Wrist Lab Presentation
advertisement
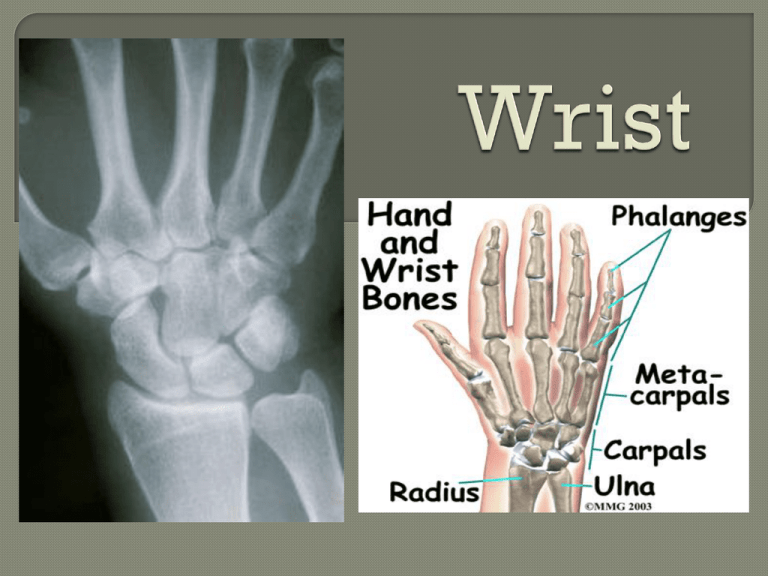
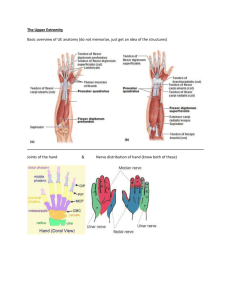
• 3 wrist flexors flexor carpi radialis flexor carpi ulnaris palmaris longus • 3 wrist extensors extensor carpi radialis longus extensor carpi radialis brevis extensor carpi ulnaris Condyloid-type joint Flexion – 70-90 degrees Extension – 65-85 degrees Abduction – 15-20 degrees Adduction – 25-40 degrees Articulation primarily occurs between the distal radius and the proximal carpal row (scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum) Movement Plane Axis Flexion (palmar flexion) Sagittal Lateral Extension (dorsiflexion) Sagittal Lateral Abduction (radial deviation, radial flexion) Frontal Anteroposterior Adduction (ulnar deviation, ulnar flexion) Frontal Anteroposterior Metacarpals Hamate Trapezium Triquetrum Trapezoid Scaphoid Pisiform Lunate Capitate Interphalangeal Joint • Collateral Ligament • Palmar Ligament Metacarpophalangeal Joint • Collatoral Ligament • Palmar Ligament • Deep Transverse Metacarpal Ligament Palmar Flexion Carpal tunnel syndrome • Swelling & inflammation can cause increased pressure in carpal tunnel resulting in decreased function of median nerve leading to reduced motor & sensation function in its distribution • particularly common with repetitive use of the hand and wrist in manual labor and clerical work such as typing and keyboarding • Often, slight modifications in work habits and hand & wrist positions during these activities can be preventative • Flexibility exercises for the wrist & finger flexors may be helpful The book said there were too numerous to mention in this discussion. Wrist Flexion • 0 to ± 80 degrees Wrist Extension • 0 to ± 70 degrees Ulnar Deviation • 0 to 30 degrees Radial Deviation • 0 to 20 degrees Collateral Ligament Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Flexor Carpi Radialis Medial epicondyle of humerus Base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpals on palmar surface -Flexion of wrist -Abduction of wrist -Weak flexion of elbow -weak pronation of forearm Median nerve (C6 and C7) Palmaris Longus Medial epicondyle of humerus Palmar aponeurosis of the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th metacarpals -Flexion of wrist -Weak flexion of elbow Median nerve (C6 and C7) Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Medial epicondyle of humerus and posterior aspect of proximal ulna Base of 5th metacarpal (palmar surface), pisiform, and hamate -Flexion of wrist -Adduction of wrist -Weak flexion of elbow Ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) Muscle Flexor Digitorum Profundus Origin Proximal ¾ of anterior and medial ulna Flexor -Medial Digitorum epicondyle of Superficialis humerus -Ulnar head: medial coronoid process -Radial head: upper 2/3 of anterior border of the radius just distal to the radial tuberosity Insertion Action Innervation Base of distal phalanges of four fingers Flexion of the four fingers at the metacarpophalangeal, proximal interphalangeal, and distal interphalangeal joints Median nerve (C8, T1) to 2nd and 3rd fingers; ulnar nerve (C8, T1) to 4th and 5th fingers Each tendon splits and attaches to the sides of middle phalanx of four fingers on palmar surface -Flexion of the fingers at the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints -Flexion of wrist -Weak flexion of elbow Median nerve (C7, C8, and T1) Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Extensor Carpi Lateral Ulnaris epicondyle of humerus and middle ½ of the posterior border of the ulnaq Base of 5th metacarpal on dorsal surface -Extension of wrist -Adduction of wrist -Weak extension of elbow Radial nerve (C6, C7, and C8) Extensor Carpi Lateral Radialis Brevis epicondyle of humerus Base of 3rd metacarpal on dorsal surface -Extension of wrist -Abduction of wrist -Weak flexion of elbow Radial nerve (C6 and C7) The flexor carpi ulnaris is important in wrist flexion or curling activities. It is one of only two muscles involved in wrist adduction or ulnar flexion. It may be strengthened with any type of wrist-curling activity against resistance. The ulnar nerve assists the flexor carpi ulnaris in • Flexion of the wrist • Adduction of the wrist • Weak flexion of the elbow therefore these movements would be most affected if the ulnar nerve gets injured. Opposition will not take place in its full range of motion. Eccentric Contraction Isometric Contraction A – wrist flexion B – wrist extension