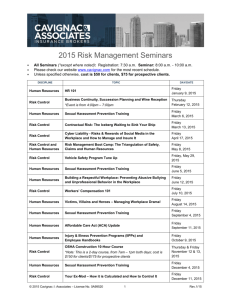
This Webcast Will Begin Shortly
If you have any technical problems with the
Webcast or the streaming audio, please contact us
via email at:
accwebcast@commpartners.com
Thank You!
The Latest Trends In EEO Law:
What’s Creating Risk in Your Workplace?
Wednesday, March 26, 2008
Association of Corporate Counsel
www.acc.com
Page 3
Shanti Atkins, Esq.
President & CEO of ELT.
Specialist in online ethics and legal
compliance training.
Advises clients across multiple
industries and of all sizes about
strategic risk management and
compliance initiatives.
Page 4
Margaret Hart Edwards, Esq.
Shareholder, Littler Mendelson.
Litigated hundreds of employment law
cases in state and federal courts since
beginning practice in 1975.
Routinely advises employers on legal
compliance and litigation prevention
measures.
Trains extensively in harassment and
discrimination prevention.
Page 5
Who We Are
Created by
Littler
Mendelson in
1996
The nation’s
largest
employment
law firm
1st to Launch
Online
Compliance
Solution
Page 6
Used by more than
1,000 organizations
More than 2,000,000
employees and managers
trained
Page 7
EEOC FY 2007 Charge Statistics
Discrimination charges for 2007 break down as
follows:
Race: 37.0%
Sex: 30.1%
Retaliation under Title VII: 28.3%
Age: 23.2%
Disability: 21.4%
National Origin: 11.4%
Religion: 3.5%
Equal Pay: 1.0%
Page 8
Agenda
1.
The Technology Revolution
2.
Politics Can Be Divisive
3.
The New Face of Sex & Gender
Discrimination
4.
Race In America
5.
Sweet Revenge
6.
Other Noteworthy Trends and
Decisions
Page 9
1. The Technology Revolution
Technology has changed all of our lives
in ways we could never have predicted.
We started with cell phones and laptops.
We have now reached an entirely new
age of technology.
Ever evolving risk profile for American
businesses.
Page 10
Who Is Posting Content Online?
“You” are doing it!
55+ % of U.S. homes have a webconnected computer.
40+% of adults get news from the web.
54% of Gen Nexters use social networking
sites.
5% of employees have a personal blog (but
could be as high as 10 million workers.)
Only 15% of companies have a policy
that addresses blogging.
Sources: 2003 U.S. Census
Pew Research Poll 2006
Pew Research Poll 2007
Employment Law Alliance Poll 2006
Page 11
Blogging, MySpace, YouTube...New
Ways of Posting Content Online
Created Every Day!
Page 12
In the News
California AAA fired 27 employees for posting
messages to MySpace that were offensive on the
basis of weight and sexual orientation.
NY City investigator fired for making racist
comments on his MySpace page.
Comcast employee fired after customer posted a
video of the employee sleeping on the
customer’s couch to YouTube.
Collectors Universe fired an employee for
posting a photo of the CEO on his MySpace
profile. The company called it identity theft.
Page 13
More and More Employment Law Cases Turn
on Inappropriate Use of Electronic Resources
Legitimacy of demotion of a manager
turned on whether e-mail comments that
another employee was “stale” and “set in
her ways” amounted to age discrimination.
Erickson v. Farmland Indus., Inc., 271 F.3d 718 (8th Cir.
2001).
An employee was properly terminated in
part because of the employee’s harassment
of a fellow manager by means of an
anonymous e-mail.
Connell v. Consolidated Edison Co. of N.Y., 109 F. Supp. 2d
202 (S.D.N.Y. 2000).
Page 14
The Risks Are Real
Employees have access to and can share
inappropriate content 24/7 and the
employer could be liable.
