geometry mock exam
advertisement

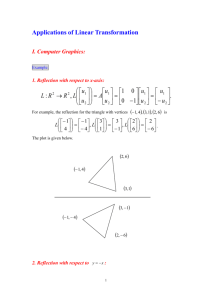
GEOMETRY MOCK EXAM 1. What term describes a transformation that does not change a figure’s size or shape? 6. A regular polygon with n sides is carried onto itself by a positive rotation about its center that is a multiple of 60°, but less than 360°. (A) similarity Which could NOT be the value of n? (B) isometry (A) 3 (C) collinearity (B) 4 (D) symmetry (C) 5 (D) 6 For questions 2–4, use the diagram showing parallelogram ABCD. 7. In the diagram, g h and B lies on line g. A E B 10 cm I H F 5 cm D G C B C 2. A reflection across EG carries parallelogram ABCD onto itself. A (A) True (B) False g 3. A rotation of 90° about I carries parallelogram ABCD onto itself. (A) True (B) False 4. A rotation of 180° about I carries parallelogram ABCD onto itself. (A) True (B) False 5. Which of these is equivalent to a translation? h The figure ABC is reflected across line g, and its image is reflected across line h. What is the distance from line g to the final image of point A? (A) 5 cm (B) 15 cm (C) 20 cm (D) 25 cm 8. What is the image of the point (–4, 6) under the transformation T x, y y, x ? (A) a reflection across one line (A) (6, 4) (B) a composition of two reflections across intersecting lines (B) (–6, –4) (C) a composition of two reflections across parallel lines (D) (–4, –6) (C) (4, 6) 9. A figure is rotated about the origin by 180°, then is translated 4 units right and one unit up. Which describes the results of the two transformations? For questions 13–16, determine if the described transformation(s) is/are an isometry. 13. A reflection is an isometry. (A) x, y x 4, y 1 (A) True (B) x, y x 4, y 1 (B) False (C) x, y y 4, x 1 (D) x, y y 4, x 1 14. A composition of two reflections is an isometry. (A) True 10. The point A(4, 3) is rotated –90° about the origin. In which quadrant is A' ? (A) I (B) False 15. A dilation is an isometry. (B) II (A) True (C) III (B) False (D) IV 11. A figure is reflected across the line y = 2, then reflected across the line y = 4. Which single transformation results in the same image? 16. A composition of a rotation and a dilation is an isometry. (A) True (B) False (A) a reflection across the line y = 3 (B) a reflection across the line y = 6 (C) a translation 2 units up (D) a translation 4 units up 12. Point A is the image of point A under a transformation T. Line is the perpendicular bisector of AA at point M. Which describes the transformation T? 17. In ABC , M is the midpoint of AB and N is the midpoint of AC . For which type of 1 triangle is MN BC ? 2 (A) equilateral only (B) isosceles only (C) scalene only (A) a reflection across (D) any triangle (B) a 90° rotation about M (C) a translation by the vector from A to M (D) a dilation about M with scale factor 2 18. After a figure is rotated, P P . Which statement(s) could be true? (A) The center of rotation is P. (B) The angle of rotation is a multiple of 360°. (C) Either A or B or both. (D) Neither A nor B. 19. Use the diagram. m 23. Given point A is located at (1, 3). What is the final image of A after this series of transformations? k 44° 22° (1) Reflect A across the y axis. (2) Translate the image such that x, y x 4, y 2 . (A) (–1, –3) (B) (–3, 5) A (C) (–3, –1) (D) (–5, 5) For questions 24–27, use the diagram where B is the reflection of A across PQ . Which series of reflections would result in a rotation of –44° about A? (A) reflect across k¸ then reflect across P (B) reflect across ¸ then reflect across k (C) reflect across ¸ then reflect across m (D) reflect across m¸ then reflect across For questions 20–21, a transformation S is defined as x, y 3x, y 1 . 20. The pre-image of A 3, 6 under S is A 9, 5 . (A) True (B) False A 24. PA = PB (A) True (B) False 25. PQ AB (A) True 21. S is an isometry. (B) False (A) True (B) False 26. AQ = QB (A) True 22. Which transformation does NOT preserve the orientation of a figure? (A) dilation (B) reflection (B) False 27. PQ 1 AB 2 (C) rotation (A) True (D) translation (B) False Q B 28. Use the figure. For questions 29–31, use the diagram where ABCD is a quadrilateral with AB CD and AD BC . Diagonals AC and BD intersect at E. B A E A transformation T is defined as x, y x, – y . Which shows the image of figure under T? C D 29. CBE ABE (A) True (A) (B) False 30. ADE ABE (A) True (B) False 31. CDE ABE (A) True (B) (B) False 32. A figure is transformed in the plane such that no point maps to itself. What type of transformation must this be? (A) dilation (B) reflection (C) (C) rotation (D) translation For questions 33–36, determine if the mapping is an isometry. 