Physics - DB Crest
advertisement

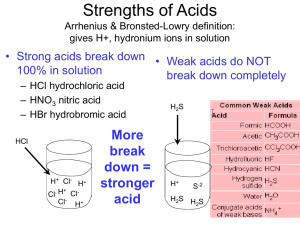
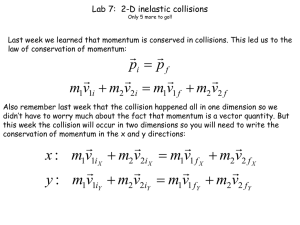
Physics Mr. Tothero Final Exam Study Guide Responses to FAQ’s: The final exam consists of 50 multiple choice questions. The final exam makes use of the Scantron® forms. Calculators and equations will be provided for the final exam. You will need to know all the measurement units of the quantities discussed. Covered Content 1. Kinematics (Motion Studies) a. Key Vocabulary Words Speed, Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration, A.D.T. Gravity b. Basic Equations v2 v1 at ; d 2 d1 v1t 12 at 2 ; v22 v12 2a d2 d1 ; d 2 d1 v1 v2 t 2 c. Graphs d vs. t, v vs. t, a vs. t How slopes and areas of one graph relate to others. d. Projectile Motion (2D Kinematics) Horizontal speed and vertical speed Half and full parabola paths 2. Forces a. Newton’s Laws (There are three) Know the mathematical relationships of F ma b. Friction Static vs. Sliding c. Mass and Weight W mg 3. Vectors a. Vectors vs. Scalars b. Analytical Vector Addition 4. Momentum a. Mathematical Definition ( p mv ) b. Collision Types Elastic vs. Inelastic c. Conservation of momentum calculations regarding each collision type Elastic: m1v1I m2v2 I m1v1F m2v2 F Inelastic: m1v1I m2v2 I m1 m2 VF 5. Energy a. Work Using W Fd cos Know when work is positive ( 0 ) or negative ( 180 ). b. Conservation of energy calculations using 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 mv1 kx1 mgy1 wother mv2 kx2 mgy2 2 2 2 2 6. Electrostatics a. Charge Attraction/Repulsion b. Coulomb’s Law kq q F 12 2 d 7. Electrical Current and Circuits a. Ohm’s Law V R I b. Circuit Types (Series vs. Parallel) c. Series/Parallel Equivalent Resistance Formulas 1 1 1 1 ReqSeries R1 R2 R3 ; ReqParallel R1 R2 R3 8. Magnetism a. Attraction and Repulsion Principles b. Magnetic Devices (Solenoid, Electromagnet, Transformer, Motor) Vs N s VP N P c. Right-Hand-Rule (Current, Force) 9. Waves a. Wave Types (Transverse vs. Longitudinal) b. Wave Parts (Amplitude, Wavelength, Crest, Trough, Frequency, Period) c. Interference Patterns Constructive (reinforcing) vs. Destructive (dampening or canceling) d. Resonance Occurs when an object is vibrated at its natural frequency and an intense amplification occurs. e. Sound f. Light g. Reflection and Refraction