Honors State and Local Govt. Study Guide 1. Which of the following
advertisement
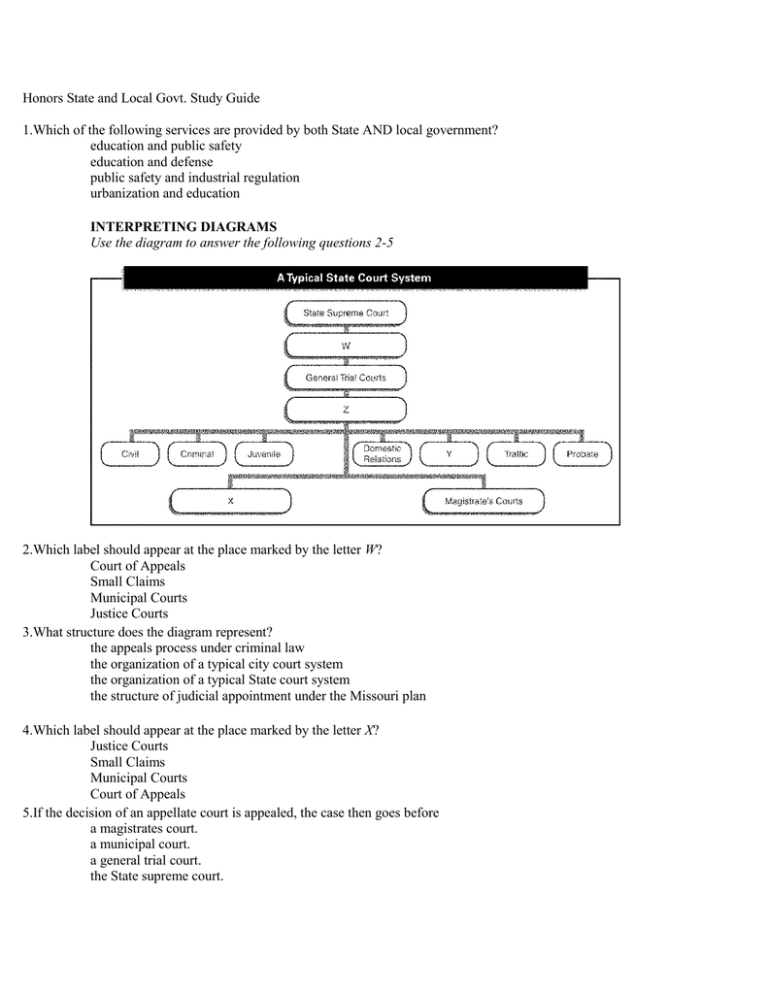
Honors State and Local Govt. Study Guide 1.Which of the following services are provided by both State AND local government? education and public safety education and defense public safety and industrial regulation urbanization and education INTERPRETING DIAGRAMS Use the diagram to answer the following questions 2-5 2.Which label should appear at the place marked by the letter W? Court of Appeals Small Claims Municipal Courts Justice Courts 3.What structure does the diagram represent? the appeals process under criminal law the organization of a typical city court system the organization of a typical State court system the structure of judicial appointment under the Missouri plan 4.Which label should appear at the place marked by the letter X? Justice Courts Small Claims Municipal Courts Court of Appeals 5.If the decision of an appellate court is appealed, the case then goes before a magistrates court. a municipal court. a general trial court. the State supreme court. 6.One major difference between the powers of most governors and those of the President is that the people look to the governor for leadership. the governor is responsible for seeing that the laws of the State are “faithfully executed.” the State budget originates with the governor. a governor often must appoint some members of the opposing party to posts in his or her administration. INTERPRETING DIAGRAMS Use the diagram to answer the following questions 7-10 7.Under the weak mayor-council plan, department administrators are directly accountable to the mayor only. municipal judges. mayor and council. council and other officials. 8.Under the strong mayor-council plan, what formal power does the mayor have to check the policies of the city council? the veto power the power to appoint judges the power to make policy no formal power is provided 9.Under the weak mayor council plan, the city council has executive power only. legislative power only. no power. both executive and legislative power. 10.Under both plans, the city council has the power to appoint municipal judges. to approve the mayor's acts. to make policy. to carry out policy. 11.Which of the following is NOT true of each State's constitution? Each State constitution details the means by which it may be amended. Each State constitution takes priority over all provisions of federal law. Each State constitution contains a bill of rights guaranteeing certain rights to the public. Each State constitution distributes power among the three branches of State government. 12.Today, the most widely used method for selecting judges to sit in State and local courts is popular election. selection by the legislature. selection by the governor. selection by judicial commission. 13.How long are the terms of State legislators? 1 or 2 years 2 or 3 years 1 or 3 years 2 or 4 years 14.The fundamental laws of each State are established by the governor. determined by State courts. never subject to change. the State constitution. 15.In 27 States, voters may propose the passage of laws by initiative. write-in ballot. optional referendum. mandatory referendum. 16.City zoning is most often opposed on the grounds that it typically raises property values. is used primarily to benefit real estate developers. denies people the right to use their property as they choose. has been declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court. 17.Which statement is true about all counties in the United States? Their size is based on the size of the State. Their size is based on the population of the State. They can only be created by the State. They serve only a judicial function. 18.The shift from rural to urban society in the United States was due to the invention of labor-reducing farm devices. improvements in transportation. growth in factory-based industries. all of the above. 19.An unreasonable tax classification would be one aimed exclusively at smokers. beer drinkers. people over 65. insurance policy holders. 20.All of the following factors contributed to the growth of the nation's suburbs after World War II EXCEPT a. the desire for cheaper land. b. the need for less privacy. c. the need for newer and better public schools. d. the desire for a higher social status. CRITICAL THINKING 21. Comparing Systems How do most States deal with the problem of juvenile crime? How does the justice administered by juvenile courts differ from the justice administered by adult courts? Do you think it is fair that a juvenile sometimes be treated as an adult in some court situations? Give reasons for your answers. ANS: Persons under 18 years old are usually treated as juveniles and tried in a separate court system, which generally emphasizes rehabilitation rather than punishment. However, depending on their age, the nature of the crime, and other extenuating factors, juvenile offenders may be treated as adults at a judge's discretion in almost every State. In fact, several States have laws stating that once a juvenile is tried as an adult, he or she will be automatically prosecuted as an adult for any later offenses. It would probably be unduly harsh to try a 10-year-old, first-time offender, as an adult unless the crime committed was extremely serious. Despite the trend toward making it easier to try juveniles as adults, it would seem that a few key questions must always be asked, such as whether the defendant is capable of knowing right from wrong and whether defendant realizes the consequences of his or her actions. 22. Drawing Conclusions Which do you think has a greater impact on the effectiveness of county governments: the structure of those governments or the people who run them? Give reasons for your answer. ANS: With executive powers divided among a governing board, various commissions, and separately elected officials, the structure of county government seems designed to be ineffective. As a result, an enormous burden is placed on officials working individually or as part of a group to operate effectively.