33. x, y x, y 2 is an isometry. (A) True (B) False 34. x, y x, y is an isometry. (B) False x, y y, x is an isometry. (A) True (B) False 36. 39. A rotation of 90° about P results in P = P. (A) True (B) False 40. A translation by the vector 6, 0 results in P = P. (A) True 35. For questions 39–41, point P is located at (6, 0) and undergoes a transformation. x, y 2x, y (A) True (B) False 41. A reflection about the x axis results in P = P. (A) True (B) False For questions 42–43, use the diagram which shows ABC has been reflected across an unknown line , then reflected across line m to produce ABC. y C A is an isometry. (A) True (B) False For questions 37–38, determine the truth of the statements about rotations. B B x A 37. Rotations preserve the orientation of a figure. (A) True C (B) False 38. Under a rotation, no point can map to itself. m 42. The equation of line is x = –0.5. (A) True (A) True (B) False (B) False 43. If ABC were reflected across line m first, then reflected across line to produce ABC, the equation of line would be x = – 0.5. (A) True (B) False For questions 44–46, consider a triangle ABC that has been transformed through rigid motions and its image compared to XYZ . Determine if the given information is sufficient to draw the provided conclusion. 44. Given A X Conclusion B Y C Z ABC XYZ Look at the figure below. Look at these three figures. I (A) True (B) False 45. II Given A X B Y Conclusion ABC XYZ BC YZ (A) True (B) False 46. Given A X Conclusion AB XY ABC XYZ BC YZ III 48. Which figures are congruent to the first figure? (A) True (A) I only (B) False (B) II only 47. Use the diagram. s r 3 4 1 2 (C) I and II only m n 8 7 (D) I, II, and III For questions 49–50, consider ABC where AB = BC and mA 40 . 6 5 Which statement would be used to prove lines r and s are parallel? (A) 1 and 3 are congruent (B) 2 and 7 are complementary (C) 4 and 1 are congruent (D) 8 and 6 are supplementary 49. mB mC 140 (A) True (B) False 50. mC 100 (A) True (B) False For questions 51–53, evaluate whether the image of a figure under the described transformation is congruent to the figure. 51. A transformation T follows the rule x, y x 3, y . The image of a figure under T is congruent to the figure. Use the Venn diagram. Quadrilaterals I Parallelograms II Rhombi Squares III IV Rectangles V (A) True (B) False Trapezoids VI VII Kites 52. A transformation T follows the rule x, y y, x . The image of a figure under T is congruent to the figure. 55. A quadrilateral ABCD has 4 lines of symmetry. Identify the area of the diagram in which ABCD resides. (A) True (B) False 53. A transformation T follows the rule x, y x, 2 y . The image of a figure under T is congruent to the figure. (A) III (B) IV (C) V (D) VII (A) True (B) False In the diagram, m n and p q . p q m 88° x° What is the value of x? (A) 44 (A) 96 square units (B) 192 square units n 54. 56. Right triangle PQR has sides of length 6 units, 8 units, and 10 units. The triangle is dilated by a scale factor of 4 about point Q. What is the area of triangle P'Q'R'? (C) 384 square units (D) 768 square units 57. The ratio of the side lengths of a triangle is 3:6:8. A second triangle is similar to the first and its shortest side measures 8.0 centimeters. What is the length of the longest side of the second triangle? (B) 88 (C) 92 (A) 3.0 cm (D) 176 (B) 10.7 cm (C) 13.0 cm (D) 21.3 cm Use the diagram below. 61. Which figure contains two similar triangles that are NOT congruent? A 4 9 H D (A) y 8 B C 58. What is the value of y? (B) (A) 13 (B) 18 (C) 27 (C) In the diagram, a student has placed a mirror on level ground, then stands so that the top of a nearby tree is visible in the mirror. 2m 3m 36 m (B) 35 m (B) 41 m (D) 59 m (B) The triangles could be similar. (C) The triangles must be similar. 63. Triangle ABC has vertices A 2, 2 , In the diagram, JG QR . Q 7 P 8 G x R 60. What is the value of x? (A) 11 (B) 6 (C) 5 (D) 3 B 5, 5 , and C 5, 3 . The triangle is J 4 62. Sally constructs a triangle where two of the angles measure 50° and 60°. Tom constructs a triangle where two of the angles measure 50° and 70°. What is true about the two triangles? (A) The triangles cannot be similar. 