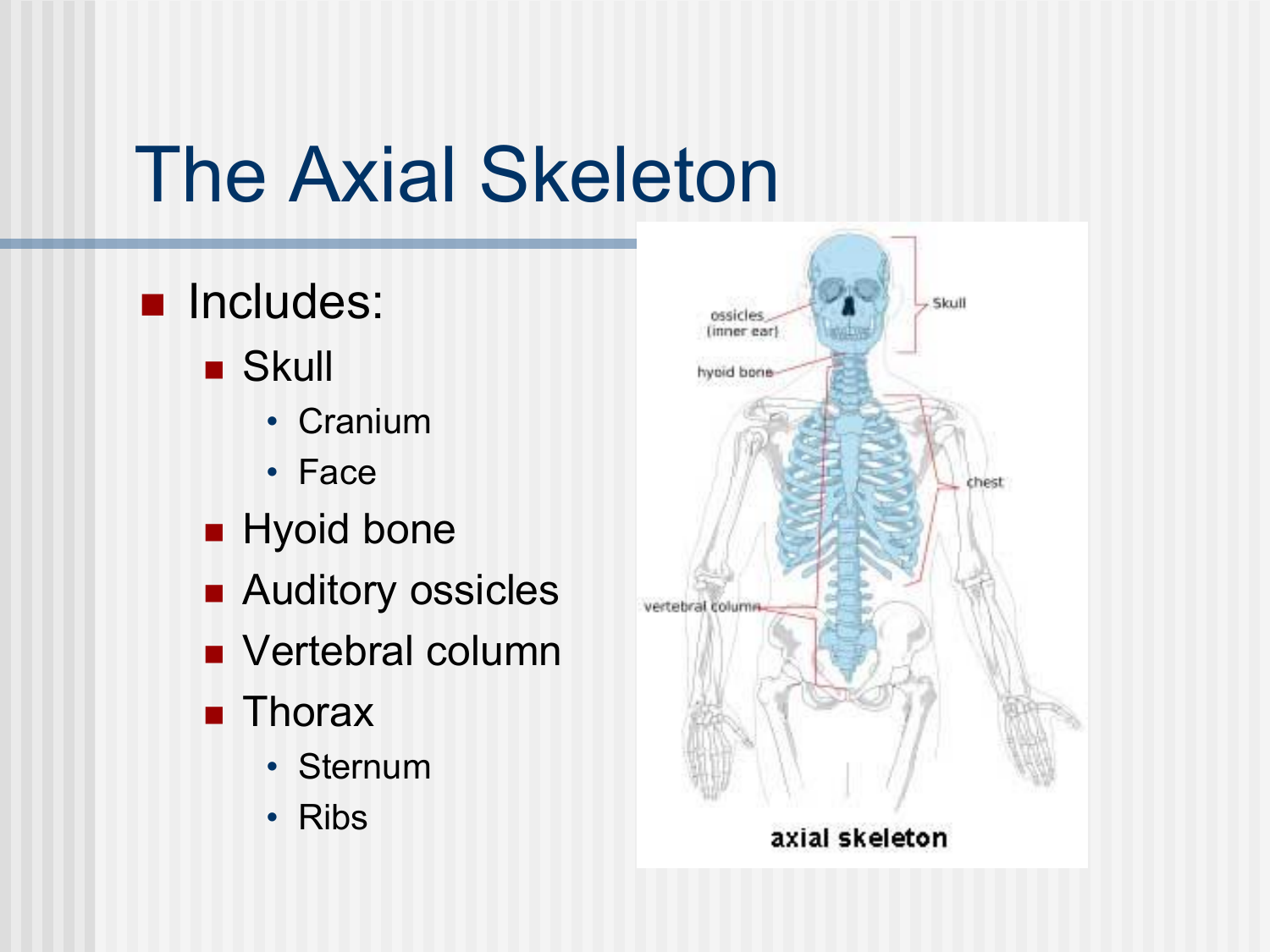
Bones of the axial skeleton (randoms)
other bones(7)
hyboid
ear ossicles(3 pairs)
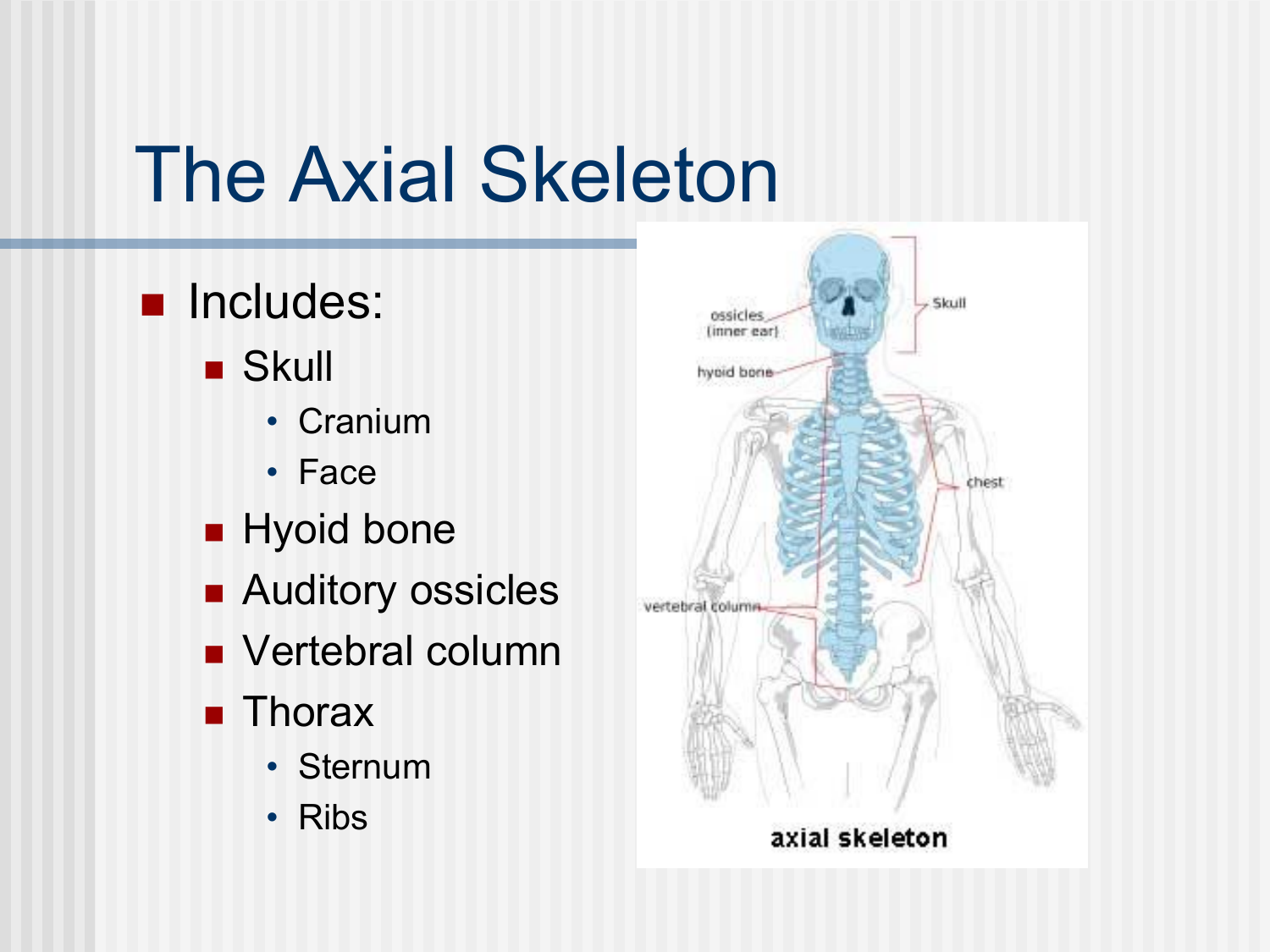
Bones of the axial skeleton (vertebral column)
Vertebral Column (26)
cervical (7)
thoracic (12)
lumbar (5)
sacrum (5*) fused
coccyx (3*) fused
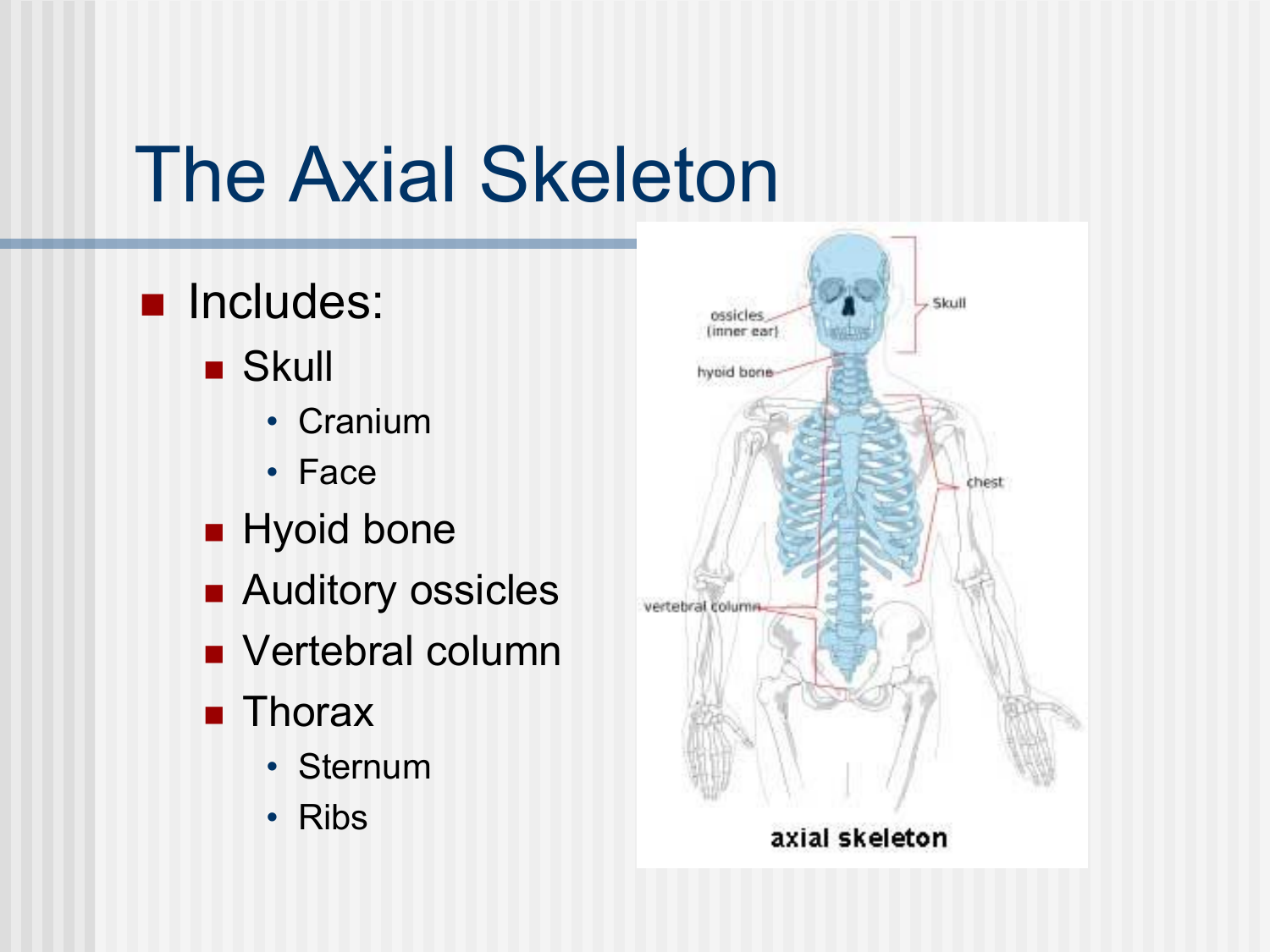
Bones of the axial skeleton (thorax)
Thorax (25)
sternum
ribs (12 pairs, 24total)
-true ribs:7
-false ribs:3
-Floating:2
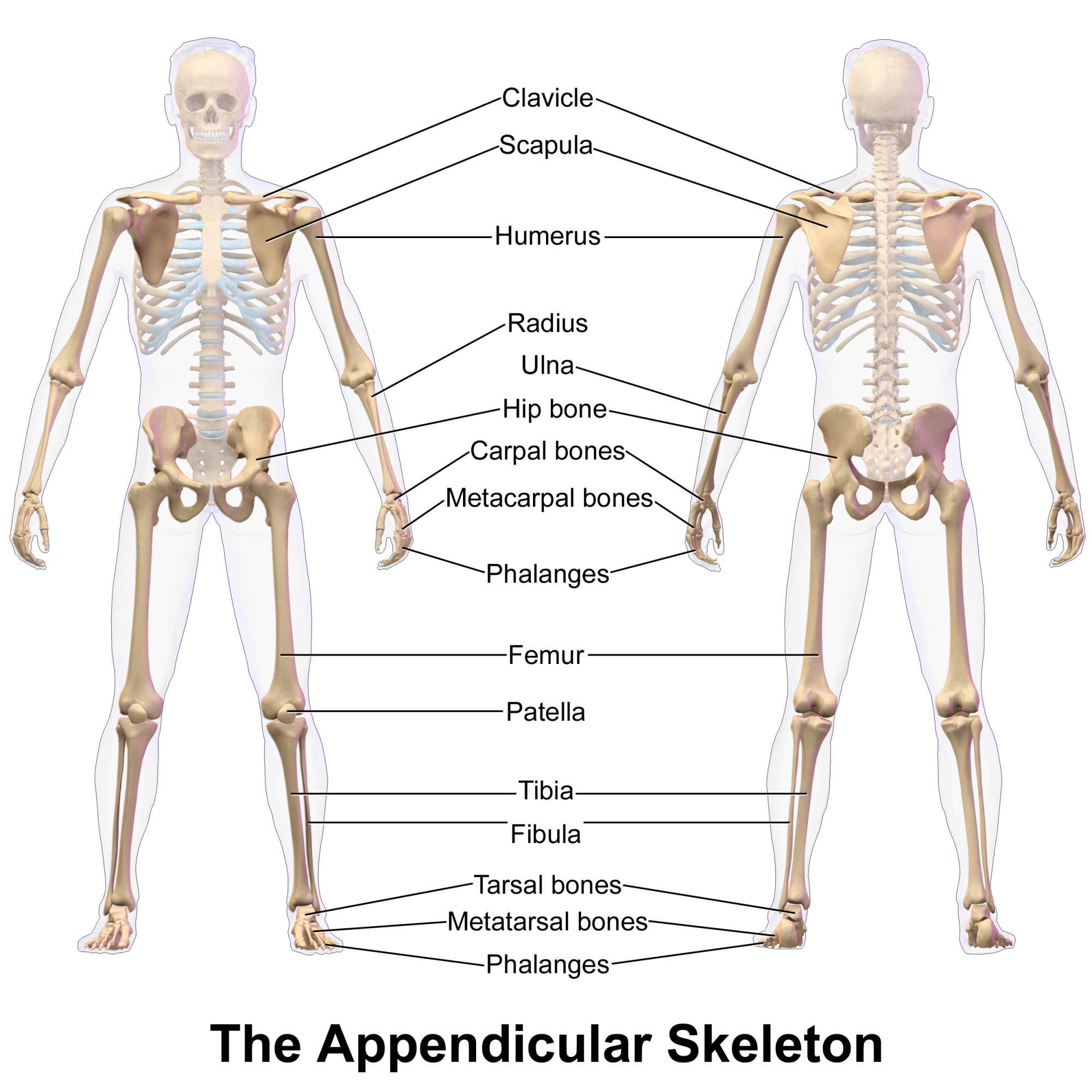
Bones of the appendicular skeleton (upper extremity)
Upper extremity (64)
scapula
clavical
humerus
ulna
radius
carpals(16)
metacarpals(10)
phalanges (28)
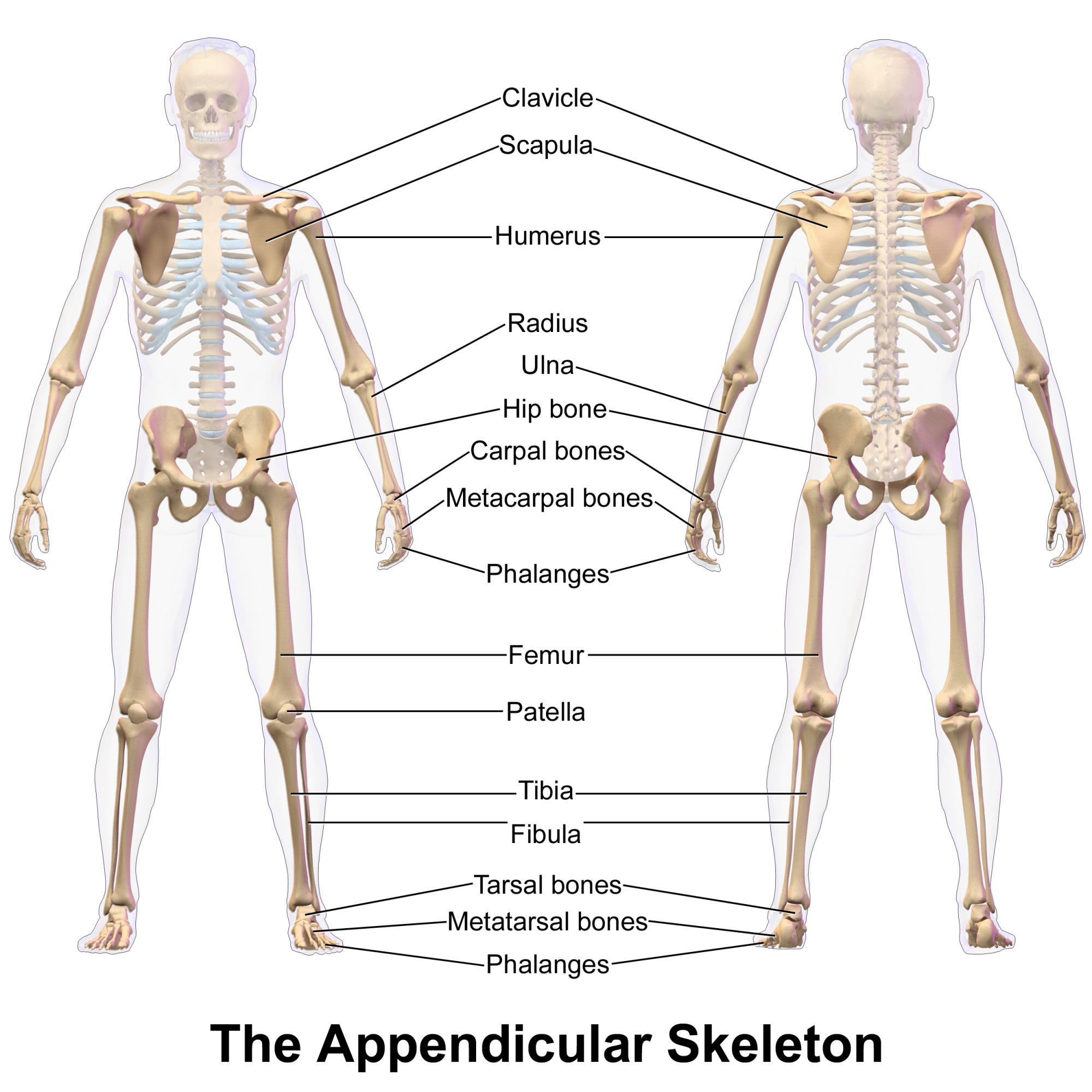
