Slide 1 - Trinity College Dublin
advertisement

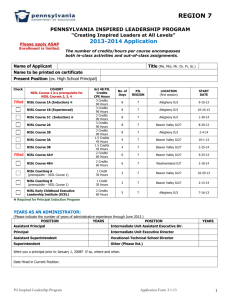
The Relationship between Physics and Philosophy By Kartik Chundru, Laura Byrne, Mark Allen and Tom Ambrose Supervisor: Prof. Stefan Hutzler Introduction Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec a nisl nisi, aliquam feugiat sapien. Cras iaculis odio sit amet diam facilisis eget dignissim erat luctus. Phasellus malesuada consectetur euismod. Duis tempus, dolor tempus gravida ultricies, purus felis placerat ipsum, ac sagittis metus mi at velit. Aenean lectus tellus, varius id vehicula nec, volutpat nec odio. Sed in nibh eget nisl aliquet commodo. Praesent risus urna, gravida at commodo et, iaculis at libero. Quisque sollicitudin velit vitae ligula porta sit amet porttitor leo fermentum. Aenean ut nisl at tortor tempor elementum. Quisque euismod tortor a nulla blandit placerat. Aliquam lacus. Natural Philosophy •The word Physics only came into use around the 19th century. Before this, what we know as Science today was called Natural Philosophy, the attempt to understand and explain the workings of the natural world in a contemplative way. •The mathematical and experiment based science of modern times set in around the 17th and 18th centuries, in what is now called the scientific revolution. Newton’s main scientific work, Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, is an example of this revolution in Natural Philosophy. •Remnants of the term Natural Philosophy still remain in physics today. For example, one of the oldest scientific journals still published is called Philosophical Magazine. Also there exists a chair in the School of Physics in Trinity called, the Erasmus Smith's Professor of Natural and Experimental Philosophy, currently held by professor Coey. Common topics of study Matter, Space, and Time What the world is made of is a question that has engaged philosophers too, from the preSocratics to the early modern. The philosopher Thales was one of the first to try describing the world without resorting to supernatural arguments. Atomic theory has its roots in Greek philosophy, indeed the word atom comes from the Greek for ‘indivisible’. Philosophers talk of what ‘substances’ the world is made of. Einstein’s theories of relativity show us that time and space are not independent quantities, and quantum mechanics (QM) tells us that words like wave, particle, position and velocity are meaningless at a certain scale. Determinism and Free Will Objective Reality As physical entities, people are systems of particles, so how The idea of an objective reality, much of our actions are as is what is knowable, is an important topic for both physics governed by the laws of physics? and philosophy. The concept of free will is central to much of philosophy. Are we Descartes set a foundation for free to make our own decisions, knowledge with his “I think or are we simply automata? therefore I am” and worked from there. Many philosophers ascribe special importance to our The Many Worlds interpretation supposed determinism of QM states that we are in just behaviour, while others believe in one world of many, free will. Others claim the two are corresponding to all possible compatible. outcomes. Is this just a mathematical formalism, or does The problem is muddied with the it have deep philosophical Copenhagen interpretation of implications? QM, that states some processes are inherently random. While different schools have different opinions on what we Some physicists, such as Wigner can know, QM states qualitatively and Penrose ascribe special and quantitatively what we importance to the role of cannot know and by how much. consciousness in QM, and vice versa. The Differences between Physics and Philosophy Philosophy Share many different schools of thought such as Realism, Idealism and Rationalism. The school of thought a philosopher believes in is entirely up to their own opinion Don’t have the same unity as physicists. They don’t have a set of theories that all philosophers agree upon also Philosophy is divided into several different branches such as: logic, metaphysics and epistemology. Some of the different branches are concerned with topics that have a very large scope like the issue of what is knowledge. (Epistemology) Tend to give more emphasis to a single author’s view rather than to a topic as a whole To educate philosophers they study the (old) writings of other philosophers, some of which date back to even before Aristotle’s time more than 2000 years ago Experimentation Physics Share the same school of thought throughout the subject, for example all Physicists believe in the existence of a material world and of things such as matter. It is only for the new and cutting-edge theories that different opinions exist in physics. Have a sense of unity flowing through their subject, for example there is a set of SI units that are used regardless of what topic of Physics is being studied. Also they agree on a on a set of theories and these theories are used countless times across all areas of physics This unity and universal agreement within Physics has enabled the subject to use textbooks to educate Physicists Study modern and up to date theories and literature and try to build upon it to try and create even newer theories Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec a nisl nisi, aliquam feugiat sapien. Cras iaculis odio sit amet diam facilisis eget dignissim erat luctus. Phasellus malesuada consectetur euismod. Duis tempus, dolor tempus gravida ultricies, purus felis placerat ipsum, ac sagittis metus mi at velit. Aenean lectus tellus, varius id vehicula nec, volutpat nec odio. Sed in nibh eget nisl aliquet commodo. Praesent risus urna, gravida at commodo et, iaculis at libero. Quisque sollicitudin velit vitae ligula porta sit amet porttitor leo fermentum. Aenean ut nisl at tortor tempor elementum. Quisque euismod tortor a nulla blandit placerat. Aliquam lacus. . Sed in nibh eget nisl aliquet commodo. Praesent risus urna, gravida at commodo et, iaculis at libero. Quisque sollicitudin velit vitae ligula porta sit amet porttitor leo fermentum. Aenean ut nisl at tortor tempor elementum. Quisque euismod tortor a nulla blandit placerat. Aliquam lacus. Conclusion: Is a conclusion necessary?? References: History of Western Philosophy, Bertrand Russell Placeholder Text Placeholder Text Placeholder Text © School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin