Bone: Principal Characteristics
Vascularized, Innervated, Produces hydroxyapatite crystals [Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2] within its ECMCollagen type 1
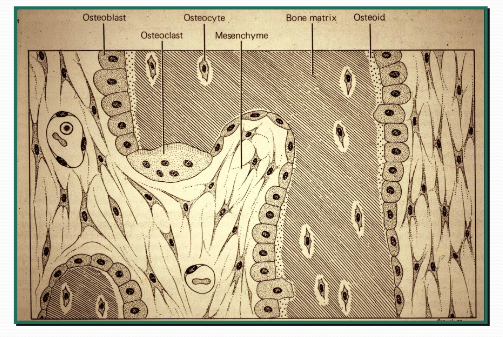
Principal Cell Types of Bone
Osteoblast, Osteocyte (fully differentiated osteoblast) and Osteoclast
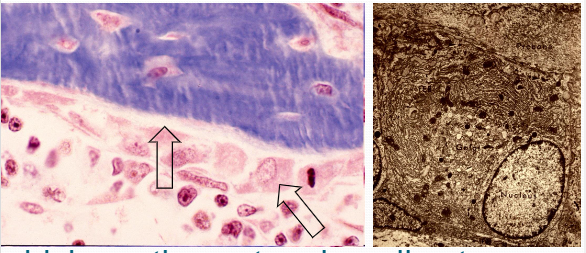
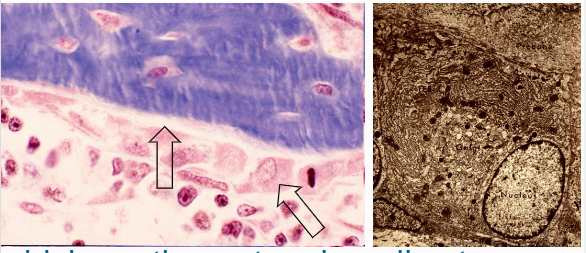
Osteoblast
Initially forms osteoid forms (pre bone)which continue to mineralize to become a bone matrix. cells within in blue are the osteocytes. Os
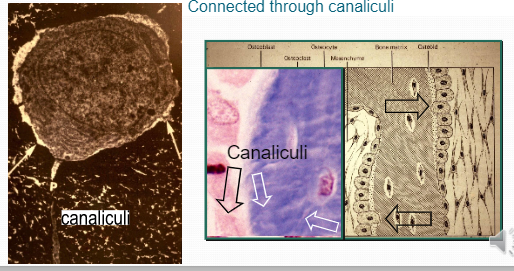
Osteocyte
Selected osteoblast that ‘remains behind ’Coated by thin layer of osteoid Connected through canaliculi
Osteocyte
the are Osteoblast that (Stays behind) and become bone. coded by thin layer of osteoid to help them exchanged through membrane.
Osteoblast
clear White part has not become bone, secreting to become bone is between the blue and pink part. The bone matrix is blue part, cells within blue area is osteocytes.
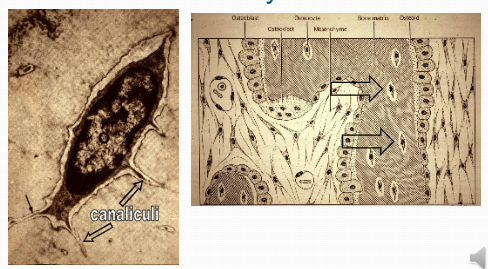
canaliculi
Connected through osteocytes through other cells are canaliculi (small tunnels in the bone that are run between cells and nerves that keep cells alive.)
Osteoclast (breakdown and rebuild)
Bone resorption (osteoclasia) and remodeling.
Originate from bone marrow, coalescing monocytes
Lysosomally rich.
Space area in bone
The Ruffled border creates a resorption bay (Howslip’slacuna).
Vesicular zone. Where lysosome secret out into the space area of bone.
Sealing zone
keep all the enzymes in the area that osteoclast wants them and keeps lysosomes from entering in areas they're not supposed to be in.
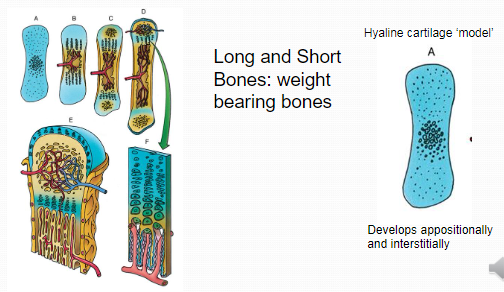
Endochondral Ossification
Blue: cartilage red: bone