Photosynthesis Notes - Liberty Union High School District
advertisement

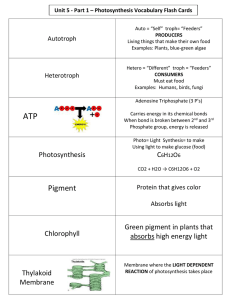
Part 1: Photosynthesis Section 4.2 & 4.3 Important molecules in cellular energy: • CO2 = carbon dioxide gas • H2O = water • C6H12O6 = glucose (sugar) • O2 = oxygen gas Important molecules in cellular energy: • ATP = chemical energy • NADPH = energy molecule that receives and gives away e- (electrons) to drive chemical reactions ATP gets recycled AdenosineTriphosphate ATP Loses a P to use energy Gains a P to make energy ADP ADP = AdenosineDIphosphate – It’s ATP that is missing 1 P! NADPH gets recycled, too Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate(+ Hydrogen) It cycles from NADPH to NADP+ back to NADPH, etc. It carries electrons (held by H) and gives them away during the second stage of photosynthesis – the Calvin Cycle. NADPH NADP+ Photosynthesis: the process for the conversion of light energy into chemical energy (ATP) stored in organic compounds (glucose) Photosynthesis Equation Carbon Water dioxide Glucose PHOTOSYNTHESIS Oxygen gas Photosynthesis happens in 2 parts: Step 1: Light Dependent- light is absorbed to make energy for light independent. • Happens in the thylakoid membrane of a chloroplast Step 2: Light Independent (Calvin Cycle)– uses energy from the light reactions to make sugar. • Happens in the stroma of a chloroplast Sketch this chloroplast! Chloroplasts Overview of Photosynthesis H 2O CO2 Chloroplast Light NADP+ ADP + P LIGHT REACTIONS (in grana) CALVIN CYCLE (in stroma) ATP NADPH O2 Sugar Light Reactions – Detailed steps: 1) Light is absorbed by chlorophyll 2) H2O molecules are split to provide eand H+ that will enter an electron transport chain to produce: ATP NADPH Will be used in the Calvin Cycle 3) Oxygen from the splitting of H2O is released as waste 2 H2O e- + 4 H+ + O2 Time for video clips! • http://youtu.be/sQK3Yr4Sc_k (2:42) Check for Understanding 1. What happens to the oxygen created during the light reactions of photosynthesis? a. It is used in the next step of photosynthesis b. It is discarded as a waste product c. It is used to make water d. It becomes a part of glucose Check for Understanding 2. What is the general purpose of the light reactions of photosynthesis? a. To make oxygen b. To convert chemical energy into light energy c. To convert light energy into chemical energy d. To make glucose. The Calvin Cycle The Calvin Cycle (sometimes called “the Dark Reactions”) Calvin Cycle: Creates glucose using ATP and NADPH from the light reactions as well as CO2 from the air Happens in the liquid stroma of a chloroplast Carbon Fixation: the incorporation (adding) of CO2 into organic compounds Happens in Calvin Cycle Plant Food The plant stores the excess sugar as starch in the roots, seeds, and fruit of the plant. Check for Understanding 2. What is the general purpose of the light independent reactions (Calvin cycle) of photosynthesis? a. To make oxygen b. To convert chemical energy into light energy c. To convert light energy into chemical energy d. To make glucose. Energy overview sun Photosynthesis plants CO2 glucose H2O animals, plants Cellular Respiration The Great Circle of Life,Mufasa! ATP O2