Government - sls
advertisement

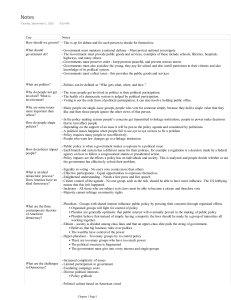
Chapter One Catherine Chou & Victoria Amoroso AP US Government Pd. 2 Basic Vocabulary Government: An institution that makes the authoritative decisions for society. Responsible for: • Maintaining national defense • Providing public services (known as public goods) • Preserving order • Socializing the young (education/morals/values) • Collecting taxes (national/state/local) Democracy: A system of selecting policy makers and of organizing government so that policy represents and responds to the public's reference. *Democracies must practice majority rule and preserve minority rule. (A fundamental democratic principle that the majority's view be respected. The Constitution originally limited majority rule) Basic Vocabulary cont. Politics is the process by which we select our government leaders and decide which policies we want them to pursue. Political participation is any way in which people get involved in politics, such as: • Voting (America does poorly at this) • Protest • Civil disobedience Harold D. Lasswell defines politics simply: "Who gets what, when, and how" • who-media, how-substance of politics & gov., how-how people participate ie-voting. Involves winners & losers. Policies - What are they, and who makes them? Policymaking system: • The process by which policy comes into being and evolves over time • Begins with the people • Determines which policies go into effect • the government's response to the priorities of its people. Policymakers are the Congress, the presidency, and the U.S. Supreme Court. The people's interests are represented to the policymakers through the media, elections, special interest groups, and political parties. These are known as linkage institutions. • Public policies affect all levels of society. Policies continued... Policymakers have a policy agenda consisting of the issues which the people are most concerned with, based on the information given to them by these linkage institutions. A government's policy agenda changes regularly. A political issue arises when policymakers disagree on the proper solution to a problem. part two. Types of Public Policy • Congressional statute - passed by Congress i.e. Social Security Act • Presidential action - decisions by the president U.S. troops in Iraq • Court decision Supreme Court ruling that school segregation is unconstitutional • Budgetary choices - legislative enactment of taxes and expenditures Federal budget • Regulation - FDA o Food and Drug Administration is responsible for ensuring products are up to regulation standards. Traditional Democratic Theory • Equality in voting: "one person, one vote". must be representative • Effective participation: citizens must have adequate and equal opportunities. • Enlightened understanding: democratic societies should have the right to control the government's policy agenda. • Citizen control of the agenda • Inclusion: government must include all those subject to its laws. (Citizenship must be open to all within a nation to call itself democratic) "Majority rule, minority rights" Theories of American Democracy Pluralist Theory: Groups with similar interests influence the public through organized effort. • Lobbying • Pluralists believe a public policy will prevail through public interest. Elite and class theory: Government is ruled by the upper class • Wealth as the basis of power (big business exempted from certain taxes, etc.) Hyperpluralism: Groups are so strong that the government is weakened. • America is an apple pie and pluralist groups have cut the pie into many slices, but they are not equal in size/influence and inevitably weaken and decentralize the government. Challenges to Democracy • Lack of technical expertise o It's more and more difficult for the general population to be well-informed. • Limited participation in government o People under the age of 25 have the lowest voter count o Apathetic • High campaign cost o Campaigning costs at least half a million dollars o Candidates fund their campaigns with money from PACs (Political Action Committees) o PACs have their own agenda • Diverse interests o Political parties have become more polarized o i.e. debt ceiling argument Political Culture Liberty. Freedom of speech, religion, etc. Egalitarianism. Not everyone is rich, but everyone has the opportunity to become rich through their own talents. Individualism. The common dream of America as a place to make it on your own without government interference. Laissez-faire. Government should interfere as little as possible in the affairs of the people; Puritan roots. Populism. Put the people first Culture war and government spending • Political parties have become more polarized (disagreeing more strongly about more issues) Yet, America is united by its political culture • 30% of our GDP is spent by our government • The government spends $3 trillion annually, employs two million people, and owns 1/3 of United States land. • 1/6th of the federal budget is devoted to national defense.