Blakey v. Continental Airlines: NJ Supreme Court
warns that, because employer must make
reasonable efforts to prevent discriminatory
and harassing conduct, employer may be held
liable for discriminatory and harassing postings
by employees if the employer had reason to
know about them. 751 A.2d 538 (N.J. 2000).
No affirmative duty to monitor...yet.
Page 15
The Risks Are Real
Easier than ever to disclose
confidential information...and get
away with it.
In the News: Bank withdraws
attempt to shut down a website that
published its confidential documents
provided anonymously by a
disgruntled employee after New York
Times story characterizes the lawsuit
as an attack on the First Amendment.
(March 2008)
Page 16
The Risks Are Real
Recruiting nightmares:
Ethnic, gender and age
screening.
Are your recruiters
misusing these sites?
Page 17
Have You Considered...
What to do if an employee posts
inappropriate content
anonymously?
Hosting ISP won’t reveal identity of poster
without a subpoena.
“Anonymous Surfing” products route
Internet traffic through an anonymizing
server and can hide blogger’s IP address
even from the ISP that is hosting the blog.
Page 18
Krinsky v. Doe 6
California Court of Appeal refuses to
subpoena Yahoo! for identity of poster on
message-board who made sexual and highly
offensive comments about a company’s senior
executive, citing poster’s right to freedom of
anonymous speech. Santa Clara County Super.
Ct. No. CV059796 (Feb. 2008)
To subpoena identity of poster, Plaintiff must
make effort to notify poster and demonstrate
a prima facie legal violation.
Page 19
Ahead of the Trends – Practical Steps
Your Cyber Policy should:
Address new technologies.
Address the employer’s right to control
communications; dispel “free speech” myths.
Set clear rules for making statements about the
workplace, employees, clients etc.
Set clear rules about accessing sites.
Explain privacy rights and responsibilities.
Emphasize trademark and confidentiality issues.
Remember to train on the policy and clearly explain
the consequences for violating it.
Page 20
2. Hot Politics: The Presidential Race
Very divisive and emotional
issues:
Abortion
Healthcare
Environment
Economics
Immigration
War on Terror
Massive Media coverage
encourages constant
discussion.
Page 21
Have You Considered...
That the 2008 presidential race has prompted even
more discussion than usual about sensitive
subjects?
Race: Did Obama do enough to denounce the
“divisive” remarks associated with his campaign?
Gender: Is Clinton playing the “gender card”?
Age: McCain as the oldest
first-time presidential candidate?
Page 22
Not All Speech is Protected!
“Fighting words” - words which by their
very utterance inflict injury or tend to
incite an immediate breach of the peace.
Harassing or discriminatory comments.
“Captive Audience” nature of workplace
limits free speech rights: The workplace
is different from sidewalks and parks workers are not so free to leave to avoid
undesired messages.
Aguilar v. Avis Rent a Car, 21 Cal.4th 121 (1999)
Page 23
Not All Speech Is Protected!
Piggee v. Carl Sandburg College: Community college's
sexual harassment policy, which precluded instructor from
giving a student religious pamphlets on sinfulness of
homosexuality, is not an unconstitutional prior restraint on
free speech. 464 F.3d 667 (7th Cir. 2006)
Ng v. Jacobs Engineering Group: Employer can terminate
employee pursuant to its anti-harassment policy for sending
religious emails to unwilling employees. Employer is not
required to accommodate an employee’s religious belief by
allowing employee to impose that belief “personally and
directly on fellow employees.” 2006 Cal. App. Unpubl. LEXIS
9142 (Cal. Ct. App. Oct. 2006)
Page 24
Where Do You Draw The Line?
Peterson v. Hewlett-Packard Co: Employee
terminated for violating harassment policy and
insubordination when he disregarded the employer's
instructions to remove anti-gay scriptural passages
from his cubicle that he posted in response to
employer's workplace diversity campaign. 358 F.3d
599 (9th Cir. 2004)
Protected speech?
Page 25
“Core Political Speech”
No. Comments were not protected because
they were intended to demean or degrade
coworkers.
