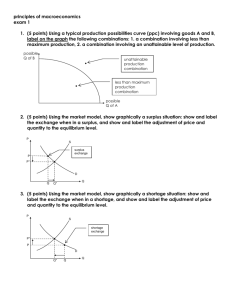
10/7 KEY - Iowa State University
advertisement
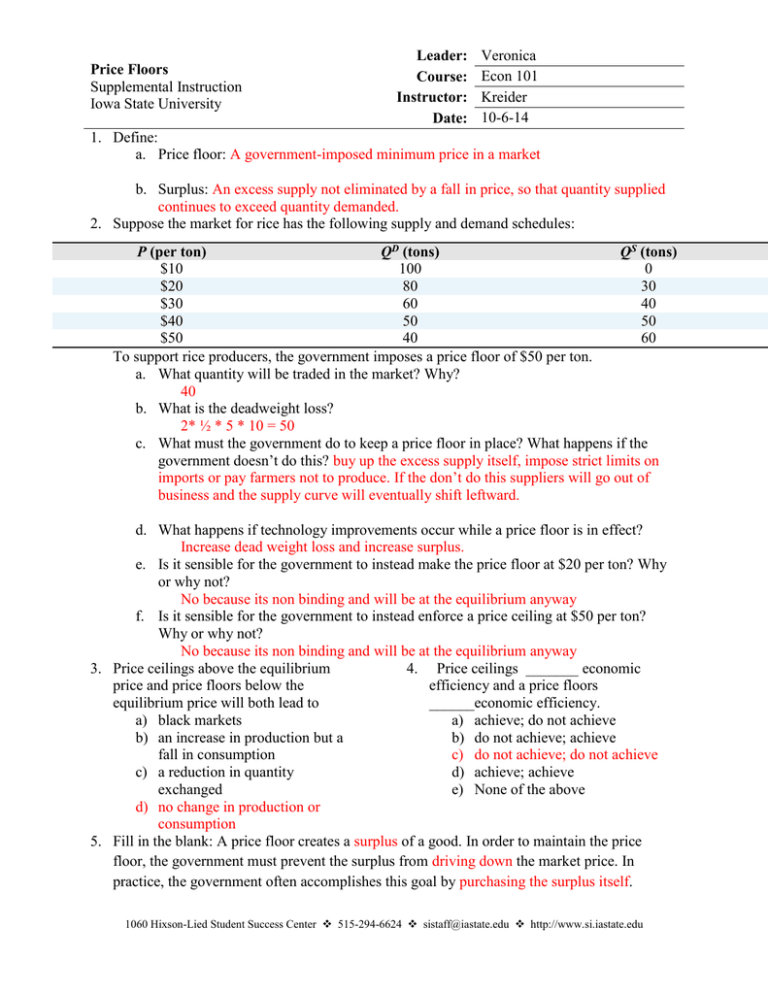
Price Floors Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Veronica Econ 101 Kreider 10-6-14 1. Define: a. Price floor: A government-imposed minimum price in a market b. Surplus: An excess supply not eliminated by a fall in price, so that quantity supplied continues to exceed quantity demanded. 2. Suppose the market for rice has the following supply and demand schedules: P (per ton) QD (tons) QS (tons) $10 100 0 $20 80 30 $30 60 40 $40 50 50 $50 40 60 To support rice producers, the government imposes a price floor of $50 per ton. a. What quantity will be traded in the market? Why? 40 b. What is the deadweight loss? 2* ½ * 5 * 10 = 50 c. What must the government do to keep a price floor in place? What happens if the government doesn’t do this? buy up the excess supply itself, impose strict limits on imports or pay farmers not to produce. If the don’t do this suppliers will go out of business and the supply curve will eventually shift leftward. d. What happens if technology improvements occur while a price floor is in effect? Increase dead weight loss and increase surplus. e. Is it sensible for the government to instead make the price floor at $20 per ton? Why or why not? No because its non binding and will be at the equilibrium anyway f. Is it sensible for the government to instead enforce a price ceiling at $50 per ton? Why or why not? No because its non binding and will be at the equilibrium anyway 3. Price ceilings above the equilibrium 4. Price ceilings _______ economic price and price floors below the efficiency and a price floors equilibrium price will both lead to ______economic efficiency. a) black markets a) achieve; do not achieve b) an increase in production but a b) do not achieve; achieve fall in consumption c) do not achieve; do not achieve c) a reduction in quantity d) achieve; achieve exchanged e) None of the above d) no change in production or consumption 5. Fill in the blank: A price floor creates a surplus of a good. In order to maintain the price floor, the government must prevent the surplus from driving down the market price. In practice, the government often accomplishes this goal by purchasing the surplus itself. 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 sistaff@iastate.edu http://www.si.iastate.edu