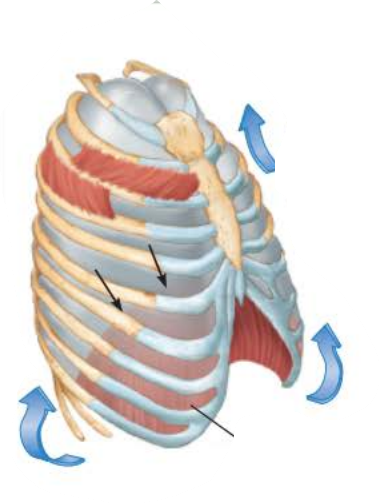
Inhalation 1/5
name the muscles involved and the action they perform
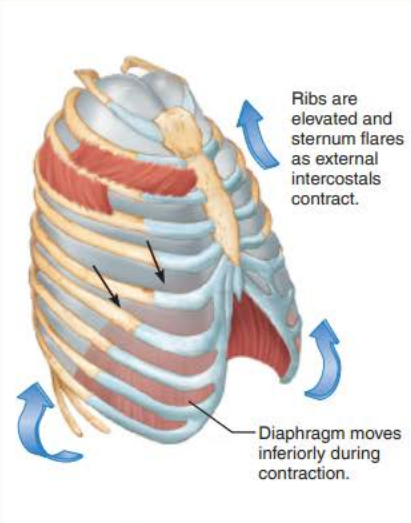
_____________ ____________ contract causing the __________ to contract and move ____________ and the __________ _______________ contract which ___________ the ____ and _________
___________ ___________
_______ ________
____________ _________ ________
_________ _________ ______
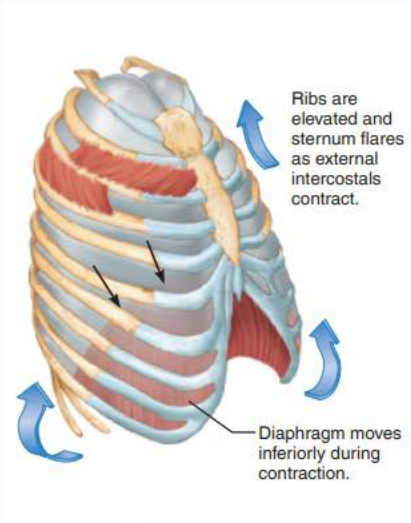
inspiratory muscles
diaphragm
inferiorly
external intercostals
elevates
ribs
sternum
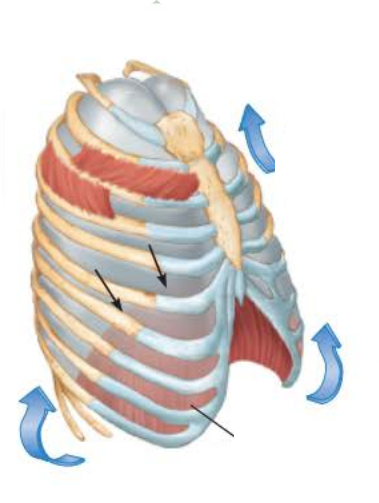
Inhalation 2/5
__________ ________ ________ ___________
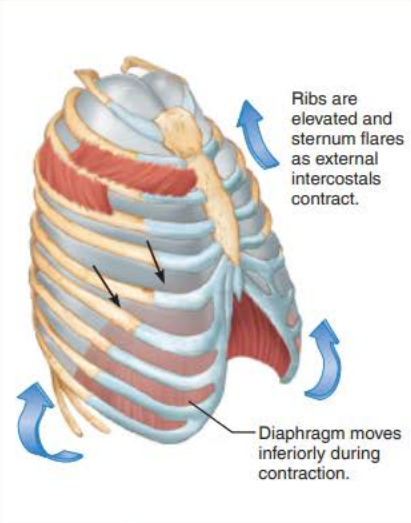
thoracic cavity volume increases
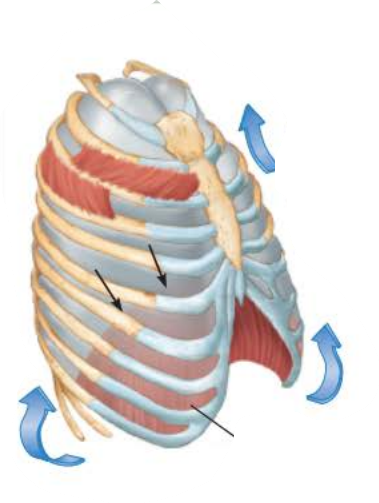
Inhalation 3/5