Comments would have been protected if
they were “core political speech” expressed political views about a
controversial political issue and not meant to
hurt the plaintiff.
Also not protected religious speech.
Page 26
Ahead of the Trend – Practical Steps
Train employees about prohibited conduct and
dispel “absolute free speech” myth.
Update your policy, which should:
Be based on realistic and enforceable rules
regarding workplace speech.
Teach your employees that respect and
inclusion are core values.
Inform employees that workplace policies are
broader than the law.
Page 27
3. The New Face Of Sex And Gender
Discrimination
“Next generation” claims
emerging:
Sexual favoritism gets noticed
It’s not just about women
anymore
Sexual Orientation and Gender
Identity
Family Responsibility
Discrimination
Page 28
Romance & Work
41% of workers between 25 and 40
admit they have had an office romance.
76% of workers think office romance is
more common than it was 10 years ago.
Why?
Employees are working longer hours.
Sexual taboos have relaxed.
Natural to look for and find a mate at
work.
Source: Harris Interactive and Spherion Corp Poll
Page 29
Sexual Favoritism Is A Time Bomb
CA court recently ruled that sexual
favoritism is actionable if widespread.
Both men and women can sue.
It doesn’t matter that relationship was
consensual.
Don’t need to show that you were subject
of sexual advances.
You sue because you were negatively
impacted by the favoritism.
You did not get the promo, job, or raise
because you were not sleeping with the
boss.
Miller v. Department of Corrections (Cal. Sup. Ct. 2005)
Page 30
Sexual Favoritism Is Newsworthy
Detroit Mayor Kwame Kilpatrick involved in
text-messaging sex scandal with a former aide.
Accusations that taxpayer funded-security was
used to cover up the relationship. Scandal
further muddied by recent “racially charged
statements.” Kilpatrick charged with perjury,
obstruction of justice and official misconduct
on 3/24/08.
Mark Everson’s immediate resignation sought
by Red Cross Board because of his romantic
involvement with subordinate. (11/07)
Paul Wolfowitz’s integrity questioned because
of his romantic relationship with a female World
Bank executive and subordinate. (4/07)
Page 31
Ahead of the Trend – Practical Tips
Consider a policy that:
Bans or discourages supervisor / subordinate
relationships.
Mandates disclosure and separates partners.
Applies to all forms of intimate relationships.
Train managers and employees:
Employees frequently unaware that the
employer even has a policy.
Training program should address risks of
sexual favoritism.
Page 32
It’s Not Just For Women Anymore….
Page 33
Sexual Orientation & Gender Identity
Protections Are Expanding
Page 34
Employment Non-Discrimination Act
Passed by House of Reps.
in November 2007.
Prohibits discrimination on
the basis of sexual
orientation.
Gender identity was
specifically removed.
Page 35
State and Local Law Protection
10 of 19 state laws that prohibit sexual
orientation discrimination include gender
identity.
Maffei v. Kolaeton Industries, Inc: Employer
who harasses an employee because the
person, as a result of surgery and
hormone treatments, is now a different
sex, violates New York City’s prohibition
against discrimination based on sex. 626
N.Y.S. 2d 391 (1995).
Page 36
Don’t Forget Anti-Harassment Laws
Even though Title VII does not
provide a cause of action for sexual
orientation discrimination,
employees can sue for same-sex
sexual harassment.
Cromer-Kendall v. District of Columbia
326 F. Supp. 2d 50 (D.D.C. 2004).
Page 37
Family Responsibility Discrimination
May 2007: EEOC issues enforcement
guidelines for unlawful disparate treatment
of workers with caregiver responsibilities.
The guidelines offer 20 concrete
examples of conduct the EEOC considers
illegal, such as treating male caregivers
more favorably than female caregivers.
Page 38
Family Responsibility Discrimination
FRD Claims have risen from 97 cases
in 1996, to 481 in 2005.
During a period when discrimination
claims overall have been dropping, FRD
bases have increased at an astonishing rate
of 400%.
