The Balance of Payments
advertisement

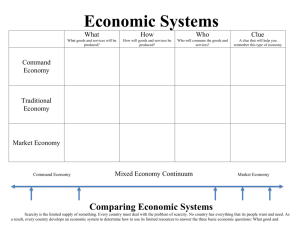
Economic Systems How are resources allocated? Topic Plan • • • • • Scarcity The Market economic system The Command economic system The mixed economy Market Vs Command systems Economic Systems • The way a nation is organised to respond to the problem of scarcity • Different economic systems use different methods to answer the Basic Economic Questions : – 1. What to produce – 2. How to produce – 3. For whom to produce Unlimited Needs and Wants Scarce Productive Resources Relative Scarcity Basic Economic Questions The Need for an Economic System Types of Economic Systems • The Market economy • The Command economy • The Mixed economy 1. Market Economies • Also called capitalist or private enterprise systems. Features are: • Productive resources are mainly owned by private individuals. Features of market economies (cont.) • Economic decision making is decentralised (i.e. decisions are made by individuals ) and the level of government intervention is low. • Economic motivation is self interest (e.g profit motive) Features of market economies (cont.) • Price is major criterion to allocate goods and resource ( price system/mechanism ). • Efficiency is valued or rewarded. 2. Command Economies • Also called socialist or centrally planned economies. Features are: • Productive resources are owned mainly by the state or the government. Features of command economies (cont.) • Economic decision making is made by a central authority or the government • Goods/services are distributed to benefit the state as a whole, rather than individuals Features of command economies (cont.) • Non-price mechanisms such as queuing, rationing coupons are used to allocate goods among people. • Equity is valued. 3. The Mixed Economy • All modern economies are said to be a mixture of - market forces ( price system ) and - government intervention • In the past, major examples of centrally planned economies were the former USSR and China. These now have allowed levels of market forces to operate Economies in Transition The ll-Out?Approach • Examples: Poland, East Germany, Russia, Czech republic • Rapid price and trade liberalisation – immediate opening of markets – privatisation of most state owned enterprises – reform of tax, legal and financial system Economies in Transition The Phased approach • Example: China • 1978 Opening the doors to joint ventures • gradual price liberalisation • Agricultural reform • Reform of state run enterprises • Relaxed restrictions on on-state?industrial firms (eg collectives, local government) Market Vs Command Systems • Advantages of market systems – eg: economic freedom, efficiency etc • Disadvantages of market systems – eg: unequal distribution of income and wealth • Advantages of command systems – eg: Equity ( in theory ) • Disadvantages of command systems – eg: inefficiencies and waste The End ?McGraw-Hill Book Company Australia, 1999 PPS t/a Economics for Business 2/e 2-16