________ become ____________ which ____________ ______________ _________
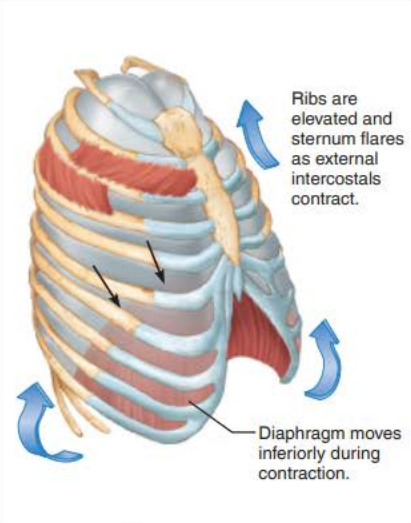
Lungs
stretched
increases intrapulmonary volume
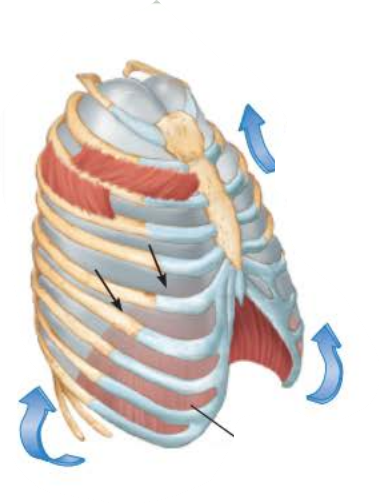
Inhalation 4/5
_____________ __________ drops to ___ _____ __
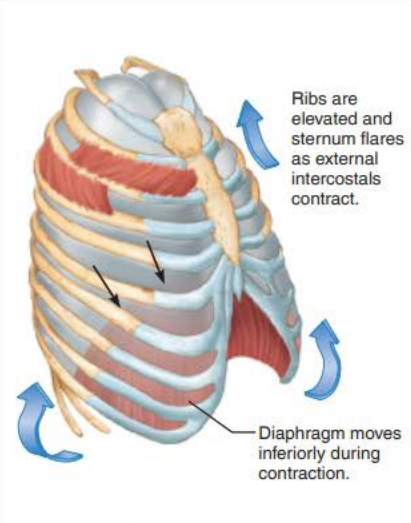
Intrapulmonary pressure drops to -1 mm Hg
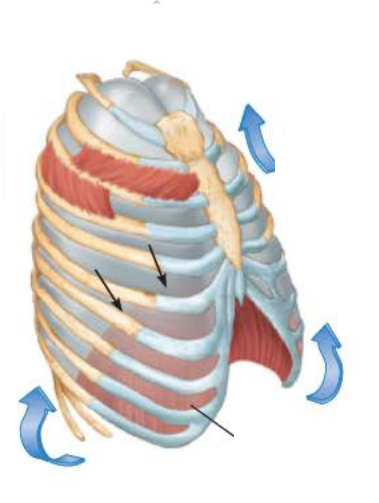
Inhalation 5/5
gasses flow into lungs down the __________ _________ until ______________ ____________ is ___ and equal to _____________ _____________
gasses flow into lungs down the pressure gradient until intrapulmonary pressure is 0 and equal to atmospheric pressure
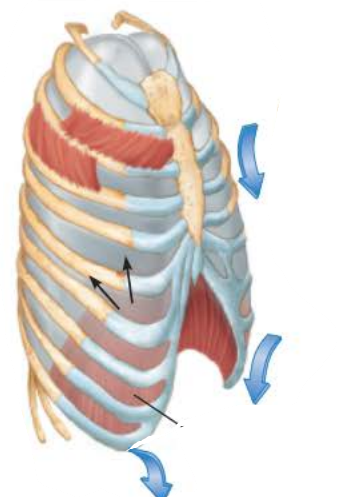
Expiration 1/5
name the muscles involved and the action they perform
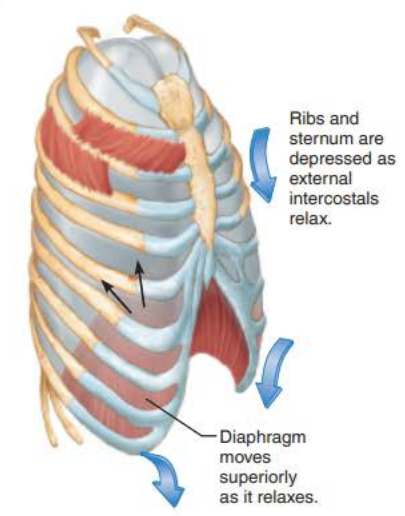
