Heart
advertisement
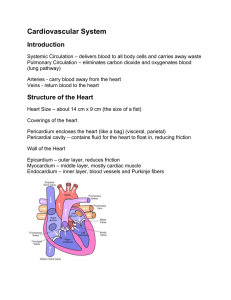
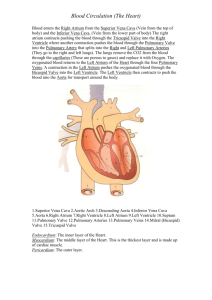
Anatomy of the Heart Video Heart Shape and Make-up • Nine (9) inches long x three (3) inches wide. – Size of a fist – Triangular • Involuntary striated muscle tissue – Only found in this organ. • Beats 60-100 times per minute – 2.5 billion times during an average lifespan. Heart Location • Base--attached to several large blood vessels and lies beneath the second rib. • Apex— – at the fifth intercostal space – Points towards the left • Located within the mediastinum, bordered laterally by the lungs, posterior is the backbone, and anterior is the sternum Pericardial Cavity • Pericardium – Located between the parietal and visceral layers • Fluid filled sack that surrounds the heart – Pericardial fluid – Several functions • Keeps the heart contained in the chest cavity • Prevents the heart from over expanding when blood volume increases • Prevents friction (rubbing with beats) Pericardium Layers • Made up of three (3) distinct layers: • Outer epicardium • Myocardium • Inner endocardium Epicardium • Corresponds to the visceral pericardium. • Functions as an outer protective layer. • Serous membrane that consists of connective tissue covered by epithelium. • Includes blood capillaries, lymph capillaries, and nerve fibers. Myocardium • Relatively thick. • Consists largely of cardiac muscle tissue responsible for forcing blood out of the heart chambers. • Muscle fibers are arranged in planes, separated by connective tissues that are richly supplied with blood capillaries, and nerve fibers. Endocardium • Consists of epithelial and connective tissue that contains many elastic and collagenous fibers. • Connective tissue also contains blood vessels and some specialized cardiacmuscle fibers called Purkinje fibers. • Lines all of the heart chambers and covers heart valves. • Is continuous with the inner lining of blood vessels--endothelium. READ Handout Anatomy of the Heart Tuesday Vena Cava • Superior Vena Cava – Bringing de-oxygenated blood • Upper body to the right atrium of the heart • Inferior Vena Cava – Bringing de-oxygenated blood • Lower body to the right atrium of the heart Chambers • Atria – Two chambers at the top – Right • Receives deoxygenated blood from the superior and inferior vena cava – Left • It receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins Chambers • Ventricles – Two chambers at the bottom – Right • It receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium – Left • It receives oxygen rich blood from the left atrium – Video Video Coronary Arteries • Coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle – oxygen-rich blood to function – oxygen-depleted blood must be carried away – consist of two main arteries • the right and left coronary arteries. Valves • Tricuspid – valve is between the right atrium and right ventricle. • Pulmonary – valve is between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. Valves • Mitral (Bicuspid) – valve is between the left atrium and left ventricle. • Aortic – valve is between the left ventricle and the aorta. • Each valve has a set of flaps (also called leaflets or cusps). When working properly, the heart valves open and close fully. Vessel Valves • Pulmonary Valve – semilunar valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and has three cusps. • Aortic Valve – It lies between the left ventricle and the aorta – video Repair of Tricuspid Valve video READ Handout Anatomy of the Heart Wednesday Importance of Coronary Arteries • Coronary artery disorder or disease – Reducing the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the heart • leads to a heart attack and possibly death. • Video – Atherosclerosis (a build-up of plaque in the inner lining of an artery causing it to narrow or become blocked) is the most common cause of heart disease. Vessels • • • • • • Video Superior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava Aorta Pulmonary Artery Pulmonary Vein Aorta • Largest single blood vessel in the body – diameter of your thumb – carries oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to the various parts of the body • Aortic Arch – Top curve of the aorta READ Handout Anatomy of the Heart Thursday Pulmonary Artery • Vessel transporting de-oxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs • A common misconception is that all arteries carry oxygen-rich blood – It is more appropriate to classify arteries as vessels carrying blood away from the heart. Pulmonary Vein • Vessel transporting oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium • A common misconception is that all veins carry de-oxygenated blood it is more appropriate to classify veins as vessels carrying blood to the heart Video-blood flow Video • video Oxygen Exchange Entire Cycle • video- blood flow • Lyrics READ Handout