Bones of the appendicular skeleton (lower extremity)
Lower extremity(62)
innominate
femur
tibia
fibula
patella
tarsals(14)
metatarsals (10)
phalanges (28)
Bone markings (depressions and openings)
•Foramen
•Fossa
•Groove
•Meatus
•Sinus
bone markings depression/ opening: Foramen
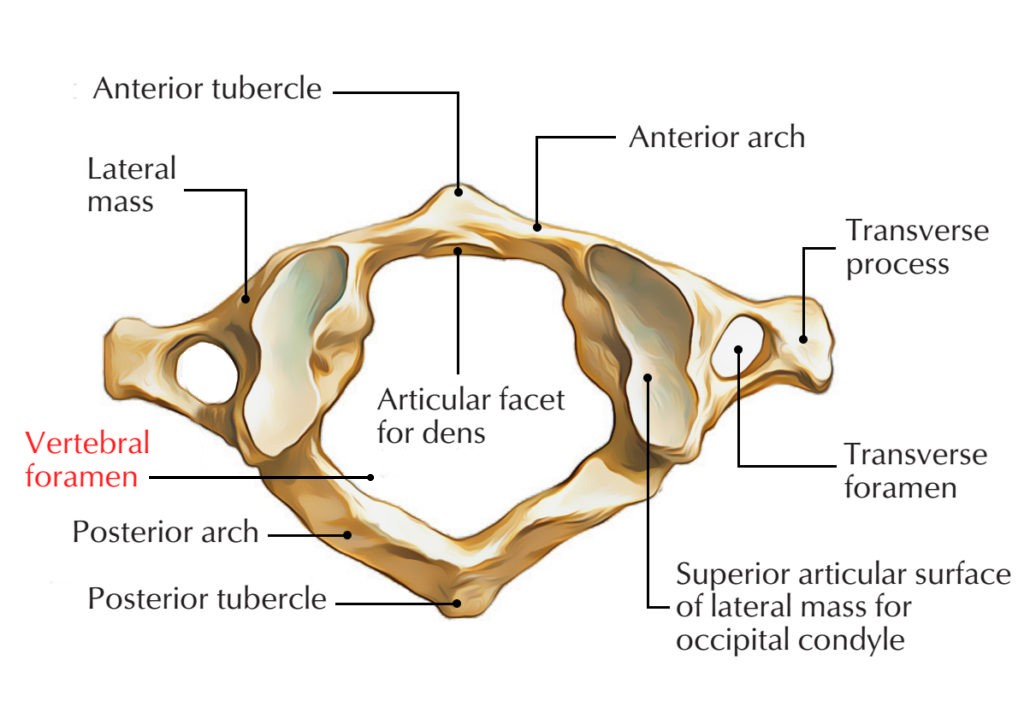
hole through which blood vessels, nerves and ligaments pass through.
ex: vertebral foramen of cervical vertebrae
Bone markings depression/ opening: fossa
