Boston Tea Party - Social Studies Mr. Selin
advertisement

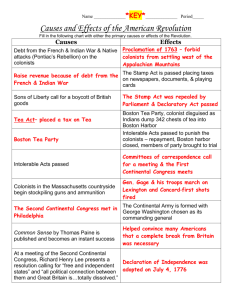
• The Boston Tea Party of December 16, 1773, took place when a group of Massachusetts Patriots, protesting the monopoly on American tea importation recently granted by Parliament to the East India Company, seized 342 chests of tea in a midnight raid on three tea ships and threw them into the harbor. 1. The “tea partiers” were not protesting a tax hike, but a corporate tax break. • The protestors who caffeinated Boston Harbor were railing against the Tea Act, which the British government enacted in the spring of 1773. Rather than inflicting new levies, however, the legislation actually reduced the total tax on tea sold in America by the East India Company and would have allowed colonists to purchase tea at half the price paid by British consumers. The Tea Act, though, did leave in place the hated three-pence-per-pound duty enacted by the Townshend Acts in 1767, and it irked colonists as another instance of taxation legislation being passed by Parliament without their input and consent. The principle of self-governance, not the burden of higher taxes, motivated political opposition to the Tea Act. 2. Commercial interests, perhaps more than political principles, motivated many protestors. • The Tea Act was a government bailout for a company on the brink of financial collapse, the flailing East India Company, which was deemed to be, in modern terms, “too big to fail.” The legislation gave the East India Company a virtual monopoly on the American tea trade, allowing it to bypass colonial merchants as middlemen and to even undercut the price of smuggled Dutch tea, which was widely consumed in the colonies. Thus, the Tea Act directly threatened the vested commercial interests of Boston’s wealthy merchants and smugglers, such as John Hancock, who fomented the revolt. 3. George Washington condemned the Boston Tea Party. • Although America’s foremost Revolutionary figure wrote in June 1774 that “the cause of Boston…ever will be considered as the cause of America,” he strongly voiced his disapproval of “their conduct in destroying the Tea.” Washington, like many other elites, held private property to be sacrosanct (most sacred or holy, not to be entered or tresspassed upon) and believed the perpetrators should compensate the East India Company for the damages. 4. It was the British reaction to the Boston Tea Party, not the event itself, that rallied Americans. • Many Americans shared Washington’s sentiment and viewed the Boston Tea Party as an act of vandalism by radicals rather than a heroic patriotic undertaking. There was less division among the colonists, however, about their opposition to the measures passed by the British government in 1774 to punish Boston. The legislation closed the port of Boston until damages were paid, annulled colonial self-government in Massachusetts and expanded the Quartering Act. Colonists referred to the measures as the “Intolerable Acts,” and they led to the formation of the first Continental Congress. 5. For decades, the identities of participants were shrouded in secrecy. • The band of protestors was tight-lipped. Even after American independence, they refused to reveal their identities, fearing they could still face civil and criminal charges as well as condemnation from elites for engaging in mob behavior and the wanton destruction of private property. Even today, only the names of some of the participants are known. 6. The event wasn’t dubbed the “Boston Tea Party” until a half-century later. • For years, Bostonians blandly referred to the protest as “the destruction of the tea.” The earliest newspaper reference to the “Boston Tea Party” doesn’t appear until 1826. In the 1830s, two books—A Retrospect of the TeaParty and Traits of the Tea Party—popularized the moniker and cemented it in popular culture. 7. Other protests There was a second Boston Tea Party. • Three months after the Boston Tea Party, Bostonians once again sent tea splashing when 60 disguised men boarded the Fortune in March 1774, forced the crew below deck and dumped tea chests into the harbor. The sequel wasn’t quite as impressive as the original, however, as only 30 chests were sent overboard. Copy cat Don’t mess with this cat !!!!! Roar, Roar 8. Subsequent “tea parties” were held in other colonies. • Tea Act protests spread to other colonies throughout 1774. In cities such as New York, Annapolis and Charleston, South Carolina, patriots dumped tea off ships or burned it in protest. 9. The financial loss was significant. • It’s estimated that the protestors tossed more than 92,000 pounds of tea into Boston Harbor. That’s enough to fill 18.5 million teabags. The present-day value of the destroyed tea has been estimated at around $1 million. 10. One “tea partier” appeared to rise from the dead. • After being knocked unconscious by a falling tea crate in the hold of a ship, John Crane was reportedly thought to be dead and hidden by his compatriots under a pile of wood shavings in a nearby carpenter’s shop. He awoke hours later, however, and was the only man harmed in the Boston Tea Party. What is being Shown in this picture? How can you tell the ships are British? What is in the foreground of this painting? What do you think is the artists point of view? • Did You Know? • It took nearly three hours for more than 100 colonists to empty the tea into Boston Harbor. The chests held more than 90,000 lbs. (45 tons) of tea, which would cost nearly $1,000,000 dollars today. This happened at midnight. Cause and Effect • A cause: • Is an event or action that makes something else happen. • An Effect: • That something else that happens is an effect. • Determining causes and effects can help you see relationships between events and find patterns in history. Explaining the importance of the tea act pages 118-119 • From your book • Identify one cause and one effect of the Boston Tea Party. Explaining the importance of the tea act • From your book • Why was the tea act passed? • What did the act do? • How did the Daughters of Liberty react? • When was the tea dumped over board? • (date and time)