the ______________ _____________ relax causing the __________ to relax and move _____________ and the _____________ ______________ relax which depresses the ______ and ____________
inspiratory muscles
diaphragm
superiorly
external intercostals
ribs
sternum
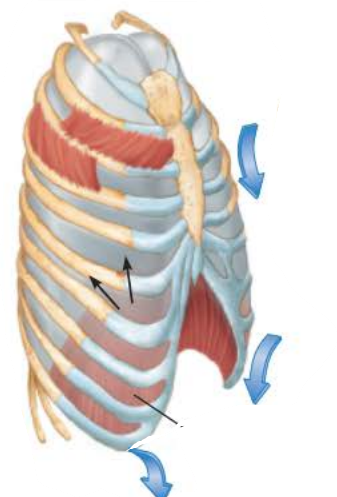
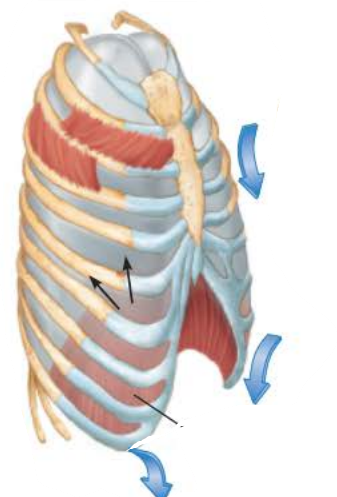
Expiration 2/5
________ _________ _______ ___________
thoracic cavity volume decreases
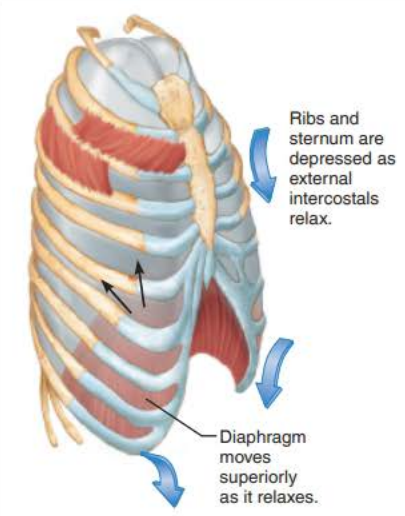
Expiration 3/5
the ___________ lungs ________ _____________ which ____________ _______________ _________________
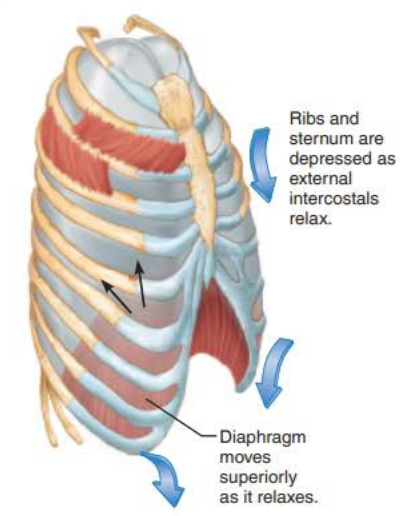
elastic
recoil
passively
decreases intrapulmonary volume
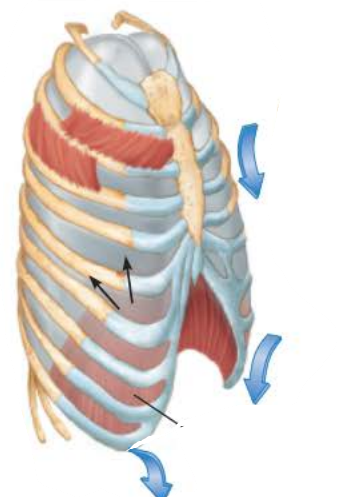
Expiration 4/5
_________________ ____________ rises to __ ____ ____
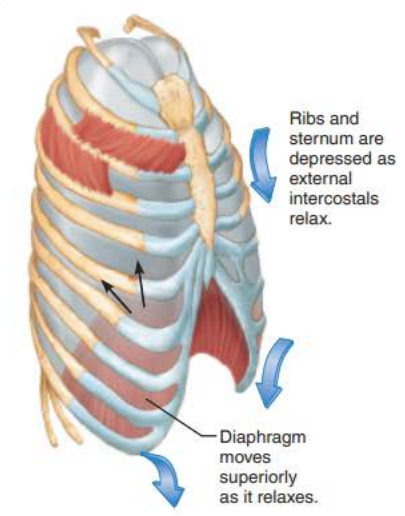