59. What is the height of the tree? (A) 24 m (D) dilated about the point 1, 1 with scale factor 4. What is the location of A' ? (A) 8, 8 (B) 10, 10 (C) 11, 5 (D) 14, 6 Use the diagram. In the diagram, segments AB and CD intersect at E, F lies on AB , and mAEC 60 . y m B D F E x 60° A 64. Dilate line m about the origin with scale factor 2. What is the equation of the line’s image? C 67. The two segments are dilated about F with 1 scale factor . What is mAEC ? 2 (A) 30° (B) 60° (A) y = 2x + 2 (B) y = 2x + 4 (C) 90° (D) 120° (C) y = 4x + 2 (D) y = 4x + 4 65. Which is NOT a criterion for triangle similarity? 68. In the diagram, ABCD is dilated with center O 1 to produce A'B'C'D', and AB AB . 3 A (A) angle-angle (B) angle-side-angle (C) side-angle-side D' (D) side-side A' F D O C' 66. J(5, 7) is the image of J(3, 3) after a dilation with scale factor 3. Where is the center of dilation? C B (A) (–3, –9) (B) (0, 0) What is (C) (2, 1) (D) (4, 5) B' (A) 1 3 (C) 2 OA ? AA (B) 1 2 (D) 3 69. Use the diagram. Use the right triangle. What is the value of x? C b 15 x a h x 8 y A D B c Which is equal to h? (A) ay (B) bx (C) xy (D) ab 72. What is the value of x? (A) 7 (B) 161 (C) 7 (D) 17 73. Consider a triangle ABC. Which statement is true? (A) c2 a2 b2 2ab cos C 70. J(5, 7) is the image of J(3, 3) after a dilation with scale factor 3. Where is the center of dilation? (B) c2 a2 b2 2ab cos C (C) c2 a2 b2 2ab cos C (D) c2 a2 b2 2ab cos C (A) (–3, –9) (B) (0, 0) (C) (2, 1) 74. Use the diagram. (D) (4, 5) A 71. Fred stands at corner A of a rectangular field shown below. He needs to get to corner C. A 7 4 B B 9m D 9 What is cos A ? 12 m C What is the shortest distance from A to C? (A) 9 m (B) 13 m (C) 15 m (D) 21 m (A) 16 56 (B) 56 16 (C) 16 56 (D) 56 16 C 75. A small airplane flies due north at 150 kilometers per hour. A wind is blowing towards the direction 60° east of north at 50 kilometers per hour. Which figure represents the final speed and direction of the airplane? (A) N (B) N (C) N (D) For questions76-78, consider a triangle ABC and each given set of measurements. N 79. The diagram shows a parallelogram ABCD. B 76. AB, AC, and mA are sufficient to solve the triangle using the Law of Sines. C (A) True 5 (B) False 77. AB, AC, and mB are sufficient to solve the triangle using the Law of Sines. (A) True (B) False 78. AB, AC, and BC are sufficient to solve the triangle using the Law of Sines. 60° A 3 D What is the parallelogram’s area? (A) 7.5 3 (B) 15 (A) True (C) 15 3 (B) False (D) 30 3 84. cos k cos 180 k 80. In the diagram, ABC is a non-right triangle. C (A) True B c Which describes the area of the triangle? (A) (B) False b a 1 ab 2 (B) ab sin C 1 (C) ab sin C 2 1 (D) ab cos C 2 81. Given: cos 26 0.90 and sin 26 0.44 A 85. Let cos A m . What is the value of sin A ? (B) 1 – m (C) 1 m2 (D) 1 m 86. In ABC , C is a right angle, sin A What is cos B? (A) 7 4 (B) 7 3 What is the approximate value of cos 154 ? (A) –0.90 (B) –0.44 (C) 0.44 (D) 0.90 For questions 82-84, use the statement below. Given: An angle measures k°, where k > 0. 82. sin k cos 90 k (A) True (B) False 83. sin k sin 180 k (A) True (B) False m (A) (C) (D) 3 4 3 7 7 . 4 87. Use the diagram. 89. Use the diagram. B 13 5 d 45° C A 12 What is the value of d ? Which statement is true? (A) sin A (A) 5 13 5 (B) 5 2 (C) 10 12 (B) cos A 13 (C) tan A (D) 10 2 For questions 90-92, let cos x m . 12 5 90. cos 180 x = m (A) True (B) False 88. Use the diagram. B A 35° x Which is the value of x? (A) x 41cos35 (B) x tan 35 41 (C) x 41 cos 35 (D) x 41 tan 35 91. cos 90 x = m 41 (A) True C (B) False 92. sin 90 x = m (A) True (B) False 93. Let a cos28 . Which statement is true? 96. What is tan 60°? (A) a cos 62 (A) 2 2 (D) a sin 152 (B) 3 2 3 94. What is cos 1 ? 2 (C) 1 3 (D) 3 (B) a cos 152 (C) a sin 62 (A) 30° 97. What is tan 1 1 ? (B) 45° (C) 60° (A) 30° (D) 90° (B) 45° 95. In the diagram, BC < BD and BD = AD. (C) 60° (D) 90° C 1 . 2 GH I is a dilation of GHI about G with a scale factor of 2. What is the sine of angle G' ? 98. In GHI , the sine of angle G equals A B D (A) 1 4 (B) 1 2 Which statement is true? (A) cos ABC sin DAB (B) cos ABC sin DAB (C) cos ABC sin DAB (C) (D) 1 3 2