Source: Hastings College of Law Worklife Center
Page 39
But Don’t Forget the Other Stuff
In 2007, sex discrimination was one of the
top 3 charges filed with EEOC (30.1%).
Sexual harassment in all forms still exists.
“Old school” stuff is still around.
Groping, jokes, and pornography.
Demeaning conduct.
26% of employed adults say they have
experienced sexual harassment at work:
17% of men
35% of women
Sources: EEOC Charges Statistics (2007), Harris
Interactive/lawyers.com Poll (2004)
Page 40
Have You Considered...
That discussions in the workplace of front page headlines
may be sexual harassment?
Discussion and jokes regarding Eliot Spitzer’s recent resignation could be
environmental harassment.
Conversations may create an intimidating, hostile or abusive work
environment that unreasonably interferes with an employee’s work
performance.
Page 41
It Is Expensive If You Get It Wrong
EEOC sued Custom Cut
Companies on behalf of 3 female,
former sales reps
Traditional harassment
Jokes, touching, retaliation, etc.
$1.1 million verdict (3/07)
Court also ordered company to
provide sexual harassment
training for all employees
Source: EEOC Press Release March 8, 2007
Page 42
Ahead of the Trend – Practical Tips
Ongoing harassment training is critical and
it should:
Explore the grey areas, not just the blatant
stuff.
Explore emerging issues such as sexual
favoritism, sexual orientation, gender
identity, and gender stereotyping.
Comply with CA’s stringent training
mandate (even if you’re not in CA).
Source: http://www.HarassmentTraining.com
Page 43
4: Race In America – Still A Big Issue
Percentage of Americans who
believe that racism is still a serious
problem:
84% of Blacks/African Americans
66% of non-Hispanic Whites
80% of white Americans have
racist feelings, and many may not
even recognize them as racist.
Sources: Gallup and CNN Polls
U. Conn. Professor Jack Dovidio Estimates
Page 44
But What’s Happening At Work
Percentage of Americans who have
experienced discrimination in the workplace
in 2006:
31% of Asian Americans
26% of African Americans
18% of Hispanic Americans
Compared to…
12% of White Americans
Source: Gallup Poll 2006
Page 45
And The Trend Continues
In 2007, the top EEOC charge
is, once again, Race
Discrimination.
Race discrimination charges
make up 37% of all EEOC
charges.
Page 46
EEOC Fights Back
EEOC E-Race Initiative (2/07)
Eradicate racism and colorism from the
workplace.
Education and outreach efforts.
Combined with EEOC’s new focus on
systemic and persistent forms of
discrimination.
We Can Expect:
Larger plaintiff cases
Big $$$
Big publicity
And more individual claims as a result of
outreach efforts
Page 47
5: Sweet Revenge: Retaliation Basics
Retaliation: taking adverse action against an
employee or job applicant because that
individual engaged in protected activity such as:
Filing a complaint or lawsuit,
Making an internal complaint, or
Participating in an investigation.
Victim does NOT need to prove the
underlying claim of harassment or
discrimination to win a retaliation lawsuit.
Most managers just don’t get it!
Page 48
The Retaliation Explosion
In 2007, retaliation claims made up 32.3% of all
EEOC claims.
Page 49
SOX & Retaliation
Right to be free from retaliation is expanding.
Sarbanes-Oxley created a new cause of
action to protect employees from retaliation
because they complained of or reported
violations of federal securities/shareholder law
(Article 8).
Separate and distinct from an EEO retaliation
claim.
Long arm reach of SOX protections?
O'Mahony v. Accenture Ltd., 07 Civ. 7916, 02/05/08
(S.D.N.Y.)
Page 50
The New Burlington Northern Standard
Standard for what may constitute retaliation
has been lowered. Not limited to clear-cut
actions like termination or demotion.
Title VII’s “anti-retaliation provision does not
confine the actions and harms it forbids to those
that are related to employment or occur at the
workplace.”
No bright line test – will require individual case
assessment making jury trials rather than summary
judgment more likely.