intrapulmonary pressure
+1mm Hg
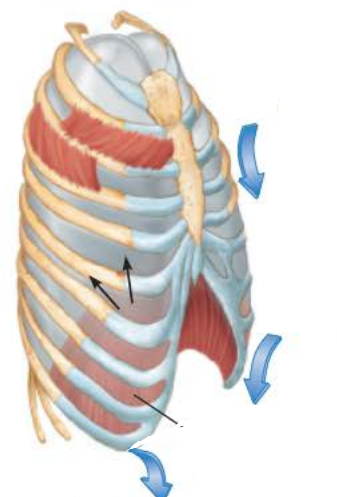
Expiration 5/5
5. _____________________________________
___________________________________________
_________________________________________
gasses flow out of the lungs down the __________ _________ until ______________ _____________ is __ and equal to ____________ ____________
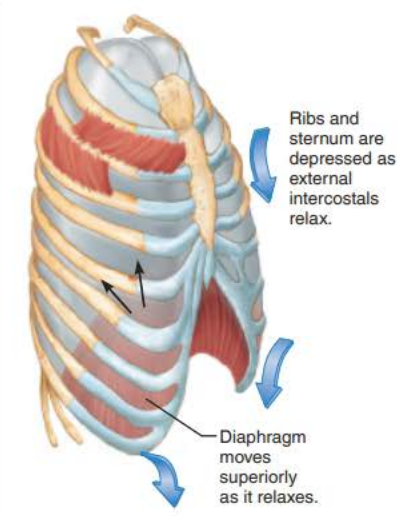
pressure gradient
intrapulmonary pressure
0
atmospheric pressure
what type of muscle is the diaphragm made of?
skeletal muscle
how is the diaphragm under involuntary control?
the diaphragm receives _______________ efferents from ______ and ________ respiratory groups through the ____________ __________
involuntary
ventral
dorsal
phrenic nerve
how is the diaphragm under voluntary control?
