CHAPTER 7 Dynamics of markets: Imperfect markets OLIGOPOLIES
advertisement

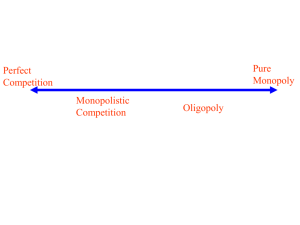
Oligopoly: a situation in which a particular market is controlled by a small group of firms. • Homogeneous product oligopoly: intermediate goods used by different industries to manufacture goods (eg steel, aluminium). • Differentiated product oligopoly: goods for personal consumption. (eg computers, cars) Example of an Oligopolistic Market 1. Few big firms dominate the market 2. Producers differentiated products as much as possible (though still substitutes) 3. Barriers to entry and exit exist from complete to free • non-price competition • access to raw materials • Licences (SA cell phone industry – gov only granted 3 licences) 4. Incomplete information • Each firm tries to prevent other firms in the industry from getting knowledge of its production processes, new products, R&D 5. Interdependence exists • firms consider rivals’ reactions while adjusting prices and outputs. 6. Collusion • Formal/informal agreement between firms to divide the market, set prices or limit production. Act as a monopoly to restrict output. 7. Firms have a kinked demand curve – prices remain fairly stable The firm faces a ‘kinked demand The principle of price, the kinked Assume the firm is charging a follow If they lower rivalsdemand will curve’ forcing stable pricing curve rests on principle that… price of R5 andthe producing an suit. structure. May be overcome by output of 100. • •non-price If a%firm raises price, its rivals change Qits <% reduction in P competition. will not follow suitR5 rivals If they charge above • inelastic demand curve would not follow suit. • If a firm lowers its price, its rivals • revenue will decrease all do the same • will elastic demand (substitutes available) Price R5 • revenue will decrease New Revenue Original Original Revenue Revenue Kinked D Curve New Revenue D = elastic D = Inelastic 100 Quantity MR & the Kinked demand Curve 8. Non-price competition • Price wars uncommon as everyone loses out Non-price competition includes… a) Product differentiation b) Product diversification/proliferation Unilever own ALL of these brands! c) Advertising d) Packaging