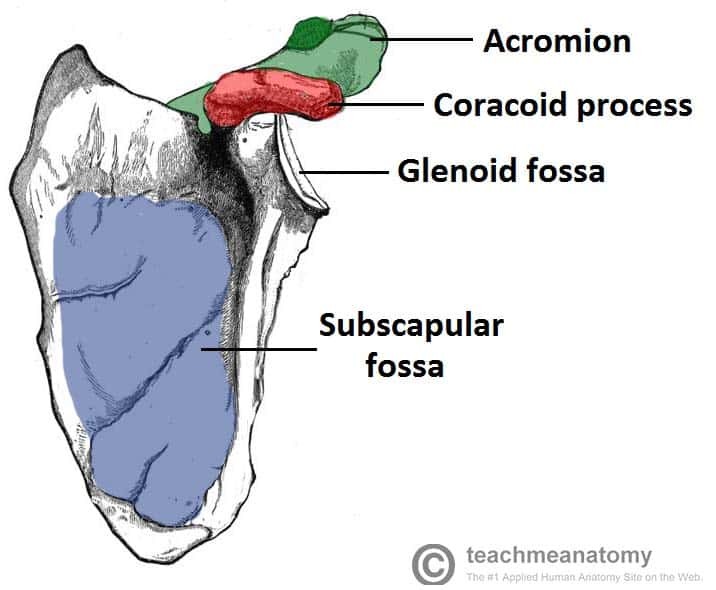
hollow or depression
ex: glenoid fossa of scapula
Bone markings depression/ opening: groove
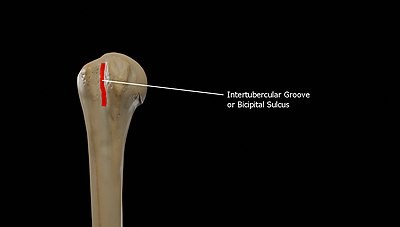
long, narrow channel containing a tendon, nerve or blood vessel.