efferents from the cerebral ___________ _________ through __________ __________ stimulate the diaphragm to bypass the _______________ ___________ ____________
efferents from the cerebral motor cortex through motor neurons stimulate the diaphragm to bypass the involuntary medullary centers
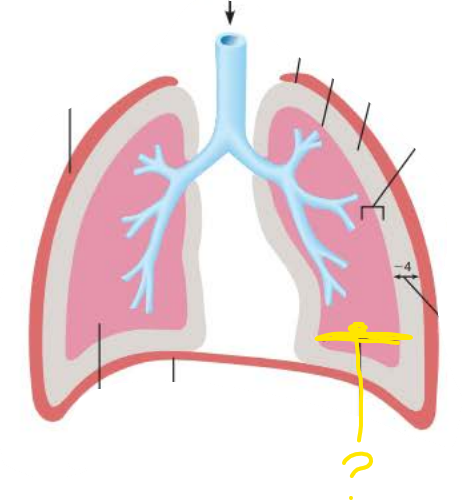
________________ ________ (Ppul) is the pressure in the ___________ it equalizes with ____________ __________ ( ____ mm Hg)
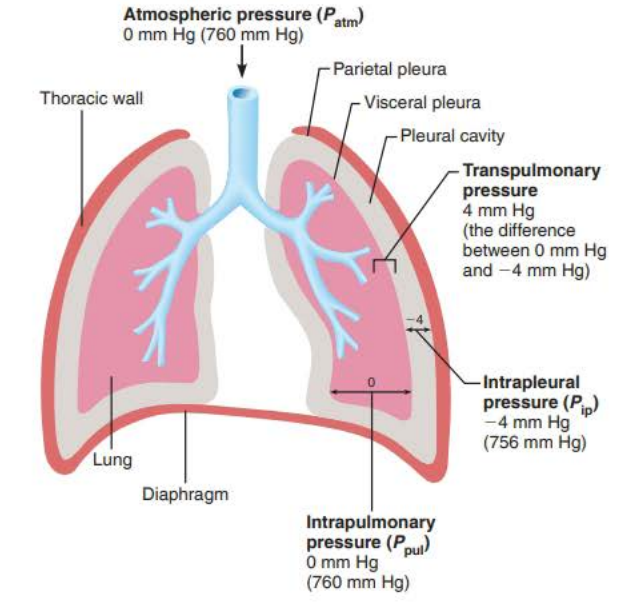
Intrapulmonary Pressure
alveoli
atmospheric pressure
760 mm Hg
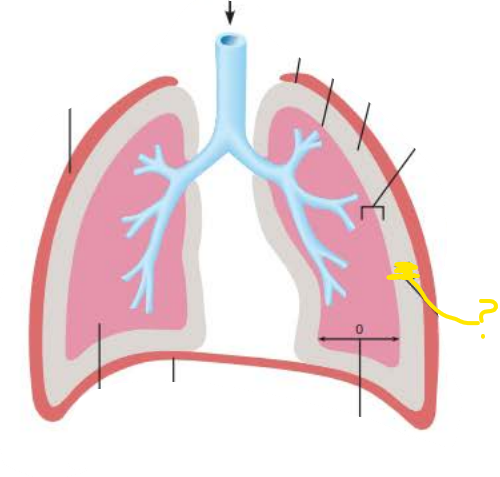
_____________ _______ (Pip) is the pressure in __________ __________ it is always ____ __ less than ______________ __________
( ____ mm Hg)
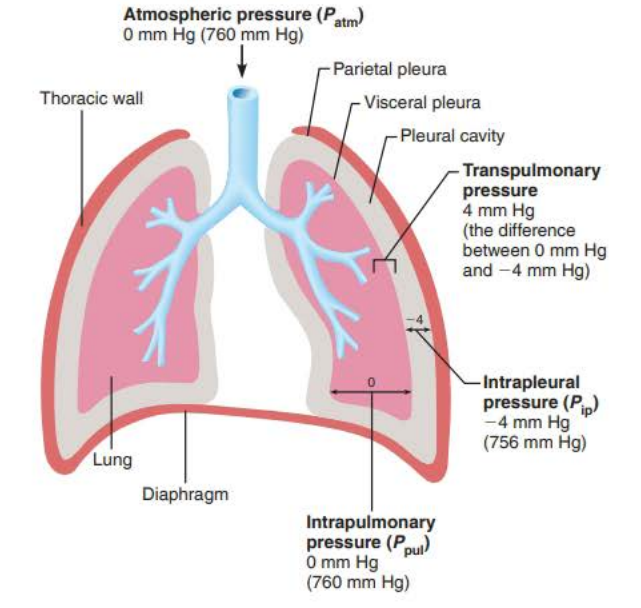
