Knight_ch10
advertisement

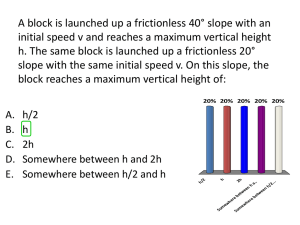
Chapter 10 Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the gravitational potential energies of balls 1 to 4. 1. (Ug)1 > (Ug)2 > (Ug)3 > (Ug)4 2. (Ug)4 > (Ug)3 > (Ug)2 > (Ug)1 3. (Ug)1 > (Ug)2 = (Ug)4 > (Ug)3 4. (Ug)3 > (Ug)2 = (Ug)4 > (Ug)1 5. (Ug)4 = (Ug)2 > (Ug)3 > (Ug)1 Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the gravitational potential energies of balls 1 to 4. 1. (Ug)1 > (Ug)2 > (Ug)3 > (Ug)4 2. (Ug)4 > (Ug)3 > (Ug)2 > (Ug)1 3. (Ug)1 > (Ug)2 = (Ug)4 > (Ug)3 4. (Ug)3 > (Ug)2 = (Ug)4 > (Ug)1 5. (Ug)4 = (Ug)2 > (Ug)3 > (Ug)1 A small child slides down the four frictionless slides A–D. Each has the same height. Rank in order, from largest to smallest, her speeds vA to vD at the bottom. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. vA = vB = vC = vD vD > vA = vB > vC vD > vA > vB > vC vC > vA = vB > vD vC > vB > vA > vD A small child slides down the four frictionless slides A–D. Each has the same height. Rank in order, from largest to smallest, her speeds vA to vD at the bottom. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. vA = vB = vC = vD vD > vA = vB > vC vD > vA > vB > vC vC > vA = vB > vD vC > vB > vA > vD A box slides along the frictionless surface shown in the figure. It is released from rest at the position shown. Is the highest point the box reaches on the other side at level a, at level b, or level c? 1. At level a 2. At level b 3. At level c A box slides along the frictionless surface shown in the figure. It is released from rest at the position shown. Is the highest point the box reaches on the other side at level a, at level b, or level c? 1. At level a 2. At level b 3. At level c The graph shows force versus displacement for three springs. Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the spring constants k1, k2, and k3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. k3 > k2 > k1 k1 = k3 > k2 k2 > k1 = k3 k1 > k2 > k3 k1 > k3 > k2 The graph shows force versus displacement for three springs. Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the spring constants k1, k2, and k3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. k3 > k2 > k1 k1 = k3 > k2 k2 > k1 = k3 k1 > k2 > k3 k1 > k3 > k2 A spring-loaded gun shoots a plastic ball with a speed of 4 m/s. If the spring is compressed twice as far, the ball’s speed will be 1. 16 m/s. 2. 8 m/s. 3. 4 m/s. 4. 2 m/s. 5. 1 m/s. A spring-loaded gun shoots a plastic ball with a speed of 4 m/s. If the spring is compressed twice as far, the ball’s speed will be 1. 16 m/s. 2. 8 m/s. 3. 4 m/s. 4. 2 m/s. 5. 1 m/s. A particle with the potential energy shown in the graph is moving to the right. It has 1 J of kinetic energy at x = 1 m. Where is the particle’s turning point? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. x=2m x=3m x=4m x=5m x=6m A particle with the potential energy shown in the graph is moving to the right. It has 1 J of kinetic energy at x = 1 m. Where is the particle’s turning point? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. x=2m x=3m x=4m x=5m x=6m Chapter 10 Reading Quiz Energy is a physical quantity with properties somewhat similar to 1. money. 2. heat. 3. a liquid. 4. work. 5. momentum. Energy is a physical quantity with properties somewhat similar to 1. money. 2. heat. 3. a liquid. 4. work. 5. momentum. Hooke’s law describes the force of 1. gravity. 2. tension. 3. a spring. 4. collisions. 5. none of the above. Hooke’s law describes the force of 1. gravity. 2. tension. 3. a spring. 4. collisions. 5. none of the above. A perfectly elastic collision is a collision 1. between two springs. 2. that conserves potential energy. 3. that conserves thermal energy. 4. that conserves kinetic energy. 5. All of 2, 3, and 4. A perfectly elastic collision is a collision 1. between two springs. 2. that conserves potential energy. 3. that conserves thermal energy. 4. that conserves kinetic energy. 5. All of 2, 3, and 4.