Burlington Northern & Sante Fe Railway
Co. v. White (U.S. Sup. Ct. 2006)
Page 51
State Supreme Court Places New Limit on Liability
for Discrimination
California Supreme Court determines that
supervisors cannot be held individually liable for
retaliation under California state antidiscrimination law.
Court leaves unresolved issue: What if retaliation
by employer takes form of harassment?
Jones v. Lodge at Torrey Pines (Cal. Sup. Ct. 2008)
Page 52
Ahead of the Trend – Practical Tips
Retaliation is one of the greatest “hidden
EEO risks” faced by your business today.
Most managers don’t even understand
retaliation basics and have no clue that the bar
was recently lowered.
Consider a stand-alone retaliation policy to
highlight the importance of this issue.
Manager training on retaliation is essential.
Page 53
6: Other Notable Trends and Decisions –
Pattern and Practice Cases
EEOC to focus on systemic discrimination
Announced new litigation initiative mid 2006.
Will pursue cases that impact broad classes of employees.
Willing to bring cases where $ may be small, but injunctive relief will
have big impact.
At the end of FY2006
43.3% (or 256)of active files involved challenges to policies or
multiple aggrieved parties.
Litigation success rate of 92.7%
What to expect:
More multi-plaintiff cases.
Plaintiffs’ attorneys will follow suit.
Page 54
Other Notable Trends – Bullying
45% of American workers feel they have been
the target of abuse. (2007 Employment Law
Alliance Poll)
Bullies are making the news – Starwood CEO
Steven Heyer ousted for being “very difficult to
work with.” (4/07)
Aggression on the job more harmful than sexual
harassment. (2008 Canadian Study)
Since 2003, 12 states have introduced 27 antibullying bills. (www.bullybuster.org)
Page 55
Other Notable Trends - Bullying
A new form of harassment? 9th Circuit
stripped employers of the “equal opportunity
jerk” defense. The same abusive conduct,
applied equally to men and women, found to
impact women more harshly.
EEOC v. National Education Association, 442 F.3d 840 (9th
Cir. 2005).
"Title VII is not a fault-based tort scheme. Title
VII is aimed at the consequences or effects of
an employment practice and not at the
motivation of co-workers or employers.”
Ellison v. Brady, 924 F.2d 872 (9th Cir. 1991).
Page 56
Notable Trend – New Military Leave
Laws
January 2008: National Defense Authorization
Act amends FMLA to extend coverage to
employees to care for family members injured
while on active military duty.
October 2007: New California law provides up
to 10 days of unpaid leave for a "qualified"
employee if the employee's military spouse is on
a leave from deployment in a combat zone with
the active duty, reserve military or National
Guard during a period of military conflict.
Page 57
Notable Decision – “Me Too”
Evidence of Discrimination
U.S. Supreme Court rules on admissibility of
“me too” evidence in discrimination cases.
"[T]he question whether evidence of
discrimination by other supervisors is relevant
... is fact-based and depends on many factors,
including how closely related the evidence is
to the plaintiff's circumstances."
Sprint/United Management Co. v. Mendelsohn
No. 06-1221 (Feb. 26, 2008)
Page 58
Putting It Back Together
Pay attention to trends, political issues, and
demographic shifts.
Stay in tune with what your employees are
doing and talking about.
Update your policies to reflect 21st century
issues.
Develop a comprehensive training plan and
train all employees and managers.
Questions?
satkins@elt-inc.com
mhedwards@littler.com
www.elt-inc.com │ 877.358.4621
Thank you for attending another presentation from
ACC’s Desktop Learning Webcasts
Please be sure to complete the evaluation form for this program as your comments and
ideas are helpful in planning future programs.
You may also contact Jacqueline Windley at windley@acc.com
This and other ACC webcasts have been recorded and are available, for one year after the
presentation date, as archived webcasts at www.webcasts.acc.com.
You can also find transcripts of these programs in ACC’s Virtual Library at
www.acc.com/vl