Intrapleural Pressure
pleural cavity
4mg Hg
intrapulmonary pressure
756 mm Hg
intrapleural pressure would exceed intrapulmonary pressure through _______________ or an increase in air above ______ __ in the ________ ________ caused by rupture of the _________ or _________ _______
pneumothorax
-4mm Hg
pleural cavity
parietal
visceral pleura
if intrapleural pressure exceeds intrapulmonary pressure then ____________ occurs which is a collapsed lung
atelectasis
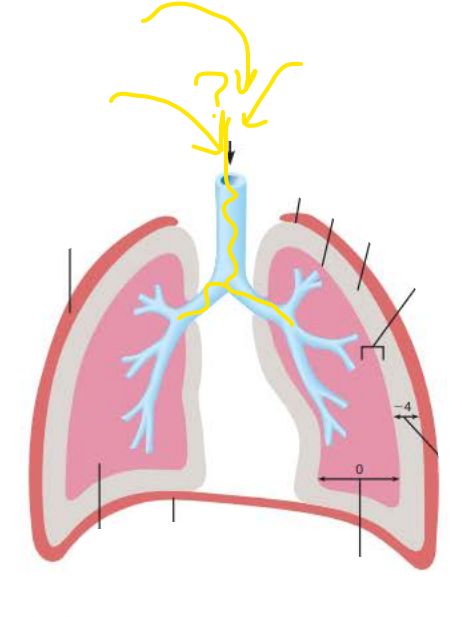
atmospheric pressure
760 mm Hg
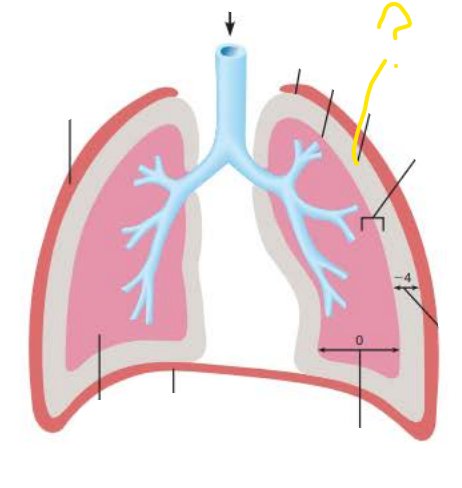
pleural cavity
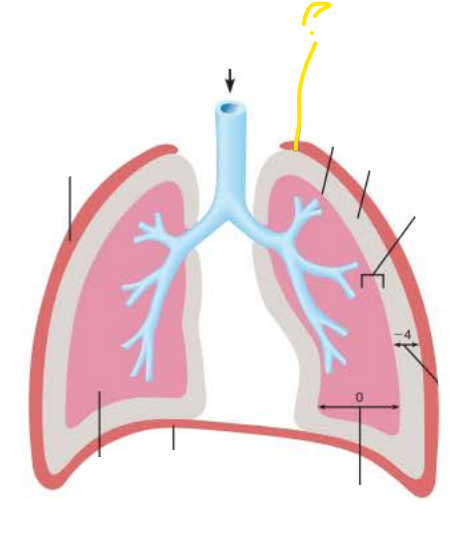
parietal pleura
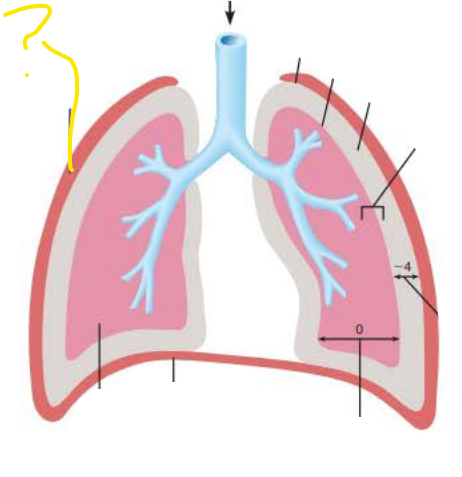
thoracic wall
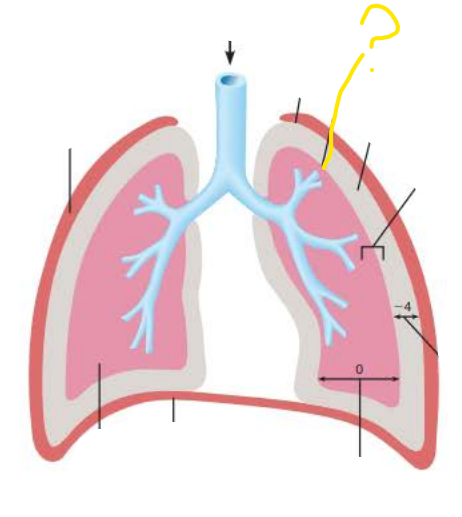
visceral pleura