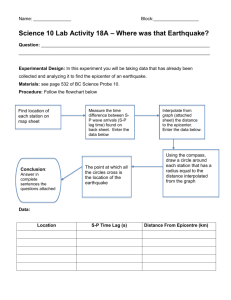
Earth Systems 3209
Unit: 4
The Forces Within Earth
Reference:
Chapters 4, 15, 16, 19; Appendix A & B
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Unit 4:
Topic 4.1
Terminology Associated with Seismic Activity
Focus on . . .
defining the following terms; seismology, earthquake,
seismic wave, foreshock, aftershock, seismograph,
seismogram, focus and epicentre.
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Terminology Associated with Earthquakes
When an earthquake occurs, the elastic energy is released
and sends out vibrations that travel throughout the Earth.
These vibrations are called seismic waves. The study of how
seismic waves behave within Earth is called seismology.
Earthquake - is the vibration of Earth produced by the
sudden, rapid release of energy. Usually along faults.
Main causes of earthquakes include:
1) Moving magma
2) Elastic rebound
3) Movement along faults
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Foreshock and Aftershock
Foreshock
a minor earthquake preceding a greater one
which originate at or near the same location.
Aftershock
small earthquake or tremor that follows a major
earthquake.
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Earthquake Focus and Epicenter
A fault is the plane or zone of fracture
separating two blocks that are abruptly
displaced during an earthquake.
The focus is the point at depth, usually
in a fault zone, where the displacement
and sudden release of elastic energy
originates. It marks the initial release of
energy associated with the earthquake.
Earth’s Surface
Epicenter
Fault
Plane
The epicenter is the point on the
surface directly above the focus.
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Focus
Seismograph and Seismogram
Earthquakes generate seismic waves
which can be detected with a sensitive
instrument called a seismograph.
How a seismograph works:
Free weight is freely suspended from a
support that is attached to bedrock.
When earthquake occurs, inertia keeps
the weight motionless while rock and
supports vibrate.
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Seismograph and Seismogram
A seismogram is a graph output by a seismograph. It is a
record of the ground motion at a measuring station.
Used to locate the epicenter of an earthquake.
These paper records are important when seismologist wants to
locate the position of the epicenter of an earthquake.
P-waves, S-waves, and Surface waves are all recorded on the
seismogram as seen below:
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Example 1:
Which branch of Earth Sciences would study the
properties of earthquake waves?
(A)
(C)
geomorphology
seismology
(B)
(D)
meteorology
volcanology
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Example 2:
In the diagram below, where is the epicentre of
the earthquake located?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
A
B
C
D
B
A
C
0 km
50 km
focus
100 km
D
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Your Turn . . .
Take the time and complete the following questions . . .
(Solutions to follow)
Question:
Which of the following instruments can help locate how far away an
earthquake occurred?
(A) seismograph
(C) tilt meter
(B) magnometer
(D) seismogram
Which is the point of origin of an earthquake?
(A) epicentre
(C) epicycle
(B) fault
(D) focus
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Solutions . . .
Question:
Which of the following instruments can help locate how
far away an earthquake occurred?
(A) seismograph
(C) tilt meter
(B) magnometer
(D) seismogram
Which is the point of origin of an earthquake?
(A) epicentre
(C) epicycle
(B) fault
(D) focus
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador
Summary . . .
Overview of Points covered:
Common terminology include;
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
Seismology
Earthquake
Seismograph
Seismogram
Focus
Epicenter
Foreshock
Aftershock
Copyright © 2014 All rights reserved, Government of Newfoundland and Labrador