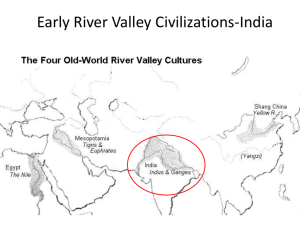
Ancient India Unit Test Review - Team Challenge
advertisement

Ancient India Unit Test Review! Team Challenge! • The board will start with position 1 and will rotate clockwise each time a new question is asked. • You may discuss with your table for the correct answer but be careful not to give away the answer to other teams! • Write the correct answer on your dry erase boards (Nice and big please!) Question #1 Because of its large size and its position in relation to large masses of land and water, India is called A. a plateau. B. an isthmus. C. an ecosystem. D. a subcontinent. Question #2 As the Brahmaputra River flows from the mountains into the valley, it becomes A. slower and deeper. B. clearer and cleaner. C. rockier and rougher. D. narrower and colder. Question #3 During the summer in India, the monsoon brings A. heavy rain. B. dust storms. C. unbearable heat. D. pleasant mornings. Question #4 On the map, find the northern tip of the Bay of Bengal. Why is the nearby soil so fertile? A. Many kinds of fish live in the bay. B. Flooding rivers deposit rich minerals. C. Pure water flows from the mountains. D. People have farmed there for centuries. Question #5 Compared with the Eastern and Western Ghats, the Deccan Plateau has A. denser forests. B. a drier climate. C. a longer coastline. D. steeper mountains. Question #6 Farmers in the Deccan Plateau use the iron-rich black soil principally to raise A. tea. B. sheep. C. cotton. D. oranges. Question #7 Which phrase best describes the Eastern and Western Ghats? A. fertile plains B. sandy beaches C. mountain ranges D. marshy wetlands Question #8 Which of the following parts of India has the most fertile farmland? A. the Hindu Kush B. the Deccan Plateau C. the Himalaya Mountains D. the plains along the Ganges Question #9 Much of the water in the Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra rivers comes from A. natural springs in the desert. B. melting ice in the mountains. C. rain-fed streams in the plateau. D. large lakes in the northern plain. Question #10 How has the location of the Himalaya Mountains benefited India? A. roads for trade routes B. consistent water supply C. protection from enemies D. prevention of earthquakes Question #11 Travelers went through the Khyber Pass to cross the A. Hindu Kush. B. Eastern Ghats. C. Deccan Plateau. D. Himalaya Mountains. Question #12 The lower Indus River (the part nearer the sea) flows through what is now the country of A. Iran. B. Tibet. C. Nepal. D. Pakistan. Question #13 A traveler in the Thar Desert would be likely to see many A. elephants. B. sand dunes. C. small farms. D. walled cities. Question #14 Where were the earliest known settlements in India? A. on the plateau B. near the desert C. beside the rivers D. in the mountains Question #15 How are the Indus and Ganges rivers similar to the Nile River in Egypt? A. They begin in the same general area. B. They carry silt that enriches the soil. C. They flow in the same general direction. D. They have big floods that prevented early settlement. Question #16 Harappan civilization, which included ancient Mohenjodaro, developed in the A. Western Ghats. B. Deccan Plateau. C. Indus River valley. D. Ganges River valley. Question #17 In which of these years was Mohenjodaro an active settlement? A. 8000 B.C.E., while people were discovering how to farm B. 2550 B.C.E., while the Great Pyramid was being built in Egypt C. 1000 B.C.E., while King David was ruling over Israel D. 600 B.C.E., while the Neo-Babylonian Empire ruled Mesopotamia Question #18 How did modern scholars learn that Mohenjodaro had ever existed? A. Astronauts saw it from space. B. Historians read ancient scrolls. C. Archaeologists found its ruins. D. Geographers studied old maps. Question #19 Part of Mohenjodaro was raised and surrounded by a wall. What does this suggest about the city? A. It had traders who stayed near the roads. B. It had religious leaders who lived separately. C. It had rich people who owned the best homes. D. It had enemies who might attack the residents. Question #20 Which fact shows that Mohenjodaro was carefully planned? A. Wheeled carts were pulled by animals. B. The workshops were made of mud bricks. C. Some of the houses were larger than others. D. Nine streets divided the lower city into blocks. Question #21 What does the list below show about the civilization that included Mohenjodaro? • Invaders • Floods • Earthquakes A. likely causes for its beginning B. theories for why it disappeared C. problems with being near a river D. reasons it was led by strong rulers Question #22 The discovery of a scale, stone weights, and a marked rod suggests that the people of Mohenjodaro A. had uniform ways to measure. B. knew how to make tools of iron. C. traded with people from far away. D. started a new kind of mathematics. Question #23 Archaeologists found a structure that was 39 feet long and 8 feet deep, with a well nearby and a drain along one side. How was it likely used? A. for bathing B. for cooking C. for making wine D. for grinding grain Question #24 What evidence shows us how men in Mohenjodaro might have dressed? A. pictographs B. an ancient statue C. a report by a visitor D. remains of an old robe Question #25 Which feature of Mohenjodaro was quite different from other settlements of that time? A. high wall B. dirt roads C. brick homes D. sewer system Question #26 Where did most of the people of Mohenjodaro live? A. in the citadel B. in the tall tower C. in the lower city D. in the courtyards Question #27 Homes in Mohenjodaro had from one to a dozen rooms. What does this suggest about the city? A. Some houses had indoor bathrooms. B. Some apartments held several families. C. Some people were wealthier than others. D. Some families had grandparents living with them. Question #28 A war game played in ancient India is thought to be an early form of A. chess. B. hockey. C. dominoes. D. basketball. Question #29 Which of these questions about Mohenjodaro would be hardest to answer on the basis of artifacts? A. What foods did people eat? B. What songs did people sing? C. What games did people play? D. What clothes did people wear? Question #30 What was the main achievement of the Maurya family? A. to unify India B. to impose Buddhism C. to build famous temples D. to improve the lives of peasants Question #31 How did Chandragupta Maurya begin building his empire? A. He sent ships to far-off islands. B. He conquered neighboring kingdoms. C. He sponsored settlements by colonists. D. He persuaded other rulers to unite with him. Question #32 Which of these would you not consider an achievement under Chandragupta’s rule? A. He created a strong central government. B. He used torture and spies to make people obey. C. He made sure farmers had water for their crops. D. He built a royal road more than one thousand miles long. Question #33 Why was Chandragupta poor in his later years? A. He put a stop to foreign trade. B. He was overthrown by his son. C. He decided to live as an ascetic. D. He lost the conquered territories. Question #34 King Ashoka was Chandragupta’s A. father. B. enemy. C. brother. D. grandson. Question #35 Ashoka expanded the Mauryan Empire until he A. moved to China. B. gave up violence. C. reached the mountains. D. surrendered to his cousin. Question #36 Which experience led to a deep change in Ashoka’s values? A. marrying a Buddhist B. seeing a very bloody battle C. hearing Buddha's first sermon D. discovering old age and illness Question #37 Which Buddhist value did these actions by Ashoka reflect? • He gave up hunting. • He became a vegetarian. A. respect for all living things B. toleration of other religions C. honesty in words and actions D. awareness that everything changes Question #38 How did Chandragupta’s rule differ from Ashoka’s? A. Chandragupta had a larger empire than Ashoka did. B. Chandragupta used Buddhism to keep his people happy. C. Chandragupta made laws that were fairer than Ashoka's laws. D. Chandragupta used force to be sure no one threatened his power. Question #39 Which of Ashoka’s actions best expressed his Buddhist values? A. allowing slavery B. keeping a strong army C. putting criminals to death D. treating all of his servants well Question #40 What did Ashoka do with the territories the Mauryas had conquered? A. returned them to their former rulers B. used them as a base for new conquests C. kept them as peaceful parts of his empire D. granted them to wealthy merchants as gifts Question #41 In what important way did Ashoka spread Buddhist teachings? A. He required conquered people to convert. B. He had edicts carved into pillars and walls. C. He had peasants taught how to read and write. D. He made speeches in many places around the empire. Question #42 What happened on the Indian subcontinent in the time period between the Mauryan and Gupta empires? A. It went through a golden age. B. It experienced a great famine. C. It was filled with small kingdoms. D. It was conquered by the Sumerians. Question #43 How did the first Gupta ruler form alliances with other rulers? A. by giving them land B. by arranging marriages C. by killing them in battle D. by sending wise advisers Question #44 How was the Gupta Empire different from the Mauryan Empire? A. It got rid of the caste system. B. It was governed with harsh laws. C. It was made up of five kingdoms. D. It gave local areas a lot of independence. Question #45 Which factors in the Gupta Empire most helped the growth of learning? A. peace and stability B. poverty and hunger C. power and conquest D. change and rebellion Question #46 Which of these finds by an archaeologist would be evidence of a golden age? A. walled cities B. fine sculptures C. metal weapons D. animal skeletons Question #47 The images of Gupta kings on coins show that the empire had people who were skilled in A. writing literature. B. planning buildings. C. conducting warfare. D. working with metal. Question #48 What change took place in Hinduism during the Gupta Empire? A. Many of its laws were improved. B. Many of its legends were written down. C. Many of its complex rituals were abandoned. D. Many of its most sacred temples were destroyed. Question #49 In the Gupta Empire, what was an important use for all the following materials? • Stone • Wood • Bronze • Terra-cotta clay A. weapons B. sculptures C. cooking pots D. wheeled carts Question #50 Which of the following groups of people made it possible to construct complex buildings like this one? A. slaves B. monks C. astrologers D. mathematicians Wager some Points!!! You may wager (bet) 0 to 20 of your points. If you answer correctly you gain the points you bet. If you answer incorrectly you lose the points you bet. Please write how many points you want to wager? Final Challenge Question! Directions: Write the following answer on your boards! How does the sculpture of Buddha illustrate a Buddhist ideal or value?