ex: bicipital groove of humerus
bone markings depression/ opening: meatus
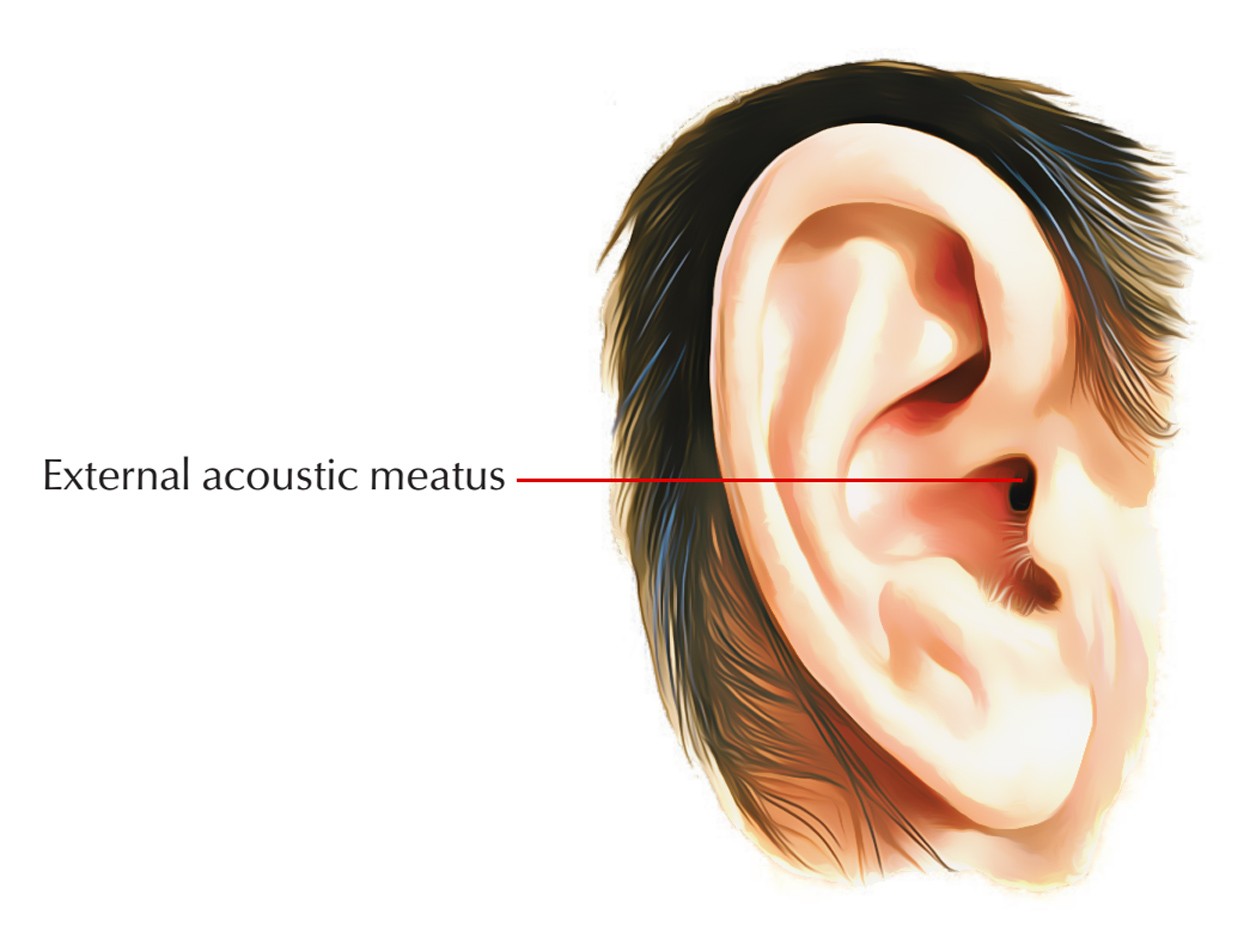
canal or tube-like opening in bone
ex: external auditory meatus
bone markings depression/ opening: sinus
air or fluid filled cavity
ex: frontal sinus