Module 2: Reinforced Concrete Slabs
advertisement

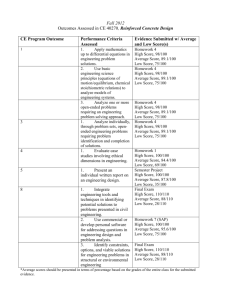
COVENANT UNIVERSITY COURSE COMPACT (2014/2015 ACADEMIC SESSION) College: Science and Technology School: Environmental Sciences Department: Architecture Programme: Architecture Course Code: ARC 415 Course Title: Building Structures V Units: 3 Course Lecturers: Dr. Eziyi O. Ibem & Arc. I. C. Ezema Semester: Alpha Semester Time: 12.00-15.00 Hrs on Mondays Location: Studio 400 CST Building a. COURSE DESCRIPTION The course is a continuation of Arc 325 (Building Structures IV).The goal of the course to further expose the students to the rudiments of reinforced concrete design. Emphasis is the design of basic structural elements such as beams, slabs, columns, and retaining walls b. COURSE OBJECTIVES At the end of this course, students are expected to be able to do the following Design simply supported RC beam showing details of the reinforcement placement Design a RC slab Design a column section, simple pad footing Ultimately, the student should be able to understand and interpret structural drawings for a RC building c. METHODS OF LECTURE DELIVERY/ TEACHING AIDS -Lecture Delivery Guided instruction Class interaction Sessions/Tutorials The use of projectors -Teaching Aids (i) The National Building Code (2006) (ii) British Standard (BS8110) (iii) Design Charts d. COURSE OUTLINE Module 1: RC Beam Design Week 1: Review of design of singly reinforced and doubly reinforced beams; design of shear Reinforcement in beams Week 2: Design of Simply Supported Beam Week 3: Design of Continuous Beam Module 2: Reinforced Concrete Slabs Week 4: Types of Slabs; Week 5: Design of One-Way Spanning solid slab Week 6: Design of a-two-way spanning slab Week 7: Evaluation Week Module 3: Foundations Week 8: Types of Foundations Week 9: Design of pad footing Module 4: Retaining Walls Week 10: Introduction to Principles of Design of Retaining walls Module 5: Reinforced Concrete Columns Week 11: Rc Column Sections Week 12: Rc Column Design Week 13: Revision e. TUTORIALS: Tutorials will focus on specific areas students may have found difficult to understand in the normal class sessions TUTORIAL QUESTIONS i What do you understand by limit state design in reinforced concrete structures? ii Itemise the basic steps to be followed according to BS8110 in the design of a simply supported reinforced concrete beam. iii A reinforced concrete beam 300mm wide and 600mm deep is made to span 6000mm between the centres of the supporting brick piers 300mm wide. The beam carries dead and imposed loads (excluding self weight) of 25KN/m and 20KN/m respectively. Assuming the following materials strength: fcu = 30N/mm2 , fy = 460N/mm2 and fyv = 250N/mm2 , design the bending and shear reinforcement of the beam for mild exposure conditions taking the density of reinforced concrete to be 24KN/m3. iv Using annotated sketches, distinguish between one-way and two-way spanning reinforced concrete slabs. v What are the different types of reinforced concrete suspended floor slabs? vi What factors influence the choice of reinforced concrete suspended slab construction?. vii A reinforced concrete floor slab is subjected to an imposed load of 3.5KN/m2 and spans 4500mm between reinforced concrete columns of 150mm thickness. Assuming the following material strengths: f cu = 35N/mm2 and fy = 460N/mm2, design the slab for mild exposure conditions taking the density of reinforced concrete to be 24KNm3 . viii What are the different types of foundation you know? Using suitable sketches describes any two types of foundation stating clearly where they can be used? ix State two conditions that might lead to foundation failure in reinforced concrete structures. x What factors influence the selection of foundation types? xi A 400mm square column carries a dead load (Gk) of 1050KN and imposed load (Qk) of 300KN. Given that the safe load bearing capacity of the soil is 170KN/m2, design a square pad foundation to resist the loads with the following material strengths: fcu = 35N/mm2 and fy = 460N/mm2. Assume a footing weight of 150KN. xii What are retaining walls and when are they recommended in structural design? xiii With annotated sketches, explain the types of retaining walls you know. xiv What do you understand by sheet piling and under what conditions is it recommended? xv What are the common structural failures of retaining walls? f. STRUCTURE OF THE PROGRAMME&METHOD OF GRADING Continuous Assessment Tests Assignment Class Participation Examination: 30 marks 20 marks 10marks 10marks 70Marks g. RULES &REGULATIONS Mandatory 90% class attendance is mandatory Lateness to class not permitted All class assignment to be submitted on time Noise making and other forms of distractive activities are prohibited Active participation in all class discussions is compulsory to all students Every student must have a functional Scientific calculator, no borrowing of calculators during classes, tests and examinations h. ASSIGNMENTS/STUDENTS’ ACTIVITIES Class assignments will basically focus on quantitative problems that has to do with the design of basic Structural elements based on BS8110. i. ALIGNMENT WITH COVENANT UNIVERSITY VISION/GOALS In line with the vision of Covenant University to graduate total graduates who will be pace setters and world changers in their various fields , this course is aimed at widening the scope of the understanding of the students in the field of building structures which is essential in enhancing their relevance in the building industry. j. CONTEMPORARY ISSUES/INDUSTRY RELEVANCE Architects are celebrated for their ideas that are successfully translated to built forms; this is made possible when the creative ability of architect is reinforced by sound understanding of the structural requirements of his designs. This course is very relevance in architecture as it further exposes the students to the design of RC v structural elements that are commonly used in building construction to achieve structural integrity. k. RECCOMMENDED READINGS 1. Arya, Chanakya (2003) (2nd Ed) Design of Structural Elements . London & New York: Spon Press 2. Mosley, W.H, Bungey, J.H. and Hulse, R. Reinforced Concrete Design. London: Macmillan 3. Reynolds, K.M.and Steedman, J.C. (1992) Examples of The Design of Reinforced Concrete Buildings To BS8110 (4th Ed.)London: Spon Press