File
advertisement

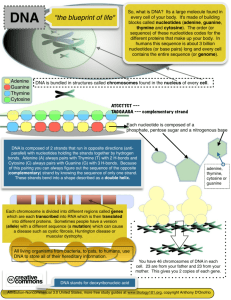
What does DNA look like? • Inherited characteristics are determined by genes, which are parts of chromosomes. • Chromosomes are structures in the nucleus of most cells. • Chromosomes are made of protein and DNA. (deoxyrybonucleic acid) Nucleotides • DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides, which consists of a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. • Nucleotides are identical except for their base, which all have a different shape. • There are Four Bases. – – – – Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Important discoveries • In the 1950’s, Erwin Chargaff found that the amount of adenine in DNA always equals the amount of thymine, and that the amount of guanine always equals the amount of cytosine. This is known as Chargaff’s Rules. • British scientist Rosalind Franklin was able to make images of DNA molecules using a process known as Xray diffraction. This revealed that DNA has a spiral shape. Watson and Crick • Once Franklin had determined the spiral shape of DNA, James Watson and Francis Crick were able to determine that DNA must look like a long, twisted ladder. • Their model perfectly fit with both Chargaff’s and Franklin’s findings and eventually was able to help explain how DNA is copied and how it functions in the cell. DNA’s Double Structure • The twisted ladder shape of DNA is known as a double helix. • The sides of the ladder are made of alternating sugars and phosphates. The rungs are made of a pair of bases. • Remember, because of Chargaff’s Rules, Adenine always pairs with Thymine, and Guanine always pairs with Cytosine. Making copies of DNA • DNA copies itself by the process of replication. • Because the bases are complimentary and can only pair with a single other base, one side of a strand of DNA will tell you what the other side is. For instance the sequence CGAC will bond with GCTG. • During Replication, DNA splits down the middle, and the base for each side of the strand are used as a pattern for a new strand. • DNA is copied every time a cell divides. Each cell gets a complete copy of all the DNA.